fishhook,facebook开源的一个可以动态绑定Mach-O符号表的库。在程序启动时与运行时会通过dyld来绑定符号表(这里有非懒加载与懒加载之分),而fishhook可以修改符号表的绑定。
验证
- 非懒加载绑定
- 懒加载绑定
非懒加载绑定
先来说说非懒加载绑定,我们最熟悉的objc_msgSend就是非懒加载绑定。新建一个空的命令行项目:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
NSLog(@"Hello, World!");
return 0;
}
在NSLog(@"Hello, World!")处打上断点,并在Debug Workflow中选中Always Show Disassembly,运行程序后执行如下操作:
可以看到slide的值为0,似乎命令行项目与iOS不同,并没有使用ASLR技术。
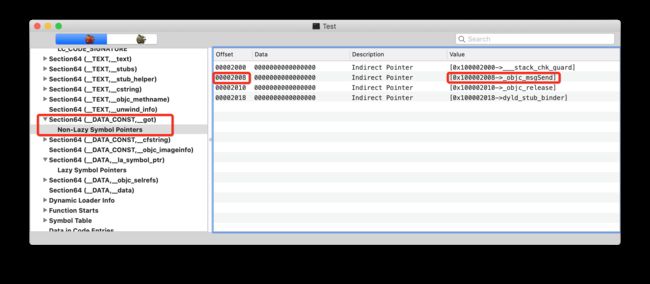
通过MachOView可以看到,objc_msgSend在MachO中的偏移量为0x2008,而由于slide为0,所以这里的虚拟地址0x100002008就是程序运行后的真实地址,在控制台中继续执行如下操作:
- 通过
image lookup -a可以看到0x100002008地址对应的确实是objc_msgSend,并且得到函数指针0x00007fff6b167040,它存储在Test.__DATA_CONST.__got中 - 通过
image lookup -n得到objc_msgSend所在动态库libobjc.A.dylib及偏移量0x0000000000006040 - 通过
image list -o -f得到libobjc.A.dylib动态库首地址0x00007fff6b161000 - 将
libobjc.A.dylib动态库首地址加上objc_msgSend偏移量得到objc_msgSend存储地址0x00007fff6b167040
这与用image lookup -a命令看到的地址完全吻合。
懒加载绑定
NSLog的偏移量为0x3000,同理,由于slide为0,这里的虚拟地址0x100003000就是真实地址。
可以看到NSLog符号存储在Test.__DATA.__la_symbol_ptr中,但是这里得到的地址0x0000000100001eac与真实的NSLog存储地址0x00007fff37702332并不相同,显然在0x0000000100001eac处必定进行了绑定操作。
在0x0000000100001eac处打上断点,继续执行程序,得到如下所示汇编代码:
这里会跳转到0x100001e9c处,继续加断点跟进:
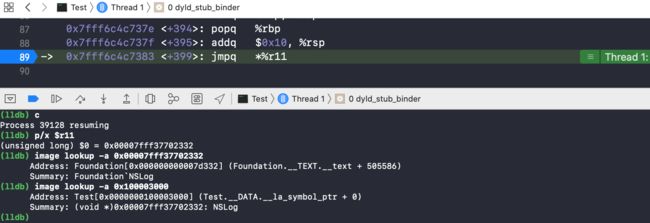
这里调用了dyld_stub_binder,NSLog的符号绑定就是通过这个函数完成的,继续跟进并在dyld_stub_binder对应的汇编代码末尾处打上断点,继续运行程序后做如下操作:
- 此时
r11存储的值为0x00007fff37702332 - 通过
image lookup -a得到这个值就是NSLog的存储地址 - 再次查看
0x100003000处信息,此时已经变成NSLog(之前为(void *)0x0000000100001eac)
以上就是符号的非懒加载绑定与懒加载绑定,顺便说一句,懒加载绑定后已经存在符号到函数的映射信息,再次调用相同函数时不存在这个绑定过程,而是直接调用。
fishhook
- fishhook的简单使用
- fishhook源码解析
fishhook的简单使用
接着上文的NSLog继续说:
void (*sys_log)(NSString *format, ...);
void my_log(NSString *format, ...) {
sys_log([format stringByAppendingFormat:@"---hello fishhook---"]);
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSLog(@"before");
struct rebinding context;
context.name = "NSLog";
context.replacement = &my_log;
context.replaced = (void *)&sys_log;
struct rebinding contexts[1] = {context};
rebind_symbols(contexts, 1);
NSLog(@"after");
}
return 0;
}
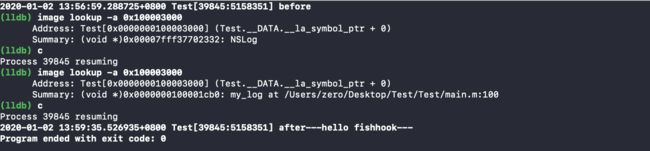
运行程序后输出如下:
显然已经成功的hook了NSLog函数,下面来看fishhook是怎么做到的。
在rebind_symbols(contexts, 1)与NSLog(@"after")处打上断点,运行程序并作如下操作:
由于在此之前已经调用过NSLog,所以懒加载符号绑定已经完成,此时0x100003000对应的就是NSLog的函数指针。继续运行程序执行rebind_symbols,在此查看0x100003000,此时此时绑定的地址变成了自定义的my_log函数,所以当再次调用NSLog时,通过符号表找到的是my_log,从而实现对NSLog的hook
fishhook源码解析
先了解一下数据结构:
struct rebinding {
const char *name;
void *replacement;
void **replaced;
};
struct rebindings_entry {
struct rebinding *rebindings;
size_t rebindings_nel;
struct rebindings_entry *next;
};
static struct rebindings_entry *_rebindings_head;
接着看Demo中调用的关键函数rebind_symbols:
rebind_symbols
int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) {
int retval = prepend_rebindings(&_rebindings_head, rebindings, rebindings_nel);
if (retval < 0) {
return retval;
}
// If this was the first call, register callback for image additions (which is also invoked for
// existing images, otherwise, just run on existing images
if (!_rebindings_head->next) {
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image);
} else {
uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) {
_rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i));
}
}
return retval;
}
这里首先调用了prepend_rebindings,这个函数是整个数据结构的关键:
prepend_rebindings
static int prepend_rebindings(struct rebindings_entry **rebindings_head,
struct rebinding rebindings[],
size_t nel) {
struct rebindings_entry *new_entry = (struct rebindings_entry *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebindings_entry));
if (!new_entry) {
return -1;
}
new_entry->rebindings = (struct rebinding *) malloc(sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
if (!new_entry->rebindings) {
free(new_entry);
return -1;
}
memcpy(new_entry->rebindings, rebindings, sizeof(struct rebinding) * nel);
new_entry->rebindings_nel = nel;
new_entry->next = *rebindings_head;
*rebindings_head = new_entry;
return 0;
}
这里生成一个新的结构体指针new_entry,将rebindings与nel扔到结构体对应的成员变量中,并将next指针指向上文提到的_rebindings_head处,而此时的_rebindings_head值为NULL,最后又将new_entry赋值给_rebindings_head。
显然,如果rebind_symbols函数调用多次,最终_rebindings_head是个单链表,prepend_rebindings函数的作用就是将新的结构体指针添加到链表头部,而这个单链表的尾部是NULL。
当然,这里涉及到一些内存申请操作,如果申请失败返回-1。
继续看prepend_rebindings函数之后的代码:
if (!_rebindings_head->next) {
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image);
} else {
uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) {
_rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i));
}
}
如果_rebindings_head->next为NULL也就是说rebind_symbols函数是首次调用,此时注册image的回调函数_rebind_symbols_for_image
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image
这个函数是dyld提供给我们的镜像加载回调函数,对应注释如下:
/*
* The following functions allow you to install callbacks which will be called
* by dyld whenever an image is loaded or unloaded. During a call to _dyld_register_func_for_add_image()
* the callback func is called for every existing image. Later, it is called as each new image
* is loaded and bound (but initializers not yet run). The callback registered with
* _dyld_register_func_for_remove_image() is called after any terminators in an image are run
* and before the image is un-memory-mapped.
*/
显然,在调用_dyld_register_func_for_add_image及有新镜像加载时,这个注册的回调函数会被每个已加载的镜像回调。
_rebind_symbols_for_image
static void _rebind_symbols_for_image(const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
rebind_symbols_for_image(_rebindings_head, header, slide);
}
回调函数直接调用rebind_symbols_for_image
rebind_symbols_for_image
这是fishhook的核心函数:
static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
Dl_info info;
if (dladdr(header, &info) == 0) {
return;
}
segment_command_t *cur_seg_cmd;
segment_command_t *linkedit_segment = NULL;
struct symtab_command* symtab_cmd = NULL;
struct dysymtab_command* dysymtab_cmd = NULL;
uintptr_t cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_LINKEDIT) == 0) {
linkedit_segment = cur_seg_cmd;
}
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SYMTAB) {
symtab_cmd = (struct symtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
} else if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_DYSYMTAB) {
dysymtab_cmd = (struct dysymtab_command*)cur_seg_cmd;
}
}
if (!symtab_cmd || !dysymtab_cmd || !linkedit_segment ||
!dysymtab_cmd->nindirectsyms) {
return;
}
...
