Tensorflow+SSD+Yolo(目标检测)文章10:YOLO_v3实现视频化以及界面化和打包操作
10.YOLO_v3实现视频化以及界面化和打包操作
(写在每篇深度学习文章系列的前面,该系列的文章是我2019年做毕设时的步骤总结,是能实现的,不和其他很多博客一样瞎糊弄人浪费时间。写下这些文章一方面为了方便后来者,一方面也为了自己以后的步骤复现等。
另外,如果我给的那些参考帖子看不了了,可以到我的博客下载区那里去下载对应的压缩文件,我把里面所有的链接网页都截了长图,所以不用担心我给的参考帖子链接失效。
其次,如果我给的参考链接侵犯了该链接博主的权益,烦请告知,必当第一时间删掉。由于本人参考帖子较多,如果侵犯了请原谅,我会删掉。也谢谢各位在路上帮助过我的,谢谢了。
还有就是,如果积分太高了,请告诉我怎么把积分降低,我也不太清楚怎么弄,积分会随着下载次数增加逐渐增加。你知道的话怎么降的话可以留言给我。
emm, 最后的最后,如果你觉得这篇博文有用,请点个赞哩,感谢!~~)
(博客下载区:https://download.csdn.net/download/lininggggggg/11224800
或者在下载区搜索名字:10.YOLO_v3实现视频化以及界面化和打包操作.zip–深度学习文章10)
正文
https://blog.csdn.net/a88770202/article/details/87108823 视频的读取!!!
https://blog.csdn.net/Lay_ZRS/article/details/88549644
https://blog.csdn.net/DumpDoctorWang/article/details/80515861
一、视频的读取
如果按照之前给的yolo.py文件里的视频软件进行测试的话会发现总是测试识别不出来,这个其实有个大坑来着。
首先,都测不到,要么标记框瞎框,有的边界都溢出int了(一度怀疑人生),后来看了一篇博文说可能是opencv的图片读取BGR顺序和Image图片的RGB读取顺序不同,然后看了一下detect_video函数发现拿图片帧去处理的是Image而用cv2.show的还是Image顺序,确实没转换过去,于是百度了一波转换方法,改了改代码就可以正常识别了。修改后代码如下:即把这段代码放到yolo.py文件里的那个同样的函数的地方,之前那个删掉即可。
def detect_video(yolo, video_path, output_path=""):
import cv2
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
if not vid.isOpened():
raise IOError("Couldn't open webcam or video")
video_FourCC = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))
video_fps = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
video_size = (int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),
int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
isOutput = True if output_path != "" else False
if isOutput:
print("!!! TYPE:", type(output_path), type(video_FourCC), type(video_fps), type(video_size))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)
accum_time = 0
curr_fps = 0
fps = "FPS: ??"
prev_time = timer()
while True:
return_value, frame = vid.read()
image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))#Opencv转PIL
image = yolo.detect_image(image)
result = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)#显示的时候再PIL转回Opencv
#
curr_time = timer()
exec_time = curr_time - prev_time
prev_time = curr_time
accum_time = accum_time + exec_time
curr_fps = curr_fps + 1
#
if accum_time > 1:
accum_time = accum_time - 1
fps = "FPS: " + str(curr_fps)
curr_fps = 0
cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
fontScale=0.50, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.namedWindow("result", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
# if isOutput:
# out.write(result)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
yolo.close_session()
然后在该文件的末尾加上下面的代码即可运行:
加法1:(没实践过)
def detect_img(yolo):
while True:
img = input('Input image filename:')
try:
image = Image.open(img)
except:
print('Open Error! Try again!')
