深入理解HashMap扩容(JDK1.8)---源码分析
HashMap如何进行put操作?
hash值如何计算?
何时进行扩容?
如何扩容?
本篇带你逐行看源码~
Let’s start.
| put方法 |
* 从HashMap的put方法入手,逐步深入:
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
从put方法的注释可以知道,当添加新的key-value键值对时,如果key值已经存在,则新value将会替换原value值(因为putVal方法的第三个参数为false)。
| hash方法 |
* 根据key计算出key值对应的hash值,看hash函数(HashMap类提供的静态方法):
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
如果key为null,则hash值为0;否则,hash值就是key的hashCode值异或key的hashCode无符号右移16位的结果(即hashCode值的高16位和低16 位的异或结果)。通过异或处理,避免了只靠低位数据计算hash值时导致的冲突,计算结果由高低位结合决定,可以使元素分布更均匀。
讲到这里,我们就可以顺便看一下jdk1.7的put方法中是如何计算hash值的。
//jdk1.7
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
// 先取key的hashCode再和hashSeed进行异或运算
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
//通过hash函数得到散列值之后,再通过indexFor方法获取实际的存储位置
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1); //保证获取的index一定在数组范围内
}
| Node节点的定义 |
* 接着看,获取到key的hash值之后,先来熟悉一下HashMap中两个Node的定义,因为接下来我们会看到它活跃的身影。
(1)Node静态内部类:
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K,V> next;
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() { return key; }
public final V getValue() { return value; }
public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }
public final int hashCode() {
return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
public final boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {
Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;
if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&
Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
(1)TreeNode静态内部类:
/**
* Entry for Tree bins. Extends LinkedHashMap.Entry (which in turn
* extends Node) so can be used as extension of either regular or
* linked node.
*/
static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> {
TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links
TreeNode<K,V> left;
TreeNode<K,V> right;
TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, val, next);
}
...
}
| putVal方法 |
* 我们已经由key计算得到hash值了,接着来看putVal的具体实现,梳理一下大体思路:
/**
* Implements Map.put and related methods
*
* @param hash hash for key
* @param key the key
* @param value the value to put
* @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value
* @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode.
* @return previous value, or null if none
*/
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
//判断table数组是否为空,如果table数组为空,则通过resize()方法创建一个新的table数组,
//将这个新的数组赋值给tab数组,并获取新table数组的长度赋值给n
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//这里调用resize方法,其实就是第一次put时,对数组进行初始化。
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 根据hash值获取桶下标中当前元素,如果为null,说明之前没有存放过与key相对应的value,直接插入
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
//如果此位置上没有数据,则创建一个新节点,并将其放到数组对应下标中
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, nul l);
else {
//处理hash碰撞的情况:
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//当该位置old节点的hash值与待添加元素的hash值相等,
//并且两者的key也相同(key的地址或者key的equals()任意一个相等就认为是key重复了)
//hash碰撞,并且当前桶中的第一个元素即为相同key
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
//则使一个新节点引用到old节点
e = p;
else if (p instanceof TreeNode) //判断old节点是否是红黑树节点:
//将最新的key、value插入到树中
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
//链表结构,遍历链表找到需要插入的位置
