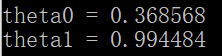C++实现梯度下降(gradient descent)算法
0.综述
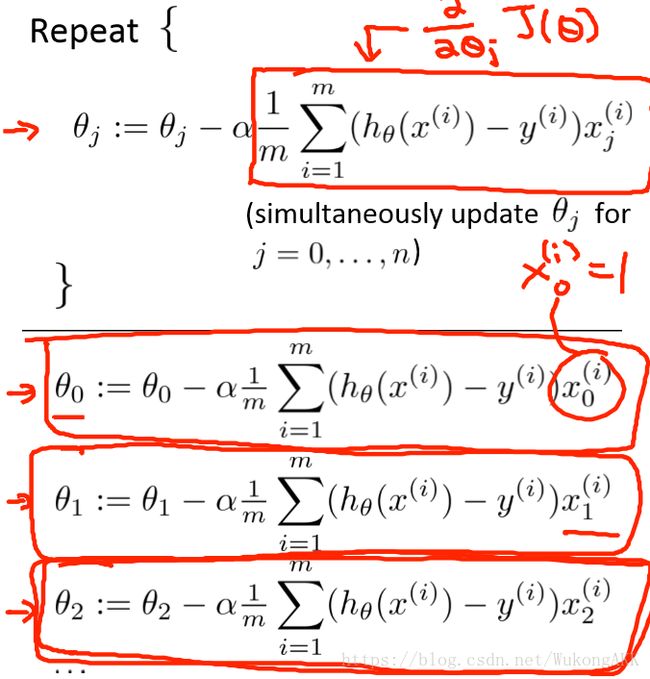
算法很好理解,求偏导然后更新theta矩阵,可以解决线性回归相关的问题。
1.几点说明
a.代码中的Matrix类是我自己写的一个矩阵相关的类,支持矩阵的加减乘除,转置运算。
b.关于学习速率alpha的确定,我的建议是alpha要保证每次梯度下降theta矩阵内元素的变化在0.01-0.05内。
c.数据超过500时,即max1,max2超过500时,使用默认的栈可能会导致栈内存不够,解决方法点这里。
2.一个直观的样例
样例点这里
数据集为(1,1)(2,2)(3,3)。。。。。
取alpha = 0.003
拟合的结果显然应该为theta0 = 0, theta1 = 1。
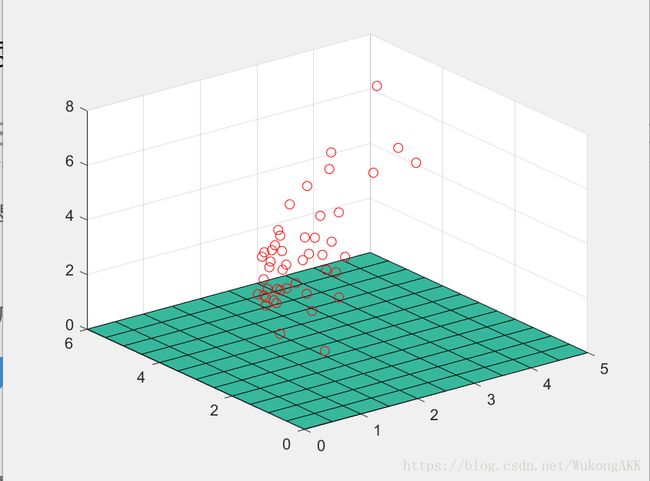
3.三维空间的一个样例
样例点这里
利用matlab展示数据
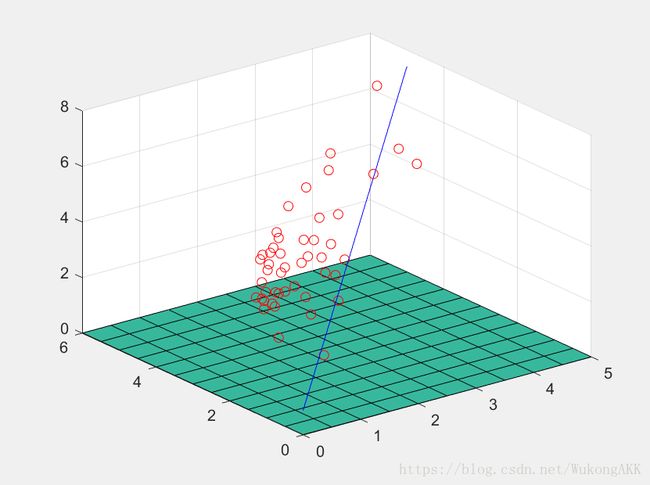
运行程序得到theta矩阵,iteration = 50000, alpha = 0.05, 画出拟合后的直线
4.源代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int max1 = 1005;
const int max2 = 1005;
int data_num, fea_num;
class Matrix{
public:
Matrix(int x = 0) : ro(x) {}
Matrix(int x, int y, double a[max1])
: ro(x), co(y){
for(int i = 1; i <= ro; i++) el[i][1] = a[i];
}
Matrix(int x, int y, double a[max1][max2])
: ro(x), co(y){
for(int i = 1; i <= ro; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= co; j++)
el[i][j] = a[i][j];
}
Matrix sum1();
Matrix transpose();
int row() const { return ro; }
int col() const { return co; }
double ele(const int& i, const int& j) const { return el[i][j]; }
void change(int i, int j, double x) { el[i][j] = x; }
double sum() { double s = 0; for(int i=1;i<=ro;i++)for(int j=1;j<=co;j++)s+=el[i][j];return s; }
void print() { for(int i=1;i<=ro;i++){for(int j=1;j<=co;j++)printf("%.3lf ",el[i][j]);printf("\n"); } }
private:
int ro;
int co;
double el[max1][max2];
};
Matrix X, Y;
Matrix Matrix::sum1(){
double temp[max1];
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
for(int i = 1; i <= this->ro; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= this->co; j++)
temp[i] += el[i][j];
return Matrix(this->ro, 1, temp);
}
Matrix Matrix::transpose(){
double temp[max1][max2];
int row = this->row();
int col = this->col();
for(int i = 1; i <= row; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= col; j++)
temp[j][i] = this->ele(i, j);
return Matrix(this->col(), this->row(), temp);
}
inline
Matrix operator + (const Matrix& lhs, const Matrix& rhs){
double temp[max1][max2];
if(lhs.row() != rhs.row() || lhs.col() != rhs.col())
return Matrix(-1);
for(int i = 1; i <= lhs.row(); i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= lhs.col(); j++)
temp[i][j] = lhs.ele(i, j) + rhs.ele(i, j);
return Matrix(lhs.row(), lhs.col(), temp);
}
inline
Matrix operator - (const Matrix& lhs, const Matrix& rhs){
double temp[max1][max2];
