使用CNN实现C-MAPSS数据集里面的剩余寿命预测(Pytorch)
1.背景
在工程领域,了解不同的工程系统和组件非常重要,不仅要了解它们当前的性能,还要了解它们的性能如何随着时间的推移而降低。这扩展到了预测领域,它试图根据系统或组件的过去和现在的状态来预测其未来。这个领域中的一个常见问题是估计剩余使用寿命,或者系统或组件功能将持续多长时间。这个问题的著名数据集是PHM和C-MAPSS数据集。这些数据集包含不同涡扇发动机随时间产生的模拟传感器数据,并已用于研究剩余使用寿命的估计。
2.C-MAPSS数据集
数据集:FD001
训练轨迹:100
测试轨迹:100
条件:一个(海平面)
故障模式:ONE(HPC降级)
数据集:FD002
训练轨迹:260
测试轨迹:259
条件:六
故障模式:ONE(HPC降级)
数据集:FD003
训练轨迹:100
测试轨迹:100
条件:一个(海平面)
故障模式:两种(HPC降级,风扇降级)
数据集:FD004
训练轨迹:248
测试轨迹:249
条件:六
故障模式:两种(HPC降级,风扇降级)
实验场景
数据集由多个多元时间序列组成。每个数据集进一步分为训练和测试子集。每个时间序列都来自不同的引擎,即,可以认为数据来自相同类型的引擎。每个发动机以不同程度的初始磨损和制造变化开始,这是用户未知的。该磨损和变化被认为是正常的,即,不被认为是故障状况。有三种对发动机性能有重大影响的运行设置。这些设置也包含在数据中。数据被传感器噪声污染。
在每个时间序列开始时,发动机均正常运行,并且在该时间序列中的某个时刻出现故障。在训练集中,故障的严重程度会不断增加,直到系统出现故障为止。在测试集中,时间序列在系统故障之前的某个时间结束。竞赛的目的是预测测试装置失效前的剩余运行循环数,即发动机将继续运行的最后一个循环后的运行循环数。还提供了测试数据的真实剩余使用寿命(RUL)值的向量。
数据以zip压缩文本文件形式提供,其中包含26列数字,并以空格分隔。每行是在单个操作周期内获取的数据的快照,每列是不同的变量。这些列对应于:
1)单位编号
2)时间,以周期为单位
3)操作设定1
4)操作设定2
5)操作设置3
6)传感器测量1
7)传感器测量2
…
26)传感器测量26
百度云盘下载:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1RXJhR3iiZGbxi4c1MbndhQ
提取码:nr9l
3.代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import preprocessing
import numpy as np
import torch.utils.data as Data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
torch.manual_seed(2020)
train_df = pd.read_csv('train_FD001.txt', sep=" ", header=None) # train_dr.shape=(20631, 28)
train_df.drop(train_df.columns[[26, 27]], axis=1, inplace=True) # 去掉26,27列并用新生成的数组替换原数组
train_df.columns = ['id', 'cycle', 'setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 's1', 's2', 's3', 's4', 's5',
's6', 's7', 's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14', 's15', 's16', 's17',
's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
# 先按照'id'列的元素进行排序,当'id'列的元素相同时按照'cycle'列进行排序
train_df = train_df.sort_values(['id', 'cycle'])
test_df = pd.read_csv('test_FD001.txt', sep=" ", header=None)
test_df.drop(test_df.columns[[26, 27]], axis=1, inplace=True)
test_df.columns = ['id', 'cycle', 'setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 's1', 's2', 's3', 's4', 's5',
's6', 's7', 's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14', 's15', 's16', 's17',
's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
truth_df = pd.read_csv('RUL_FD001.txt', sep=" ", header=None)
truth_df.drop(truth_df.columns[[1]], axis=1, inplace=True)
"""Data Labeling - generate column RUL"""
# 按照'id'来进行分组,并求出每个组里面'cycle'的最大值,此时它的索引列将变为id
# 所以用reset_index()将索引列还原为最初的索引
rul = pd.DataFrame(train_df.groupby('id')['cycle'].max()).reset_index()
rul.columns = ['id', 'max']
# 将rul通过'id'合并到train_df上,即在相同'id'时将rul里的max值附在train_df的最后一列
train_df = train_df.merge(rul, on=['id'], how='left')
# 加一列,列名为'RUL'
train_df['RUL'] = train_df['max'] - train_df['cycle']
# 将'max'这一列从train_df中去掉
train_df.drop('max', axis=1, inplace=True)
"""MinMax normalization train"""
# 将'cycle'这一列复制给新的一列'cycle_norm'
train_df['cycle_norm'] = train_df['cycle']
# 在列名里面去掉'id', 'cycle', 'RUL'这三个列名
cols_normalize = train_df.columns.difference(['id', 'cycle', 'RUL'])
# 对剩下名字的每一列分别进行特征放缩
min_max_scaler = preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
norm_train_df = pd.DataFrame(min_max_scaler.fit_transform(train_df[cols_normalize]),
columns=cols_normalize,
index=train_df.index)
