DDSM数据库转换图像格式——LJPEG转为PNG格式
Digital Database for Screening Mammography (DDSM)数据库是一个非常大的乳腺图像数据库,有一万多张图像,但是图像格式是LJPEG,现有的图像软件(如photoshop、ACCDsee、windows自带的图像查看软件)以及编程软件(如matlab)都无法读取,需要将其转换成其他常见的格式才能使用。我从网上搜到了很多方法,试过之后都不成功,其中包括该数据库的创建者——南佛罗里达大学自己写的一个程序[1],一个医学图像格式转换软件XMedCon[2]。最后成功的方法是使用曼彻斯特大学的Dr. Chris Rose写的一个完整的程序,在他的程序基础上做了些修改,成功的将图像格式转换成了PNG格式。他的程序链接见http://microserf.org.uk/academic/Software.html (PS. 最近发现此链接地址已失效,所以我把源程序放在了我的github上,地址:https://github.com/hd11224/DDSM,包括了所有需要的工具和软件)
从上面给出的链接下载到的程序中,有用户手册告诉你怎么使用这个程序。这个程序是用Ruby语言写的,需要在Cygwin下运行,用户手册中有介绍如何安装Cygwin及其他需要的工具。程序工作流程是使用者手动输入图像名称,程序先从FTP上下载该图像,然后经过几步转换,最终转换为PNG格式。我在按照用户手册运行这个程序时没有成功,用VS2013打开get-ddsm-mammo文件查看源码,发现是从FTP上下载图像环节出了问题,做了修改后,最终运行成功。我修改后的程序如下:
#!/usr/bin/ruby
# This program gets a specified mammogram from the DDSM website and
# converts it to a PNG image. See the help message for full details.
require 'net/ftp'
# Specify the name of the info-file.
def info_file_name
'info-file.txt'
end
def image_names
'image_name.txt'
end
# Get an FTP file as specified by a DDSM path (e.g.,
# /pub/DDSM/cases/cancers/cancer_06/case1141/A-1141-1.ics) and return the
# local path to the file, or return nil if the file could not be dowloaded.
def get_file_via_ftp(ddsm_path)
ftp = Net::FTP.new('figment.csee.usf.edu')
ftp.passive = true
ftp.login
ftp.chdir(File.dirname(ddsm_path))
puts File.basename(ddsm_path)
ftp.getbinaryfile(File.basename(ddsm_path))
#ftp.getbinaryfile(ddsm_path)
# Will be stored local to this program, under the same file name
# Check to make sure that we managed to get the file.
if !FileTest.exist?(File.basename(ddsm_path))
puts "Could not get the file #{File.basename(ddsm_path)} from the DDSM FTP server; perhaps the server is busy."
exit(-1)
end
return File.basename(ddsm_path)
end
# Return the string input with the system's filesep at the end; if there
# is one there already then return input.
def ensure_filesep_terminated(input)
if input[input.length-1].chr != File::SEPARATOR
input += File::SEPARATOR
end
return input
end
# Check program input; input is the program input (i.e ARGV).
def check_inputs(input)
if input.length != 1
puts get_help
exit(-1)
end
# See if the user wanted the help docs.
if input[0] == '--help'
puts get_help
exit(-1)
end
# Check to make sure that the info file exists.
if !FileTest.exist?(info_file_name)
puts "The file #{info_file_name} does not exist; use catalogue-ddsm-ftp-server.rb"
exit(-1)
end
end
# Given the name of a DDSM image, return the path to the
# .ics file associated with the image name. If we can't find the
# path, then we return nil.
def get_ics_path_for_image(image_name)
# Does image_name look right?
if image_name[/._\d{4,4}_.\..+/].nil?
raise 'image_name seems to be wrong. It is: ' + image_name
end
# Edit the image name, as .ics files have the format 'A-0384-1.ics';
# there is no '.RIGHT_CC' (for example).
image_name = image_name[0..(image_name.rindex('.')-1)] # Strip everything after and including the last '.'.
image_name[1] = '-'
image_name[6] = '-' # Change the '_'s to '-'s (better regexp-based approach?).
image_name+='.ics' # Add the file suffix.
# Get the path to the .ics file for the specified image.
File.open(info_file_name) do |file|
file.each_line do |line|
# Does this line specify the .ics file for the specified image name?
if !line[/.+#{image_name}/].nil?
# If so, we can stop looking
return line
end
end
end
# If we get here, then we did not find a match, so we will return nil.
return nil
end
# Given a line from a .ics file, return a string that specifies the
# number of rows and cols in the image described by the line. The
# string would be '123 456' if the image has 123 rows and 456 cols.
def get_image_dims(line)
rows = line[/.+LINES\s\d+/][/\d+/]
cols = line[/.+PIXELS_PER_LINE\s\d+/][/PIXELS_PER_LINE\s\d+/][/\d+/]
return rows + ' ' + cols
end
# Given an image name and a string representing the location of a
# local .ics file, get the image dimensions and digitizer name for
# image_name. Return a hash which :image_dims maps to a string of the
# image dims (which would be '123 456' if the image has 123 rows and
# 456 cols) and :digitizer maps to the digitizer name. If we can't
# determine the dimensions and/or digitizer name, the corresponding
# entry in the hash will be nil.
def get_image_dims_and_digitizer(image_name, ics_file)
# Get the name of the image view (e.g. 'RIGHT_CC')
image_view = image_name[image_name.rindex('.')+1..image_name.length-1]
image_dims = nil
digitizer = nil
# Read the image dimensions and digitizer name from the file.
File.open(ics_file, 'r') do |file|
file.each_line do |line|
if !line[/#{image_view}.+/].nil?