continue
else:
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
r_image.show()
yolo.close_session()
if __name__ == '__main__':
if (int(input("Please input detect_type 1->image, 2->video\n")) == 1):
detect_img(YOLO())
else:
detect_video(YOLO(), input("Input video filename:\n"))
加法2:
def detect_img(yolo, img_path='test.png'):
image = Image.open(img_path)
import time
t1 = time.time()
####
outdir="E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5\photo/store"
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
r_image.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(img_path)))
####
print('time: {}'.format(time.time() - t1))
r_image.show()
# yolo.close_session()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1.15, 0.24
yolo = YOLO()
#
video = '.\photo/ee.mp4'
detect_video(yolo, video, output_path="ee_result5.mp4")
# #
# video = ''
# detect_video(yolo, video, output_path="ee_result8.mp4")
最后的yolo.py的最终代码如下:
# """
# Class definition of YOLO_v3 style detection model on image and video
# """
# # 我记得应该是运行yolo1才能正常运行全部功能
# import colorsys
# from timeit import default_timer as timer
#
# import numpy as np
# from keras import backend as K
# from keras.models import load_model
# from keras.layers import Input
# from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
#
# from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
# from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
# import os
# from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
#
# class YOLO(object):
# _defaults = {
# "model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5',
# "anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
# "classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
# "score" : 0.3,
# "iou" : 0.45,
# "model_image_size" : (416, 416),
# "gpu_num" : 1,
# }
#
# @classmethod
# def get_defaults(cls, n):
# if n in cls._defaults:
# return cls._defaults[n]
# else:
# return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#
# def __init__(self, **kwargs):
# self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
# self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
# self.class_names = self._get_class()
# self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
# self.sess = K.get_session()
# self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
#
# def _get_class(self):
# classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
# with open(classes_path) as f:
# class_names = f.readlines()
# class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
# return class_names
#
# def _get_anchors(self):
# anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
# with open(anchors_path) as f:
# anchors = f.readline()
# anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
# return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
#
# def generate(self):
# model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
# assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
#
# # Load model, or construct model and load weights.
# num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
# num_classes = len(self.class_names)
# is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
# try:
# self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
# except:
# self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
# if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
# self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
# else:
# assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
# num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
# 'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
#
# print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
#
# # Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
# hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
# for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
# self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
# self.colors = list(
# map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
# self.colors))
# np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
# np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
# np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
#
# # Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
# self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
# if self.gpu_num>=2:
# self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
# boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
# len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
# score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
# return boxes, scores, classes
#
# def close_session(self):
# self.sess.close()
#
#
# if __name__ == '__main__':
#
# # #
# # detect_img(YOLO(), img_path='.\photo/00002.jpg')
#
# #
# video = '.\photo/ee.mp4'
# detect_video(YOLO(), video, output_path="ee_result5.mp4")
#
# # #
# # video = ''
# # detect_video(YOLO(), video, output_path="")
#
#
# # i = 0
# # #
# # path = 'E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5\pic/'
# # if i<=11:
# # i += 1
# # image_names = os.path.join(path, i, '.jpg')
# # detect_img(YOLO(), img_path='image_names') #
# #
#
#
"""
Class definition of YOLO_v3 style detection model on image and video
"""
# 我记得应该是运行yolo1才能正常运行全部功能
import colorsys
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.layers import Input
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
import os
from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
class YOLO(object):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"score" : 0.3,
"iou" : 0.45,
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
self.class_names = self._get_class()
self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
self.sess = K.get_session()
self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
def _get_class(self):
classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
with open(classes_path) as f:
class_names = f.readlines()
class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
return class_names
def _get_anchors(self):
anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
with open(anchors_path) as f:
anchors = f.readline()
anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
def generate(self):
model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
# Load model, or construct model and load weights.
num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
num_classes = len(self.class_names)
is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
try:
self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
except:
self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
else:
assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
# Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
self.colors = list(
map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
self.colors))
np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
# Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
if self.gpu_num>=2:
self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
return boxes, scores, classes
def detect_image(self, image):
start = timer()
if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
else:
new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
image.height - (image.height % 32))
boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
print(image_data.shape)
image_data /= 255.