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
//当遍历至链表尾部时
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
//将新节点插入至链表尾部
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//插入新节点之后,如果链表长度>=树化阈值,则调用树化方法
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
//如果在遍历链表的过程中,发现有节点的hash值与新节点的hash值相等,
//并且两者的key也相同(key的地址或者key的equals()任意一个相等就认为是key重复了),
//则跳出当前for循环
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
//hash碰撞的最终处理:
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
//当onlyIfAbsent为false,或者原节点的value值为null时,使用新值覆盖旧值
//添加元素时onlyIfAbsent默认是false
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
// 用于LinkedHashMap的回调方法,HashMap为空实现
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
/**
* The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in
* the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
//新键值对的添加属于"Structural modifications", modCount要自增
++modCount;
//当键值对数量超过threshold阈值时,调用resize方法进行数组扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
//用于LinkedHashMap的回调方法,HashMap为空实现
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
我们简单总结一下putVal主要做了哪些事:
- 判断桶数组table是否为空,如果为空,则通过resize扩容的方式进行初始化。
- 根据(n-1) & hash得到桶数组的索引值,判断该位置是否已有节点元素。如果没有元素,则直接将新节点添加到此索引位置处。添加成功之后,如果HashMap中键值对数量超过threshold扩容阈值,则调用扩容方法。
- 如果索引位置处已有节点,则需要分析三种情况:
(1)当桶数组索引处的节点的hash值与新元素的hash值相等,并且两者的key值也相同时,新元素的value值将覆盖旧值;
(2)当桶数组索引处的节点是红黑树节点时,将新元素插入到红黑树中;
(3)当桶数组索引处的节点是链表节点时,遍历此链表到尾部,将新元素插入到链表尾部,插入成功之后再根据链表长度与树化阈值的比较判断是否需要进行树化(如果链表元素个数达到8,并且当前数组长度小于MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY,则通过resize()方法扩容;否则就进行链表转红黑树的操作)。如果在遍历链表的过程中有某一节点的hash值与新元素hash相等,并且两者的key值也相同,则新元素的value值将覆盖旧值。
| resize方法 |
接下来终于到了要讲的resize核心扩容方法。
resize方法:初始化数组或对数组进行两倍扩容。如果数组为null,则分配的内存与threshold中保存的初始容量大小一致(指定初始容量的构造函数初始化HashMap),如果threshold为0就按照默认值16进行分配( 无参构造函数实例化HashMap)。由于我们使用2次幂进行扩展,每个bin中的元素在新table数组的位置要么还是原位置,要么是原位置再移动2次幂的位置(即原位置+原数组容量的位置)。
/**
* Initializes or doubles table size. If null, allocates in
* accord with initial capacity target held in field threshold.
* Otherwise, because we are using power-of-two expansion, the
* elements from each bin must either stay at same index, or move
* with a power of two offset in the new table.
*
* @return the table
*/
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
//原table数组容量
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
//原扩容阈值
int oldThr = threshold;
//新table数组容量、扩容阈值
int newCap, newThr = 0;
//如果原table数组容量大于0
if (oldCap > 0) {
//原数组容量已经达到最大容量(1<<30,即2的30次方)时,
//扩容阈值设置为Integer的最大值(2147483647),
//并返回原table数组
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
//如果原数组容量小于最大容量,则原数组容量2倍扩容,
//如果新数组容量<最大容量,并且原数组容量>=默认初始容量16,
//则新扩容阈值为原扩容阈值的2倍
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
//进入此if中说明数组为空,且创建HashMap时使用了带参数的构造函数:
//public HashMap(int initialCapacity)或者public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor)
//这两个构造函数最终都会执行this.threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
//tableSizeFor方法会返回最接近于initialCapacity的2的幂次方,此值即为初始数组容量
newCap = oldThr;
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
//进入此if说明数组为空,且创建HashMap时使用了无参构造函数,
//则初始化数组容量大小为16,扩容阈值为0.75*16=12
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
//由上述逻辑判断可知,进入此if有两种可能:
//第一种:在“if(oldCap>0)”条件中,且不满足其中的两个if条件
