muduo网络库Timestamp类
1 Timestamp类主要的文件
muduo/base/Timestamp.cc
muduo/base/Timestamp.h
muduo/base/copyable.h
muduo/base/Types.h
其中Timestamp.cc和Timestamp.h 是类的文件。
copyable.h文件中包括的空类是一个标识类,表示继承该类的所有类都是可复制的,是值语义。
Types.h文件主要使用了该文件中对string类的包含。
2 Timestamp.h
#ifndef MUDUO_BASE_TIMESTAMP_H
#define MUDUO_BASE_TIMESTAMP_H
#include
#include
#include
namespace muduo
{
///
/// Time stamp in UTC, in microseconds resolution.
///
/// This class is immutable.
/// It's recommended to pass it by value, since it's passed in register on x64.
///
class Timestamp : public muduo::copyable,
public boost::less_than_comparable
{
public:
///
/// Constucts an invalid Timestamp.
///
Timestamp()
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(0)
{
}
///
/// Constucts a Timestamp at specific time
///
/// @param microSecondsSinceEpoch
explicit Timestamp(int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch);
void swap(Timestamp& that)
{
std::swap(microSecondsSinceEpoch_, that.microSecondsSinceEpoch_);
}
// default copy/assignment/dtor are Okay
string toString() const;
string toFormattedString() const;
bool valid() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_ > 0; }
// for internal usage.
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch() const { return microSecondsSinceEpoch_; }
time_t secondsSinceEpoch() const
{ return static_cast(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond); }
///
/// Get time of now.
///
static Timestamp now();
static Timestamp invalid();
static const int kMicroSecondsPerSecond = 1000 * 1000;
private:
int64_t microSecondsSinceEpoch_;
};
inline bool operator<(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() < rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
inline bool operator==(Timestamp lhs, Timestamp rhs)
{
return lhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch() == rhs.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
}
///
/// Gets time difference of two timestamps, result in seconds.
///
/// @param high, low
/// @return (high-low) in seconds
/// @c double has 52-bit precision, enough for one-microseciond
/// resolution for next 100 years.
inline double timeDifference(Timestamp high, Timestamp low)
{
int64_t diff = high.microSecondsSinceEpoch() - low.microSecondsSinceEpoch();
return static_cast(diff) / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
}
///
/// Add @c seconds to given timestamp.
///
/// @return timestamp+seconds as Timestamp
///
inline Timestamp addTime(Timestamp timestamp, double seconds)
{
int64_t delta = static_cast(seconds * Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
return Timestamp(timestamp.microSecondsSinceEpoch() + delta);
}
}
#endif // MUDUO_BASE_TIMESTAMP_H
3 继承boost::less_than_comparable
boost::less_than_comparable<>是模版类,继承这个类,表明要求实现<,然后就自动实现>,<=,>=这些比较运算符。这种编程是一种模版元的编程思想。
可以减少实现的代码。
4 Timestamp.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#define __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS
#include
#undef __STDC_FORMAT_MACROS
#include
using namespace muduo;
BOOST_STATIC_ASSERT(sizeof(Timestamp) == sizeof(int64_t));
Timestamp::Timestamp(int64_t microseconds)
: microSecondsSinceEpoch_(microseconds)
{
}
string Timestamp::toString() const
{
char buf[32] = {0};
int64_t seconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
int64_t microseconds = microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond;
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf)-1, "%" PRId64 ".%06" PRId64 "", seconds, microseconds);
return buf;
}
string Timestamp::toFormattedString() const
{
char buf[32] = {0};
time_t seconds = static_cast(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ / kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
int microseconds = static_cast(microSecondsSinceEpoch_ % kMicroSecondsPerSecond);
struct tm tm_time;
gmtime_r(&seconds, &tm_time);//thread safe function
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%4d%02d%02d %02d:%02d:%02d.%06d",
tm_time.tm_year + 1900, tm_time.tm_mon + 1, tm_time.tm_mday,
tm_time.tm_hour, tm_time.tm_min, tm_time.tm_sec,
microseconds);
return buf;
}
Timestamp Timestamp::now()
{
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
int64_t seconds = tv.tv_sec;
return Timestamp(seconds * kMicroSecondsPerSecond + tv.tv_usec);
}
Timestamp Timestamp::invalid()
{
return Timestamp();
}
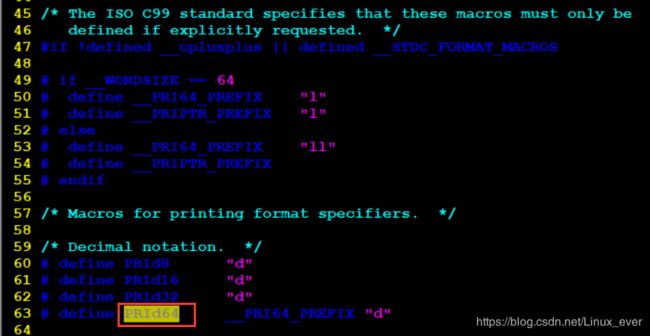
5 PRId64 是什么东东
是头文件/usr/include/inttypes.h中定义的一个宏。可以自动根据操作系统的版本,来表示是"ld"还是"lld"。
6 gmtime_r函数
struct tm *gmtime(const time_t *timep);
struct tm *gmtime_r(const time_t *timep, struct tm *result);
gmtime(线程不安全的)是把日期和时间转换为格林威治(GMT)时间的函数。将参数timep 所指的time_t 结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构tm返回。使用gmtime后要立即处理结果,否则返回的指针指向的内容可能会被覆盖。
一个好的方法是使用gmtime_r(线程安全的),gmtime_r()函数功能与此相同,但是它可以将数据存储到用户提供的结构体中,由于使用了用户分配的内存,是不会出错的。
7 测试用例
muduo/base/tests/Timestamp_unittest.cc文件是该类的测试文件。
#include
#include
#include
using muduo::Timestamp;
void passByConstReference(const Timestamp& x)
{
printf("%s\n", x.toString().c_str());
}
void passByValue(Timestamp x)
{
printf("%s\n", x.toString().c_str());
}
void benchmark()
{
const int kNumber = 1000*1000;
std::vector stamps;
stamps.reserve(kNumber);
for (int i = 0; i < kNumber; ++i)
{
stamps.push_back(Timestamp::now());
}
printf("front: %s\n", stamps.front().toString().c_str());
printf("back: %s\n", stamps.back().toString().c_str());
printf("back-front: %f\n", timeDifference(stamps.back(), stamps.front()));
int increments[100] = { 0 };
int64_t start = stamps.front().microSecondsSinceEpoch();
for (int i = 1; i < kNumber; ++i)
{
int64_t next = stamps[i].microSecondsSinceEpoch();
int64_t inc = next - start;
start = next;
if (inc < 0)
{
printf("reverse!\n");
}
else if (inc < 100)
{
++increments[inc];
}
else
{
printf("big gap %d\n", static_cast(inc));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i)
{
printf("%2d: %d\n", i, increments[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
Timestamp now(Timestamp::now());
printf("%s\n", now.toString().c_str());
passByValue(now);
passByConstReference(now);
benchmark();
}