image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
[self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
feed_dict={
self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
K.learning_phase(): 0
})
print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
box = out_boxes[i]
score = out_scores[i]
top, left, bottom, right = box
top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
label = '{} {:.2f} '.format(predicted_class, score) + '({} {}) '.format(np.floor((top+bottom)/2+0.5).astype('int32'), np.floor((left+right)/2+0.5).astype('int32'))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
else:
text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
# My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle(
[left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
outline=self.colors[c])
draw.rectangle(
[tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
fill=self.colors[c])
# draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font) # fill=(0,0,0)是黑色
draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(255, 255, 255), font=font) # fill=(255, 255, 255)是白色
del draw
end = timer()
print(end - start)
return image
def close_session(self):
self.sess.close()
def detect_video(yolo, video, output_path=""):
import cv2
video_path = os.path.join(video)
if (os.path.exists(video_path) and video != ''):
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
else:
vid = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
video = 'your_camera.mp4'
if not vid.isOpened():
raise IOError("Couldn't open webcam or video")
video_FourCC = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))
video_fps = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
video_size = (int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),
int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
isOutput = True if output_path != "" else False
if isOutput:
print("!!! TYPE:", type(output_path), type(video_FourCC), type(video_fps), type(video_size))
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)
accum_time = 0
curr_fps = 0
fps = "FPS: ??"
prev_time = timer()
while True:
return_value, frame = vid.read()
if frame is None:
break
image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
image = yolo.detect_image(image)
result = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
#
curr_time = timer()
exec_time = curr_time - prev_time
prev_time = curr_time
accum_time = accum_time + exec_time
curr_fps = curr_fps + 1
#
if accum_time > 1:
accum_time = accum_time - 1
fps = "FPS: " + str(curr_fps)
curr_fps = 0
# cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# fontScale=0.50, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
fontScale=0.5, color=(255, 255, 255), thickness=2) # 更改字体大小和颜色
cv2.namedWindow("result", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("result", result)
if isOutput:
out.write(result)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# yolo.close_session()
def detect_img(yolo, img_path='test.png'):
image = Image.open(img_path)
import time
t1 = time.time()
####
outdir="E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5\photo/store"
r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
r_image.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(img_path)))
####
print('time: {}'.format(time.time() - t1))
r_image.show()