}
先通过dladdr函数查看是否可以加载到mach_header *对应的info,如果加载不到,直接return。
这里说一下Dl_info的数据结构:
typedef struct dl_info {
const char *dli_fname; /* Pathname of shared object */
void *dli_fbase; /* Base address of shared object */
const char *dli_sname; /* Name of nearest symbol */
void *dli_saddr; /* Address of nearest symbol */
} Dl_info;
比如,Demo对应的info信息如下:
接着定义了4个结构体指针,以64位架构为例:
-
segment_command_t就是segment_command_64 -
symtab_command为Load Commands中LC_SYMTAB对应的结构体 -
dysymtab_command为Load Commands中LC_DYSYMTAB对应的结构体
然后跳过MachO Header,开始遍历Load Commands,将对应的LC分别放到linkedit_segment、symtab_cmd、dysymtab_cmd这三个结构体指针中。
完成循环后对结构体指针判空,如果有满足为空条件的,直接return。
static void rebind_symbols_for_image(struct rebindings_entry *rebindings,
const struct mach_header *header,
intptr_t slide) {
...
// Find base symbol/string table addresses
uintptr_t linkedit_base = (uintptr_t)slide + linkedit_segment->vmaddr - linkedit_segment->fileoff;
nlist_t *symtab = (nlist_t *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->symoff);
char *strtab = (char *)(linkedit_base + symtab_cmd->stroff);
// Get indirect symbol table (array of uint32_t indices into symbol table)
uint32_t *indirect_symtab = (uint32_t *)(linkedit_base + dysymtab_cmd->indirectsymoff);
cur = (uintptr_t)header + sizeof(mach_header_t);
for (uint i = 0; i < header->ncmds; i++, cur += cur_seg_cmd->cmdsize) {
cur_seg_cmd = (segment_command_t *)cur;
if (cur_seg_cmd->cmd == LC_SEGMENT_ARCH_DEPENDENT) {
if (strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA) != 0 &&
strcmp(cur_seg_cmd->segname, SEG_DATA_CONST) != 0) {
continue;
}
for (uint j = 0; j < cur_seg_cmd->nsects; j++) {
section_t *sect =
(section_t *)(cur + sizeof(segment_command_t)) + j;
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
if ((sect->flags & SECTION_TYPE) == S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS) {
perform_rebinding_with_section(rebindings, sect, slide, symtab, strtab, indirect_symtab);
}
}
}
}
}
- 获取当前镜像
SEG_LINKEDIT经ASLR偏移后的首地址 - 获取符号表地址
- 获取字符串表地址
- 获取动态符号表地址
- 再次遍历
Load Commands找到__DATA与__DATA_CONST中对应的__nl_symbol_ptr与__la_symbol_ptr进行重新绑定
perform_rebinding_with_section的功能就是,遍历当前符号表是否有与链表中每个结构体指针对应的name字段匹配,如果有则重新绑定。至此。fishhook的rebind就完成了。
再回到rebind_symbols,来看对应的else部分代码:
int rebind_symbols(struct rebinding rebindings[], size_t rebindings_nel) {
int retval = prepend_rebindings(&_rebindings_head, rebindings, rebindings_nel);
if (retval < 0) {
return retval;
}
// If this was the first call, register callback for image additions (which is also invoked for
// existing images, otherwise, just run on existing images
if (!_rebindings_head->next) {
_dyld_register_func_for_add_image(_rebind_symbols_for_image);
} else {
uint32_t c = _dyld_image_count();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < c; i++) {
_rebind_symbols_for_image(_dyld_get_image_header(i), _dyld_get_image_vmaddr_slide(i));
}
}
return retval;
}
上文说过,_dyld_register_func_for_add_image只有在调用或者有新镜像加载时才会调用注册的回调函数。对于同一个镜像来说,当rebind_symbols被多次调用时,注册的回调函数_rebind_symbols_for_image已经不会再被调用,此时先获取当前已加载镜像,然后逐个手动调用_rebind_symbols_for_image即可。
Have fun!