LDAP介绍
LDAP概述
LDAP是轻量目录访问协议,(LDAP, Lightweight Directory Access Protocol)LDAP是用于访问目录服务(特别是基于X.500的目录服务),LDAP在TCP/IP或其他面向连接的传输服务上运行。LDAP是IETF标准的跟踪协议。
LDAP是目录非关系型的,不存储BLOB,读写是非对称的,读方便,写麻烦,适合于查询搜索。LDAP不支持数据库的事务和回滚机制。
LDAP支持负载的查询过滤器,使用树状结构,类似于互联网域名、公司组织结构、文件的目录结构等。
LDAP优势
- 读写效率高:可以将LDAP看作是对读操作进行优化的一种"树状数据库",在读写比例大于7:1时,LDAP性能表现很好,比较适合身份认证。
- 开放的标准协议:不同于SQL数据库,LDAP客户端是跨平台的,对几乎所有的程序语言都是标准的API接口。
- 强认证方式:具有很高的安全级别,在国际化方面,LDAP使用UTF-8编码存储各种语言的字符。
- OpenLDAP实现开源:开源软件OpenLDAP包括了很多新功能,最轻便且消耗系统资源最少,可以基于OpenLDAP进行开发新功能。
- 灵活添加数据类型:LDAP根据schema的内容定义各种属性之间的从属关系以及匹配模式。在关系型数据库中若要为用户添加一个属性,需要在表中增加一个字段,如果已有的数据表中增加一个字段,需要更改表的结构,变更比较困难。而LDAP只需要在schema中加入新的属性,属性的增加不会影响性能。
- 树状结构的数据存储:LDAP底层是B/B+树数据结构,整棵树的任何一个分支都可以单独放在一个服务器中进行分布式管理,这不仅有利于做服务器的负载均衡,也便于跨地域的服务器部署。在查询负载大或者企业在不同区域都设有分公司时进行部署突出优势。
LDAP的主要应用场景
- 机器认证
- 用户认证
- 用户/系统组
- 地址簿
- 组织代表
- 资产追踪
- 电话信息存储
- 用户资源管理
- 电子邮件地址查询
- 应用配置存储
LDAP工作方式
LDAP是无状态的客户端-服务器的工作模式,一台或多台包含了由目录信息树组成数据的LDAP服务器。客户端连接到服务器并询问一个问题,服务器以一个答案或者指针(客户端可以获取其他信息的指针,通常是另一个LDAP服务器)进行响应。无论客户端连接了哪一台LDAP服务器,都是看到的相同目录视图。
LDAP基本术语
Directory 目录
Directory 目录是用于存放信息的单元,基于域的命名。
Entry条目
Entry是目录管理的对象,是LDAP最基本的单元,类似于数据库中的每一条record记录。对LDAP的增删改查都是以Entry为基本单元进行操作的。
每个Entry都有一个唯一的标识(DN,Distinguished Name),DN在语法上是由多个相对的标识名注册,之间由逗号隔开,如du:cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org,通过这种层次型语法结构,可以很方便表示出条目在LDAP目录树中的位置。
Attribute属性
每个条目都有很多的Attribute属性,比如个人信息类有姓名、地址、邮箱等属性,每个属性都有名称以及对应的值,每个属性值可以是单个,也可以是多个。一些常见的属性如下:
| 属性 | 别名 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| cn | common name | 通常指一个对象的名称 |
| dn | distinguished name | 唯一标识名,类似于绝对路径,每个对象都有一个唯一标识名,如cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org |
| rdn | relative distinguished name | 相对标识名,类似于相对路径,如cn=Manager |
| dc | domain component | 通常指定一个域名,比如org.apache.hadoop写成dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org |
| ou | organizationl unit | 指定一个组织单元的名称,如ou=groups |
| sn | sur name | 通常指一个人的姓氏,比如sn:Chen |
AttributeType属性类型
每个属性多有唯一的属性类型,属性类型是约定属性值的数据格式以及语法类型,属性类型约定属性值可以有多少个并约定属性查询时的匹配规则、排序、大小写等规则。
ObjectClass对象类
ObjectClass对象类是属性的集合,可以将多个属性封装成一个对象,比如人员信息这个对象类,包含了姓名,地址,电话等属性,学生是人员信息的继承类,除了上面的几个属性,还可以有额外的学校、年级、班级等属性。
通过对象类可以方便的定义条目Entry类型,每个条目可以继承多个对象类,从而获得多个属性。
Schema模式
对象类、属性类型、语法分别约定了条目、属性、值,这些构成了模式,模式中的每个元素都有唯一的oid编号。
LDIF:LDAP Interchange Format
在RFC2849中定义的标准,用于规范LDAP的配置和目录内容等详细信息的保存,我们一般可以使用.ldif结尾的文件进行LDAP相关配置和目录内容的增删改查。
LDAP目录树
LDAP中,目录条目以分层的树状结构排列。
传统指定方式
传统意义上,这种结构反映的是地理或者组织边界,代表国家的条目是在树的顶部显示,在国家下面是代表州和国家组织的条目。在他们下面可能是代表组织单位、人员、打印机、文档条目。

网络指定方式
LDAP的树状结构也可以是基于网络域名来排列,这种命名方式因为DNS定位服务目录而流行。
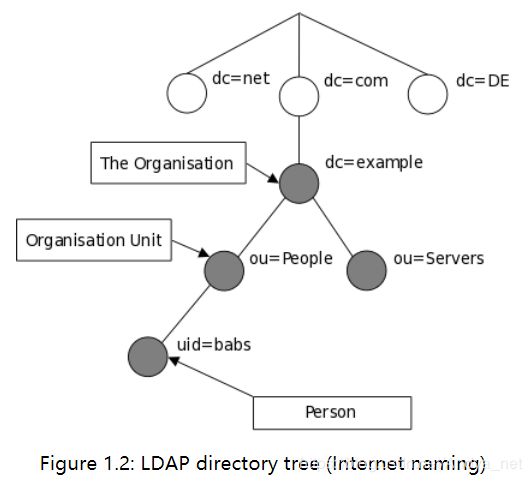
LDAP常用命令介绍
常用参数说明
- -f:
-f file.ldif,从文件file.ldif中读取操作。 - -x:简单认证。
- -D:
-D binddn,绑定DN。 - -H:
-H URI,通过LDAP统一的资源标识符。 - -h:
-h host,LDAP服务器的ip或者hostname。 - -W:提示绑定密码,即不在命令上写密码,如
ldapadd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -W。 - -w:
-w passwd,需要在命令上指定密码进行简单认证,如ldapadd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w 123456。 - -p:
-p port,LDAP服务器的端口。 - -v:显示运行详情。
ldapadd命令