# yolo.close_session()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1.15, 0.24
yolo = YOLO()
detect_img(yolo, img_path='.\photo/0.jpg')
detect_img(yolo, img_path='.\photo/1.jpg')
detect_img(yolo, img_path='.\photo/2.jpg')
detect_img(yolo, img_path='.\photo/3.jpg')
# #
# video = '.\photo/ee.mp4'
# detect_video(yolo, video, output_path="ee_result5.mp4")
# #
# video = ''
# detect_video(yolo, video, output_path="ee_result8.mp4")
# i = 0
# #
# path = 'E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5\pic/'
# if i<=11:
# i += 1
# image_names = os.path.join(path, i, '.jpg')
# detect_img(yolo, img_path='image_names') #
#
二、pyqt5界面的搭建
较好的博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37606112/article/details/78419892 !!!
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41929524/article/details/81456308 !!!(该作者有四篇博文组成一个系列,都要看)
第一步,先按照博文https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37606112/article/details/78419892 !(同帖子链接4)
https://blog.csdn.net/niuyongjie/article/details/81161559
的步骤来。
(1)安装各类库pyqt5,pyqt5-tools,指令为pip install pyqt5 ;pip install pyqt5-tools
(2)进行pycharm的环境配置
打开pycharm,进入file-setting-tools-external tools。
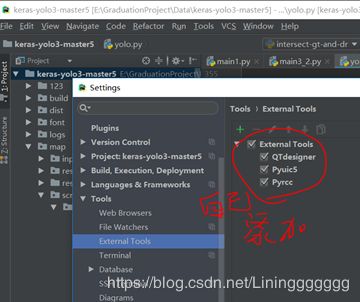
(3)点击“+”号,后增加Qtdesigner、Pyuic5和Pyrcc(下面那段文字是复制的,如果看不懂可以直接和下面的三个图对比直接设置修改)
1、在增加Qtdesigner时,名称可以自己按照喜好键入,不必和exe文件保持一致。
首先需要下面第一个空格内点击“…”,按照目录找到exe文件,选中即可。这个exe文件应当在刚安装的pyqt5-tools目录下。
2、在第二个空格内,“parameters”是指exe文件执行时的参数,就是我们将要操作的文件,点击后面的“宏命令”,选择filedirfiledir f i l e n a m e , 也 就 是 我 们 将 要 操 作 的 文 件 , 则 每 次 点 击 时 都 会 打 开 所 选 中 的 u i 文 件 , 如 果 保 持 空 的 , 则 每 次 打 开 就 是 最 初 的 界 面 。 第 三 个 空 格 即 是 文 件 的 存 放 目 录 , 点 击 “ 宏 命 令 ” , 选 择 , 也 就 是 我 们 将 要 操 作 的 文 件 , 则 每 次 点 击 时 都 会 打 开 所 选 中 的 u i 文 件 , 如 果 保 持 空 的 , 则 每 次 打 开 就 是 最 初 的 界 面 。 第 三 个 空 格 即 是 文 件 的 存 放 目 录 , 点 击 “ 宏 命 令 ” , 选 择 f i l e d i r filename,也就是我们将要操作的文件,则每次点击时都会打开所选中的ui文件,如果保持空的,则每次打开就是最初的界面。第三个空格即是文件的存放目录,点击“宏命令”,选择,也就是我们将要操作的文件,则每次点击时都会打开所选中的ui文件,如果保持空的,则每次打开就是最初的界面。第三个空格即是文件的存放目录,点击“宏命令”,选择filedir filename,也就是我们将要操作的文件,则每次点击时都会打开所选中的ui文件,如果保持空的,则每次打开就是最初的界面。第三个空格即是文件的存放目录,点击“宏命令”,选择,也就是我们将要操作的文件,则每次点击时都会打开所选中的ui文件,如果保持空的,则每次打开就是最初的界面。第三个空格即是文件的存放目录,点击“宏命令”,选择filedir即可。
3、接下来增加pyuic5,首先输入名字,可以按照喜好自己确定。
第一个空格内选择pyuic5.exe文件,应该在scripts目录下,
第二个空格内的输入需要用到“宏命令”,其实就是pyuic5 file.ui -o file.py
命令的抽象。这一步和老版本存在较大的差别,在网上的诸多教程中,都是在第一个空格内填写python.exe,第二个空格内填写pyuic5 file.ui -o file.py这个命令,我尝试了不行。
第三个空格直接用宏命令即可。pyrcc的配置和pyuic的一致。
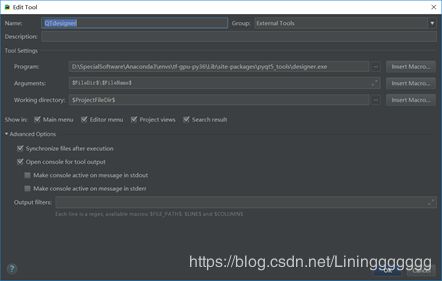


第二步,参考博文https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37606112/article/details/78556683
https://blog.csdn.net/niuyongjie/article/details/81161937 !!!
对里面的步骤稍微走几遍,走不通也暂时没事,知道怎么走就行。
(1)启动Pycharm,打开之前的yolo项目工程,然后点击TOOLEXTERNAL TOOL选择Qt Designer,会启动Qt Designer工具,制作界面,点击create后即可进行下一步操作。
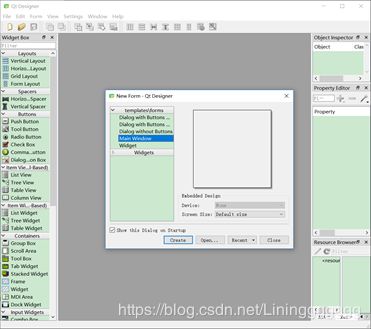
(2)注意,控件的添加是通过拖过去而不是点击过去来添加的。
(3)在添加完控件后,可以对其进行相应的调整等。(有的控件可以进行界面化的编辑函数)
(4)添加控件并调整后,保存界面为mainUi.ui。即在PyCharm界面中,在mainUi.ui文件上单击鼠标右键,选择Extern tool工具中的PyUIC,将mainUI.ui转换为mainUi.py

(5)这些代码都是自动生成的,大家最好不需要动(因为一旦再次改动界面,如果在)。
在生成的文件中有一个Ui_MainWindow类,这个类继承自object,这个类就是一个空的类,里面什么都没有,就是提供了一个容器,在容器内部生成了一个名字叫MainWindow的对象,设置对象的大小,然后将这个对象MainWindow作为父类生成了一个子对象centralwidget。centralwidget作为这个容器类的内部成员,这个对象centralwidget就是将来程序要运行的主窗口,在这个窗口内部放置了很多的控件,具体不详细论述了。
函数retranslateUi(self, MainWindow)的主要作用是设置控件的各种属性。
(6)然后在Pycharm中添加一个新的py文件main.py,代码如下:(该代码是我改过了的)