# 将之前去掉的再加回特征放缩后的列表里面
join_df = train_df[train_df.columns.difference(cols_normalize)].join(norm_train_df)
# 恢复原来的索引
train_df = join_df.reindex(columns=train_df.columns)
"""MinMax normalization test"""
# 与上面操作相似,但没有'RUL'这一列
test_df['cycle_norm'] = test_df['cycle']
norm_test_df = pd.DataFrame(min_max_scaler.transform(test_df[cols_normalize]),
columns=cols_normalize,
index=test_df.index)
test_join_df = test_df[test_df.columns.difference(cols_normalize)].join(norm_test_df)
test_df = test_join_df.reindex(columns=test_df.columns)
test_df = test_df.reset_index(drop=True)
"""generate column max for test data"""
# 第一列是id,第二列是同一个id对应的最大cycle值
rul = pd.DataFrame(test_df.groupby('id')['cycle'].max()).reset_index()
# 将列名改为id和max
rul.columns = ['id', 'max']
# 给rul文件里的数据列命名为'more'
truth_df.columns = ['more']
# 给truth_df增加id列,值为truth_df的索引加一
truth_df['id'] = truth_df.index + 1
# 给truth_df增加max列,值为rul的max列值加truth_df的more列,
# truth_df['max']的元素是测试集里面每个id的最大cycle值加rul里每个id的真实剩余寿命
truth_df['max'] = rul['max'] + truth_df['more']
# 将'more'这一列从truth_df中去掉
truth_df.drop('more', axis=1, inplace=True)
"""generate RUL for test data"""
test_df = test_df.merge(truth_df, on=['id'], how='left')
test_df['RUL'] = test_df['max'] - test_df['cycle']
test_df.drop('max', axis=1, inplace=True)
"""
test_df(13096, 28)
id cycle setting1 setting2 ... s20 s21 cycle_norm RUL
0 1 1 0.632184 0.750000 ... 0.558140 0.661834 0.00000 142
1 1 2 0.344828 0.250000 ... 0.682171 0.686827 0.00277 141
2 1 3 0.517241 0.583333 ... 0.728682 0.721348 0.00554 140
3 1 4 0.741379 0.500000 ... 0.666667 0.662110 0.00831 139
...
"""
"""pick a large window size of 50 cycles"""
sequence_length = 50
def gen_sequence(id_df, seq_length, seq_cols):
data_array = id_df[seq_cols].values
num_elements = data_array.shape[0]
for start, stop in zip(range(0, num_elements - seq_length), range(seq_length, num_elements)):
yield data_array[start:stop, :]
"""pick the feature columns"""
sensor_cols = ['s' + str(i) for i in range(1, 22)]
sequence_cols = ['setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 'cycle_norm']
sequence_cols.extend(sensor_cols)
'''
sequence_cols=['setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 'cycle_norm', 's1', 's2', 's3', 's4', 's5', 's6', 's7',
's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14', 's15', 's16', 's17', 's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
'''
# 下一行所用的gen_sequence()中第一个参数是训练集中id为1的部分,第二个参数是50, 第三个参数如下所示
val = list(gen_sequence(train_df[train_df['id'] == 1], sequence_length, sequence_cols))
val_array = np.array(val) # val_array.shape=(142, 50, 25) 142=192-50
'''
sequence_length= 50
sequence_cols= ['setting1', 'setting2', 'setting3', 'cycle_norm', 's1', 's2', 's3', 's4', 's5', 's6',
's7', 's8', 's9', 's10', 's11', 's12', 's13', 's14', 's15', 's16', 's17', 's18', 's19', 's20', 's21']
train_df[train_df['id'] == 1]=
id cycle setting1 setting2 ... s20 s21 RUL cycle_norm
0 1 1 0.459770 0.166667 ... 0.713178 0.724662 191 0.000000
1 1 2 0.609195 0.250000 ... 0.666667 0.731014 190 0.002770
2 1 3 0.252874 0.750000 ... 0.627907 0.621375 189 0.005540
3 1 4 0.540230 0.500000 ... 0.573643 0.662386 188 0.008310
4 1 5 0.390805 0.333333 ... 0.589147 0.704502 187 0.011080