for(int i = 1; i <= rhs.row(); i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= rhs.col(); j++)
temp[i][j] = -rhs.ele(i, j);
return lhs + Matrix(rhs.row(), rhs.col(), temp);
}
inline
Matrix operator * (const Matrix& lhs, const Matrix& rhs){
if(lhs.col() != rhs.row())
return Matrix(-1);
double temp[max1][max2];
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
for(int i = 1; i <= lhs.row(); i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= rhs.col(); j++)
for(int k = 1; k <= lhs.col(); k++)
temp[i][j] += lhs.ele(i, k) * rhs.ele(k, j);
return Matrix(lhs.row(), rhs.col(), temp);
}
inline
Matrix operator / (const Matrix& lhs, const int& rhs){
double temp[max1][max2];
for(int i = 1; i <= lhs.row(); i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= lhs.col(); j++)
temp[i][j] = lhs.ele(i, j) / rhs;
return Matrix(lhs.row(), lhs.col(), temp);
}
void read(){
scanf("%d%d", &data_num, &fea_num);
double temp[max1][max2];
double temp2[max1];
for(int i = 1; i <= data_num; i++)
temp[i][1] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= data_num; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= fea_num; j++)
scanf("%lf", &temp[i][j+1]);
scanf("%lf", &temp2[i]);
}
X = Matrix(data_num, fea_num+1, temp);
Y = Matrix(data_num, 1, temp2);
}
void gradient_descent(Matrix& theta, int iteration, double alpha)
{
//X.print();
//theta.print();
//(X*theta - Y).print();
//(X*theta - Y).transpose().print();
//((X*theta - Y).transpose() * (X*theta - Y)).print();
//Matrix H = X*theta;
//Matrix Z = H - Y;
//Z.print();
for(int i = 1; i <= iteration; i++){
double cost = ((X*theta - Y).transpose() * (X*theta - Y)).sum() / (2*data_num);
printf("iteration %d\t cost = %lf\n", i, cost);
//X.transpose().print();
//(X.transpose() * ((X*theta) - Y)).print();
theta = theta - (X.transpose() * ((X*theta) - Y)).sum1() / (data_num/alpha);
//theta.print();
}
}
Matrix solve(){
double temp[max1];
for(int i = 1; i <= X.col(); i++)
temp[i] = rand()%1000/100;
Matrix theta(X.col(), 1, temp);
gradient_descent(theta, 50000, 0.005);
return theta;
}
void print(const Matrix& ans){
for(int i = 1; i <= ans.row(); i++)
printf("theta%d = %lf\n", i-1, ans.ele(i, 1));
//X.print();
//theta.print();
//(X*ans - Y).print();
//(X*theta - Y).transpose().print();
//((X*ans - Y).transpose() * (X*ans - Y)).print();
//Matrix H = X*theta;
//Matrix Z = H - Y;
//Z.print();
}
int main()
{
freopen("ztest.txt","r",stdin);
srand(time(NULL));
read();
print(solve());
return 0;
}