# # import sys
# # from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
# # app = QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
# # label = QtWidgets.QLabel("hello world")
# # label.show()
# # sys.exit(app.exec_())
# # ### 简单输出一个框
#
#
#
# # from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
# # from aaa import Ui_MainWindow
# #
# # class mywindow(QtWidgets.QWidget, Ui_MainWindow):
# # def __init__ (self):
# # super(mywindow, self).__init__()
# # self.setupUi(self)
# #
# # if __name__=="__main__":
# # import sys
# # app=QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
# # ui = mywindow()
# # ui.show()
# # sys.exit(app.exec_())
# # ### 简单例程
#
# from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
# from aaa2 import Ui_MainWindow # 导入ui文件转换后的py文件
# from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QFileDialog
# import pandas as pd
# # from yolo import YOLO
# import os
# import colorsys
# import os
# from timeit import default_timer as timer
#
# import numpy as np
# import pandas as pd
# from keras import backend as K
# from keras.models import load_model
# from keras.layers import Input
# from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
#
# from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
# from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
# import os
# from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
# import cv2
# import colorsys
# from timeit import default_timer as timer
#
# import numpy as np
# from keras import backend as K
# from keras.models import load_model
# from keras.layers import Input
# from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
#
# from yolo3.model import yolo_eval, yolo_body, tiny_yolo_body
# from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
# import os
# from keras.utils import multi_gpu_model
#
#
# class YOLO(object):
# _defaults = {
# "model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5',
# "anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
# "classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
# "score" : 0.3,
# "iou" : 0.45,
# "model_image_size" : (416, 416),
# "gpu_num" : 1,
# }
#
#
# class mywindow(QtWidgets.QWidget, Ui_MainWindow, YOLO):
# def __init__ (self, **kwargs):
# super(mywindow, self).__init__()
# self.setupUi(self)
# self.pushButton_2.clicked.connect(self.write_folder)
# self.pushButton.clicked.connect(self.read_file)
# self.ok.clicked.connect(self.process)
# self.__dict__.update(self._defaults) # set up default values
# self.__dict__.update(kwargs) # and update with user overrides
# self.class_names = self._get_class()
# self.anchors = self._get_anchors()
# self.sess = K.get_session()
# self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes = self.generate()
#
# def get_defaults(cls, n):
# if n in cls._defaults:
# return cls._defaults[n]
# else:
# return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
#
# def _get_class(self):
# classes_path = os.path.expanduser(self.classes_path)
# with open(classes_path) as f:
# class_names = f.readlines()
# class_names = [c.strip() for c in class_names]
# return class_names
#
# def _get_anchors(self):
# anchors_path = os.path.expanduser(self.anchors_path)
# with open(anchors_path) as f:
# anchors = f.readline()
# anchors = [float(x) for x in anchors.split(',')]
# return np.array(anchors).reshape(-1, 2)
#
# def generate(self):
# model_path = os.path.expanduser(self.model_path)
# assert model_path.endswith('.h5'), 'Keras model or weights must be a .h5 file.'
#
# # Load model, or construct model and load weights.