为LDAP服务器增加或修改条目Entry。
如:ldapadd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -W -f init.ldif
ldapdelete命令
从LDAP服务器删除条目Entry。
如:ldapdelete -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w 123456 -h 172.0.0.1 "uid=hdfstest,ou=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org"
ldapmodify命令
为LDAP服务器增加或修改条目Entry。可以使用.ldif文件
如:ldapmodify -a -H ldap://172.0.0.1:389 -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w 123456 -f modifybarbara.ldif
ldapmodrdn命令
修改条目名称,重命名。即修改dn。
如:ldapmodrdn -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w123456 "uid=hdfstest,ou=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" "uid=hivetest"
ldapsearch命令
从LDAP服务器中搜索条目。
如:ldapsearch -x -h 172.0.0.1 -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w 123456
ldappasswd命令
为LDAP服务器更改密码。
- -S:交互式提示用户输入新密码
- -s password:指定新密码,明文的,不建议使用
- -a oldpasswd :指定旧密码,自动生成新密码
- -A :提示输入旧密码,自动生成新密码
1)-S 交互式提示用户输入新密
ldappasswd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w123456 -h172.0.0.1 "cn=guolitao,ou=mysql,ou=研发中心,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -S
2)-s 指定新密码,明文的,不建议使用
ldappasswd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w123456 -h172.0.0.1 "uid=zhan_z,ou=运维部,ou=研发中心,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -s 123456
3)-a 指定旧密码,自动随机生成新密码
ldappasswd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w123456 -h172.0.0.1 "uid=zhan_z,ou=运维部,ou=研发中心,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -a 123456
4)-A 提示输入旧密码,自动随机生成新密码
ldappasswd -x -D "cn=Manager,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -w123456 -h172.0.0.1 "uid=zhan_z,ou=运维部,ou=研发中心,dc=hadoop,dc=apache,dc=org" -A
附录:LDAP命令参数详解
ldapadd命令
$ ldapadd --help
Add or modify entries from an LDAP server
usage: ldapadd [options]
The list of desired operations are read from stdin or from the file
specified by "-f file".
Add or modify options:
-a add values (default)
-c continuous operation mode (do not stop on errors)
-E [!]ext=extparam modify extensions (! indicate s criticality)
-f file read operations from `file'
-M enable Manage DSA IT control (-MM to make critical)
-P version protocol version (default: 3)
-S file write skipped modifications to `file'
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldapdelete命令
$ ldapdelete --help
Delete entries from an LDAP server
usage: ldapdelete [options] [dn]...
dn: list of DNs to delete. If not given, it will be readed from stdin
or from the file specified with "-f file".
Delete Options:
-c continuous operation mode (do not stop on errors)
-f file read operations from `file'
-M enable Manage DSA IT control (-MM to make critical)
-P version protocol version (default: 3)
-r delete recursively
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldapmodify命令
$ ldapmodify --help
Add or modify entries from an LDAP server
usage: ldapmodify [options]
The list of desired operations are read from stdin or from the file
specified by "-f file".