//第二种:满足“else if(oldThr>0)”
//第一种是扩容的情况,第二种是map进行第一次put的情况
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
//初始化table或者扩容, 实际上都是通过新建一个table数组来完成的
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
//确定容量的Node数组
table = newTab;
//如果原数组不为空,则说明是扩容;否则,直接返回table;
if (oldTab != null) {
//循环遍历原数组,对非空元素进行处理
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
//获取数组索引为j处的元素,当索引j处有元素时:
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
//清除原数组索引j处对Node节点的引用
oldTab[j] = null;
//如果该存储桶里面只有一个bin, 就直接将它放到新表的目标位置
//它在新数组中的位置是通过e.hash & (newCap - 1)确定下来的
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
//如果这个节点是红黑树节点,则拆分树(这个就先不在这里讲了,以后再写这个吧)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
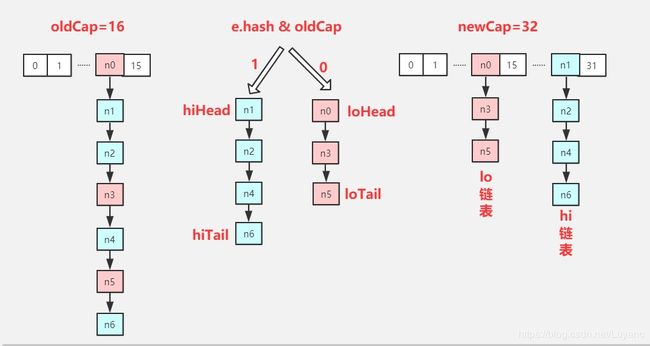
else { // preserve order
//链表情况(慢慢看,不着急)
//首先定义四个Node,还不知道要干啥?那就接着往下看
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
//保存下一个Node节点
Node<K,V> next;
//遍历链表元素(数组索引j处)
do {
next = e.next;
//新位置=原索引位置
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
//首先是loHead和loTail都指向e节点,
//然后下一个节点将插入到上一节点的后面
//最后将loTail指向新插入的节点
//(其实就是链表元素的插入操作而已)
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
//新位置=原索引+原数组容量
else {
//首先是hiHead和hiTail都指向e节点,
//然后下一个节点将插入到上一节点的后面
//最后将hiTail指向新插入的节点
//(其实就是链表元素的插入操作而已)
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
//对于索引j处的链表,根据在新数组中的索引位置,链表可能会拆分成两个链表:
//在新数组的位置正好是原索引位置处或者在原索引+原数组容量位置处
if (loTail != null) {
//对于不需要移动位置的链表(loHead为首,loTail为尾)
//设置尾节点loTail的下一节点为null
loTail.next = null;
//将此链表添加到新数组的原索引j处
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
//对于需要移动位置的链表(hiHead为首,hiTail为尾)
//设置尾节点hiTail的下一节点为null
hiTail.next = null;
//将此链表添加到新数组的原索引j + oldCap处
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
//至此,我们应该就能看出来loHead、loTail、hiHead、hiTail四个节点的作用了。
//如果索引j处是链表,则此链表按照在新数组的位置可能会被拆分成两个链表:
//(1)loHead、loTail链表:在新数组的位置还是原索引位置处
//(2)hiHead、hiTail链表:在新数组的位置=原索引+oldCap
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
最后,再来讲讲resize方法中的(e.hash & oldCap) == 0
通过对resize方法的分析,我们可以知道,(e.hash & oldCap) == 0这个拆分条件把索引j处的链表拆分成了两个链表,这两个链表在新数组的位置只有两种可能:原索引位置处,或者是原索引+oldCap位置处。
首先我们先明确三个点:
(1)oldCap一定是2的幂次方,假设是2^m;
(2)newCap一定是oldCap的2倍,即2^(m+1);
(3)假设数组容量是n,根据key的hash值确定其在数组中的索引是由(n - 1) & hash计算得来的(其实仅用到了hash的低m位进行运算)。
为什么仅用到了hash的低m位?很简单,我们看下面的举例:
假设数组容量是16,即2^4,则m=4,16-1=15,15的二进制表示如下:
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111
可以看到,除了低四位,其余高位都是0,与hash进行&运算之后对应位还是0,所以,我们假设某一节点的hash值的低四位用abcd表示(四个0、1的任意组合)。
那么,当数组容量两倍扩容变为32,即2^5,节点在新数组中的索引位置就变成了(32 - 1) & hash,其实是取了hash的低5位进行运算。31的二进制表示如下:
0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 1111
对于同一个Node,其hash值是不变的,低五位的取值无非是两种情况:
0abcd或者1abcd
对于0abcd这种情况,(16 - 1) & hash的计算结果与(32 - 1) & hash的计算结果是一致的,表明节点在新数组中的索引位置还是原索引位置处。
对于1abcd这种情况,1abcd = 0abcd + 10000 = 0abcd + oldCap,即节点在新数组中的索引位置=原索引+扩容前数组容量。
所以,虽然数组容量扩大一倍,但是对于同一个key,它在新旧数组中的索引位置是有联系的:要么一致,要么相差一个oldCap。而索引位置是否一致体现在hash的第4位(在此例中,我们把最低位称作第0位),如何拿到hash的第4位呢?我们只需要这样做:
hash & 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 0000
总结归纳之后,它其实就等效于 hash & oldCap。
由此,我们可以得出一个结论:
如果 (e.hash & oldCap) == 0 ,则该节点在新表的下标位置与旧表一致,都为 j;
否则,该节点在新表的下标位置为 j + oldCap。
如此巧妙,既省去了重新计算hash值的时间,同时又把冲突的节点随机分散到了不同的桶上。无比佩服源码作者!
| 总结 |
最后的最后,来一张亲自画的put(K key, V value)操作的流程图吧~

感谢您的阅读~