# num_anchors = len(self.anchors)
# num_classes = len(self.class_names)
# is_tiny_version = num_anchors==6 # default setting
# try:
# self.yolo_model = load_model(model_path, compile=False)
# except:
# self.yolo_model = tiny_yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//2, num_classes) \
# if is_tiny_version else yolo_body(Input(shape=(None,None,3)), num_anchors//3, num_classes)
# self.yolo_model.load_weights(self.model_path) # make sure model, anchors and classes match
# else:
# assert self.yolo_model.layers[-1].output_shape[-1] == \
# num_anchors/len(self.yolo_model.output) * (num_classes + 5), \
# 'Mismatch between model and given anchor and class sizes'
#
# print('{} model, anchors, and classes loaded.'.format(model_path))
#
# # Generate colors for drawing bounding boxes.
# hsv_tuples = [(x / len(self.class_names), 1., 1.)
# for x in range(len(self.class_names))]
# self.colors = list(map(lambda x: colorsys.hsv_to_rgb(*x), hsv_tuples))
# self.colors = list(
# map(lambda x: (int(x[0] * 255), int(x[1] * 255), int(x[2] * 255)),
# self.colors))
# np.random.seed(10101) # Fixed seed for consistent colors across runs.
# np.random.shuffle(self.colors) # Shuffle colors to decorrelate adjacent classes.
# np.random.seed(None) # Reset seed to default.
#
# # Generate output tensor targets for filtered bounding boxes.
# self.input_image_shape = K.placeholder(shape=(2, ))
# if self.gpu_num>=2:
# self.yolo_model = multi_gpu_model(self.yolo_model, gpus=self.gpu_num)
# boxes, scores, classes = yolo_eval(self.yolo_model.output, self.anchors,
# len(self.class_names), self.input_image_shape,
# score_threshold=self.score, iou_threshold=self.iou)
# return boxes, scores, classes
#
# def close_session(self):
# self.sess.close()
#
# def read_file(self):
# # 选取文件
# # filename, filetype =QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "选取文件", "E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5/", "Python Files(*.py);;All Files(*)")
# filename, filetype =QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "选取文件", "E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5/", "Files(*.jpg);;Files(*.mp4);;All Files(*)")
# print(filename, filetype)
# self.lineEdit.setText(filename)
# self.lineEdit_3.setText(filetype)
#
# def write_folder(self):
# #选取文件夹
# foldername = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, "选取文件夹", "C:/")
# print(foldername)
# self.lineEdit_2.setText(foldername)
#
# # 进行处理
# def detect_image(self, image):
# start = timer()
#
# if self.model_image_size != (None, None):
# assert self.model_image_size[0]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
# assert self.model_image_size[1]%32 == 0, 'Multiples of 32 required'
# boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, tuple(reversed(self.model_image_size)))
# else:
# new_image_size = (image.width - (image.width % 32),
# image.height - (image.height % 32))
# boxed_image = letterbox_image(image, new_image_size)
# image_data = np.array(boxed_image, dtype='float32')
#
# print(image_data.shape)
# image_data /= 255.
# image_data = np.expand_dims(image_data, 0) # Add batch dimension.
#
# out_boxes, out_scores, out_classes = self.sess.run(
# [self.boxes, self.scores, self.classes],
# feed_dict={
# self.yolo_model.input: image_data,
# self.input_image_shape: [image.size[1], image.size[0]],
# K.learning_phase(): 0
# })
#
# print('Found {} boxes for {}'.format(len(out_boxes), 'img'))
#
# font = ImageFont.truetype(font='font/FiraMono-Medium.otf',
# size=np.floor(3e-2 * image.size[1] + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# thickness = (image.size[0] + image.size[1]) // 300
#
# for i, c in reversed(list(enumerate(out_classes))):
# predicted_class = self.class_names[c]
# box = out_boxes[i]
# score = out_scores[i]
#
# top, left, bottom, right = box
# top = max(0, np.floor(top + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# left = max(0, np.floor(left + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# bottom = min(image.size[1], np.floor(bottom + 0.5).astype('int32'))
# right = min(image.size[0], np.floor(right + 0.5).astype('int32'))
#
# label = '{} {:.2f} '.format(predicted_class, score) + '({} {}) '.format(np.floor((top+bottom)/2+0.5).astype('int32'), np.floor((left+right)/2+0.5).astype('int32'))
# draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# label_size = draw.textsize(label, font)
# print(label, (left, top), (right, bottom))
#
# if top - label_size[1] >= 0:
# text_origin = np.array([left, top - label_size[1]])
# else:
# text_origin = np.array([left, top + 1])
#
# # My kingdom for a good redistributable image drawing library.
# for i in range(thickness):
# draw.rectangle(
# [left + i, top + i, right - i, bottom - i],
# outline=self.colors[c])
# draw.rectangle(
# [tuple(text_origin), tuple(text_origin + label_size)],
# fill=self.colors[c])
# draw.text(text_origin, label, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
# del draw
#
# end = timer()
# print(end - start)
# return image
#
# def process(self):
# try:
# yes1 = r'运行加载中'
# self.label_3.setText(yes1)
# # 获取文件路径
# file_path = self.lineEdit.text()
# # 获取文件格式
# file_type = self.lineEdit_3.text()
# # 获取文件夹路径
# folder_path = self.lineEdit_2.text()
# if ( file_type == 'Files(*.jpg)'):
# img_path = file_path
# detect_img(YOLO(), img_path)
# print('111')
# else:
# video = file_path
# detect_video(YOLO(), video, output_path=folder_path + "/ee_result7.mp4")
# print('000')
# # #######################################版本1,直接运行指定路径文件
# # # # detect_img(YOLO(), img_path=file_path) # 检测输入图片的路径
# # # os.system("python E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5/yolo.py")
# #
# # video = '.\photo/ee.mp4'
# # detect_video(YOLO(), video, output_path="ee_result5.mp4")
# # ##########################################
# success_result = r'转换成功!'
# self.label_3.setText(success_result)
# except:
# fail_result = r'转换失败!'
# self.label_3.setText(fail_result)
# # yolo.close_session()
#
#
#
# def detect_video(yolo, video, output_path=""):
# import cv2
#
# video_path = os.path.join(video)
#
# if (os.path.exists(video_path) and video != ''):
# vid = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# else:
# vid = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# video = 'your_camera.mp4'
#
# if not vid.isOpened():
# raise IOError("Couldn't open webcam or video")
# video_FourCC = int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FOURCC))
# video_fps = vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
# video_size = (int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)),
# int(vid.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)))
# isOutput = True if output_path != "" else False
# if isOutput:
# print("!!! TYPE:", type(output_path), type(video_FourCC), type(video_fps), type(video_size))
# out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, video_FourCC, video_fps, video_size)
# accum_time = 0
# curr_fps = 0
# fps = "FPS: ??"
# prev_time = timer()
# while True:
# return_value, frame = vid.read()
# if frame is None:
# break
# image = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
# image = yolo.detect_image(image)
# result = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# #
# curr_time = timer()
# exec_time = curr_time - prev_time
# prev_time = curr_time
# accum_time = accum_time + exec_time
# curr_fps = curr_fps + 1
# #
# if accum_time > 1:
# accum_time = accum_time - 1
# fps = "FPS: " + str(curr_fps)
# curr_fps = 0
# cv2.putText(result, text=fps, org=(3, 15), fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# fontScale=0.50, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=2)
# cv2.namedWindow("result", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# cv2.imshow("result", result)
# if isOutput:
# out.write(result)
# if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
# break
# # yolo.close_session()
#
#
# def detect_img(yolo, img_path='test.png'):
# image = Image.open(img_path)
# import time
# t1 = time.time()
#
# ####
# outdir = "E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5\photo/store"
# r_image = yolo.detect_image(image)
# r_image.save(os.path.join(outdir, os.path.basename(img_path)))
# ####
#
# print('time: {}'.format(time.time() - t1))
# r_image.show()
#
# # yolo.close_session()
#
#
# if __name__=="__main__":
# import sys
# app=QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
# ui = mywindow()
# ui.show()
# sys.exit(app.exec_())
from PyQt5 import QtWidgets