Add or modify options:
-a add values (default is to replace)
-c continuous operation mode (do not stop on errors)
-E [!]ext=extparam modify extensions (! indicate s criticality)
-f file read operations from `file'
-M enable Manage DSA IT control (-MM to make critical)
-P version protocol version (default: 3)
-S file write skipped modifications to `file'
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldapmodrdn命令
$ ldapmodrdn --help
Rename LDAP entries
usage: ldapmodrdn [options] [dn rdn]
dn rdn: If given, rdn will replace the RDN of the entry specified by DN
If not given, the list of modifications is read from stdin or
from the file specified by "-f file" (see man page).
Rename options:
-c continuous operation mode (do not stop on errors)
-f file read operations from `file'
-M enable Manage DSA IT control (-MM to make critical)
-P version protocol version (default: 3)
-r remove old RDN
-s newsup new superior entry
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldapsearch命令
$ ldapsearch -help
usage: ldapsearch [options] [filter [attributes...]]
Search options:
-a deref one of never (default), always, search, or find
-A retrieve attribute names only (no values)
-b basedn base dn for search
-c continuous operation mode (do not stop on errors)
-E [!][=] search extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]domainScope (domain scope)
!dontUseCopy (Don't Use Copy)
[!]mv= (RFC 3876 matched values filter)
[!]pr=[/prompt|noprompt] (RFC 2696 paged results/prompt)
[!]sss=[-][/[-]...]
(RFC 2891 server side sorting)
[!]subentries[=true|false] (RFC 3672 subentries)
[!]sync=ro[/] (RFC 4533 LDAP Sync refreshOnly)
rp[/][/] (refreshAndPersist)
[!]vlv=/(//|:)
(ldapv3-vlv-09 virtual list views)
[!]deref=derefAttr:attr[,...][;derefAttr:attr[,...][;...]]
[!][=:] (generic control; no response handling)
-f file read operations from `file'
-F prefix URL prefix for files (default: file:///tmp/)
-l limit time limit (in seconds, or "none" or "max") for search
-L print responses in LDIFv1 format
-LL print responses in LDIF format without comments
-LLL print responses in LDIF format without comments
and version
-M enable Manage DSA IT control (-MM to make critical)
-P version protocol version (default: 3)
-s scope one of base, one, sub or children (search scope)
-S attr sort the results by attribute `attr'
-t write binary values to files in temporary directory
-tt write all values to files in temporary directory
-T path write files to directory specified by path (default: /tmp)
-u include User Friendly entry names in the output
-z limit size limit (in entries, or "none" or "max") for search
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldappasswd命令
$ ldappasswd --help
Change password of an LDAP user
usage: ldappasswd [options] [user]
user: the authentication identity, commonly a DN
Password change options:
-a secret old password
-A prompt for old password
-t file read file for old password
-s secret new password
-S prompt for new password
-T file read file for new password
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
ldapwhoami命令
$ ldapwhoami --help
Issue LDAP Who am I? operation to request user's authzid
usage: ldapwhoami [options]
Common options:
-d level set LDAP debugging level to `level'
-D binddn bind DN
-e [!][=] general extensions (! indicates criticality)
[!]assert= (RFC 4528; a RFC 4515 Filter string)
[!]authzid= (RFC 4370; "dn:" or "u:")
[!]chaining[=[/]]
one of "chainingPreferred", "chainingRequired",
"referralsPreferred", "referralsRequired"
[!]manageDSAit (RFC 3296)
[!]noop
ppolicy
[!]postread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]preread[=] (RFC 4527; comma-separated attr list)
[!]relax
[!]sessiontracking
abandon, cancel, ignore (SIGINT sends abandon/cancel,
or ignores response; if critical, doesn't wait for SIGINT.
not really controls)
-h host LDAP server
-H URI LDAP Uniform Resource Identifier(s)
-I use SASL Interactive mode
-n show what would be done but don't actually do it
-N do not use reverse DNS to canonicalize SASL host name
-O props SASL security properties
-o [=] general options
nettimeout= (in seconds, or "none" or "max")
ldif-wrap= (in columns, or "no" for no wrapping)
-p port port on LDAP server
-Q use SASL Quiet mode
-R realm SASL realm
-U authcid SASL authentication identity
-v run in verbose mode (diagnostics to standard output)
-V print version info (-VV only)
-w passwd bind password (for simple authentication)
-W prompt for bind password
-x Simple authentication
-X authzid SASL authorization identity ("dn:" or "u:")
-y file Read password from file
-Y mech SASL mechanism
-Z Start TLS request (-ZZ to require successful response)
参考
openldap文档