.. .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
187 1 188 0.114943 0.750000 ... 0.286822 0.089202 4 0.518006
188 1 189 0.465517 0.666667 ... 0.263566 0.301712 3 0.520776
189 1 190 0.344828 0.583333 ... 0.271318 0.239299 2 0.523546
190 1 191 0.500000 0.166667 ... 0.240310 0.324910 1 0.526316
191 1 192 0.551724 0.500000 ... 0.263566 0.097625 0 0.529086
[192 rows x 28 columns]
'''
# 将每个id对应的训练集转换为一个sequence
seq_gen = (list(gen_sequence(train_df[train_df['id'] == id], sequence_length, sequence_cols))
for id in train_df['id'].unique())
# 生成sequence并把它转换成np array
# 在train_FD001.txt中按照id分成了100组数据,对每一组进行sequence后每组会减少window_size的大小
# 20631-100*50 = 15631
seq_array = np.concatenate(list(seq_gen)).astype(np.float32) # seq_array.shape=(15631, 50, 25)
seq_tensor = torch.tensor(seq_array)
seq_tensor = seq_tensor.view(15631, 1, 50, 25).to(device)
print("seq_tensor_shape=", seq_tensor.shape)
print(seq_tensor[0].shape)
"""generate labels"""
def gen_labels(id_df, seq_length, label):
data_array = id_df[label].values
num_elements = data_array.shape[0]
return data_array[seq_length:num_elements, :]
label_gen = [gen_labels(train_df[train_df['id'] == id], sequence_length, ['RUL'])
for id in train_df['id'].unique()]
label_array = np.concatenate(label_gen).astype(np.float32) # label_array.shape=(15631, 1)
label_scale = (label_array-np.min(label_array))/(np.max(label_array)-np.min(label_array))
label_tensor = torch.tensor(label_scale)
label_tensor = label_tensor.view(-1)
label_tensor = label_tensor.to(device)
print("label=", label_tensor[:142])
num_sample = len(label_array)
print("num_sample=", num_sample)
input_size = seq_array.shape[2]
hidden_size = 100
num_layers = 2
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d( # 输入conv1的形状(50, 1, 50, 25)-->输出conv1的形状(50, 20, 26, 13)
in_channels=1, # 输入卷积层的图片通道数
out_channels=20, # 输出的通道数
kernel_size=3, # 卷积核的大小,长宽相等
stride=1, # 滑动步长为1
padding=2 # 给输入矩阵周围添两圈0,这样的话在卷积核为3*3时能将输入矩阵的所有元素考虑进去
),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.fc = nn.Linear(20*26*13, 1) # 将conv1的输出flatten后为(50, 20*26*13)-->经过全连接变为(50, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # 将conv1的输出flatten
# x, _ = self.lstm2(x)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
cnn = CNN().to(device)
print(cnn)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(cnn.parameters(), lr=0.01) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.MSELoss() # the target label is not one-hotted
for epoch in range(20):
for i in range(0, 142): # 分配 batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
b_x = seq_tensor[i].view(1, 1, 50, 25)
b_y = label_tensor[i]
output = cnn(b_x) # cnn output
loss = loss_func(output, b_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
output_sum = output
output = cnn(seq_tensor[0:192-50]) # 将第一个sample放进去
output = output.cpu().detach().numpy()
label_array = label_tensor[0:192-50].cpu().detach().numpy()
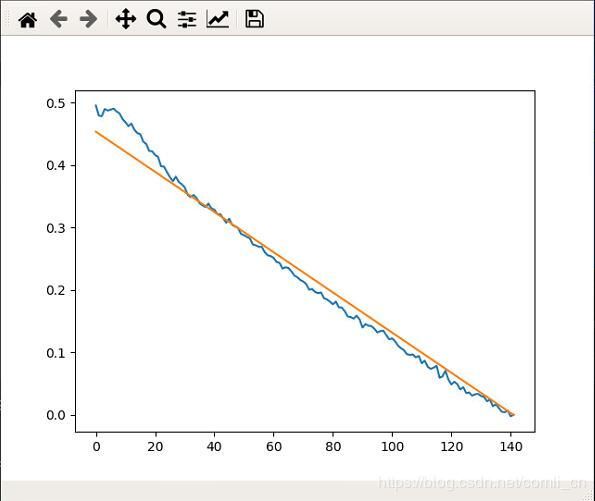
plt.plot(output)
plt.plot(label_array)
plt.show()
'''
seq_array_tensor = torch.tensor(seq_array, dtype=torch.float32)
print(seq_array_tensor.shape)
seq_array_tensor = seq_array_tensor.view(15631, 1, 50, 25)
print(seq_array_tensor.shape)
input_tensor = seq_array_tensor
out_put = cnn(seq_array_tensor)
print(out_put.shape)