from aaa2 import Ui_MainWindow # 导入ui文件转换后的py文件
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QFileDialog
from yolo import YOLO, detect_video, detect_img
from timeit import default_timer as timer
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from PIL import Image, ImageFont, ImageDraw
from yolo3.utils import letterbox_image
import os
class mywindow(QtWidgets.QWidget, Ui_MainWindow, YOLO):
_defaults = {
"model_path": 'model_data/yolo.h5',
"anchors_path": 'model_data/yolo_anchors.txt',
"classes_path": 'model_data/coco_classes.txt',
"score" : 0.3,
"iou" : 0.45,
"model_image_size" : (416, 416),
"gpu_num" : 1,
}
@classmethod
def get_defaults(cls, n):
if n in cls._defaults:
return cls._defaults[n]
else:
return "Unrecognized attribute name '" + n + "'"
def __init__ (self):
super(mywindow, self).__init__()
self.setupUi(self)
self.pushButton_2.clicked.connect(self.write_folder)
self.pushButton.clicked.connect(self.read_file)
self.ok.clicked.connect(self.process)
def read_file(self):
# 选取文件
filename, filetype =QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "选取文件", "C:/", "Files(*.jpg);;Files(*.mp4);;All Files(*)")
print(filename, filetype)
self.lineEdit.setText(filename)
self.lineEdit_3.setText(filetype)
def write_folder(self):
#选取文件夹
foldername = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, "选取文件夹", "C:/")
print(foldername)
self.lineEdit_2.setText(foldername)
# 进行处理
def process(self):
# yolo = YOLO()
yes1 = r'运行加载中'
self.label_3.setText(yes1)
try:
# 获取文件路径
file_path = self.lineEdit.text()
# 获取文件格式
file_type = self.lineEdit_3.text()
# 获取文件夹路径
folder_path = self.lineEdit_2.text()
if ( file_type == 'Files(*.jpg)'):
print('图片识别')
img_path = file_path
detect_img(yolo, img_path)
else:
print('视频识别')
video = file_path
detect_video(yolo, video, output_path=folder_path + "/ee_result7.mp4")
# #######################################版本1,直接运行指定路径文件
# # # detect_img(yolo, img_path=file_path) # 检测输入图片的路径
# # os.system("python E:\GraduationProject\Data\keras-yolo3-master5/yolo.py")
#
# video = '.\photo/ee.mp4'
# detect_video(yolo, video, output_path="ee_result5.mp4")
# ##########################################
success_result = r'转换成功!'
self.label_3.setText(success_result)
except:
fail_result = r'转换失败!'
self.label_3.setText(fail_result)
# yolo.close_session()
if __name__=="__main__":
import sys
yolo = YOLO()
app=QtWidgets.QApplication(sys.argv)
ui = mywindow()
ui.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
第三步,按照该作者的几篇一个系列的博文一路走下来即可!!!
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41929524/article/details/81456308
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41929524/article/details/81460203
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41929524/article/details/81475935
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41929524/article/details/81484806 (编写打包的代码)
(注意,本电脑的环境有些混乱,所以打包时是通过新建的另一个虚拟环境来实现的)
补充的参考博文
https://www.jianshu.com/p/094928ac0b73
https://blog.csdn.net/sunshinezhihuo/article/details/80942993
三、打包项目文件
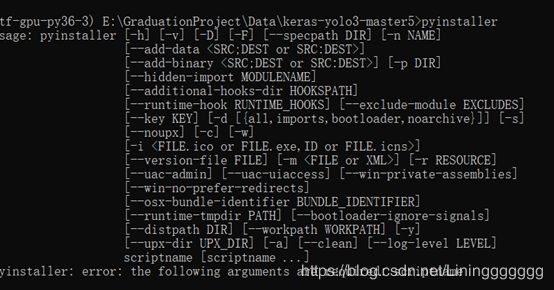
第一步,先安装pyinstaller 指令为 pip install PyInstaller
安装完后在cmd中输入pyinstaller指令,如果出现下图则说明安装工具包成功。
第二步,进行封装
在cmd中cd到主目录下,输入pyinstaller -F -w main3_2.py指令,其中的main3_2.py是依据自己的实际文件命名来的。
这里解释一下-F与-w的含义:
-F:将所有内容全部打包成一个exe可执行文件,而不会有其它的一些奇奇怪怪的小依赖文件。
-w:运行生成的exe文件时,不会弹出命令行窗口,而是直接弹出我们做的GUI。
运行完之后,桌面上就会弹出一个dist文件夹,然后里面就是一个exe文件了。将该文件复制到主目录下即可直接运行。