# Read the image dimensions
image_dims = get_image_dims(line)
end
if !line[/DIGITIZER.+/].nil?
# Read the digitizer type from the file.
digitizer = line.split[1].downcase # Get the second word in the DIGITIZER line.
# There are two types of Howtek scanner and they are
# distinguished by the first letter in image_name.
if digitizer == 'howtek'
if image_name[0..0].upcase == 'A'
digitizer += '-mgh'
elsif image_name[0..0].upcase == 'D'
digitizer += '-ismd'
else
raise 'Error trying to determine Howtek digitizer variant.'
end
end
end
end
end
# Return an associative array specifying the image dimensions and
# digitizer used.
return {:image_dims => image_dims, :digitizer =>digitizer}
end
# Given the name of a DDSM image, return a string that describes
# the image dimensions and the name of the digitizer that was used to
# capture it. If
def do_get_image_info(image_name)
# Get the path to the ics file for image_name.
ftp_path = get_ics_path_for_image(image_name)
ftp_path.chomp!
# Get the ics file; providing us with a string representing
# the local location of the file.
ics_file = get_file_via_ftp(ftp_path)
# Get the image dimensions and digitizer for image_name.
image_dims_and_digitizer = get_image_dims_and_digitizer(image_name, ics_file)
# Remove the .ics file as we don't need it any more.
File.delete(ics_file)
return image_dims_and_digitizer
end
# Given a mammogram name and the path to the image info file, get the
# image dimensions and digitizer name string.
def get_image_info(image_name)
# Get the image dimensions and digitizer type for the specified
# image as a string.
image_info = do_get_image_info(image_name)
# Now output the result to standard output.
all_ok = !image_info[:image_dims].nil? && !image_info[:digitizer].nil? # Is everything OK?
if all_ok
ret_val = image_info[:image_dims] + ' ' + image_info[:digitizer]
end
return ret_val
end
# Return a non-existant random filename.
def get_temp_filename
rand_name = "#{rand(10000000)}" # A longish string
if FileTest.exist?(rand_name)
rand_name = get_temp_filename
end
return rand_name
end
# Retrieve the LJPEG file for the mammogram with the specified
# image_name, given the path to the info file. Return the path to the
# local file if successful. If we can't get the file, then return nil.
def get_ljpeg(image_name)
# Get the path to the image file on the mirror of the FTP server.
path = nil
File.open(info_file_name) do |file|
file.each_line do |line|
if !line[/.+#{image_name}\.LJPEG/].nil?
# We've found it, so get the file.
line.chomp!
local_path = get_file_via_ftp(line)
return local_path
end
end
end
# If we get here we didn't find where the file is on the server.
return nil
end
# Given the path to the dir containing the jpeg program, the path to a
# LJPEG file, convert it to a PNM file. Return the path to the PNM
# file.
def ljpeg_to_pnm(ljpeg_file, dims_and_digitizer)
# First convert it to raw format.
command = "./jpeg.exe -d -s #{ljpeg_file}"
`#{command}` # Run it.
raw_file = ljpeg_file + '.1' # The jpeg program adds a .1 suffix.
# See if the .1 file was created.
if !FileTest.exist?(raw_file)
raise 'Could not convert from LJPEG to raw.'
end
# Now convert the raw file to PNM and delete the raw file.
command = "./ddsmraw2pnm.exe #{raw_file} #{dims_and_digitizer}"
pnm_file = `#{command}`
File.delete(raw_file)
if $? != 0
raise 'Could not convert from raw to PNM.'
end
# Return the path to the PNM file.
return pnm_file.split[0]
end
# Convert a PNM file to a PNG file. pnm_file is the path to the pnm file
# and target_png_file is the name of the PNG file that we want created.
def pnm_to_png(pnm_file, target_png_file)
command = "convert -depth 16 #{pnm_file} #{target_png_file}"
`#{command}`
if !FileTest.exist?(target_png_file)
raise 'Could not convert from PNM to PNG.'
end
return target_png_file
end
#write image_names to image_nama.txt
def write_image_names(name)
namefile=File.open(image_names,'a')
namefile.puts name
namefile.puts "\r\n"
namefile.close
end
# The entry point of the program.
def main
# Check to see if the input is sensible.
#check_inputs(ARGV)
#image_name = ARGV[0]
File.open('read_names.txt','r') do |file|
file.each_line do |line|
image_name = line
image_name.chomp!
# Get the image dimensions and digitizer name string for the
# specified image.
image_info = get_image_info(image_name)
# Get the LJPEG file from the mirror of the FTP site, returning the
# path to the local file.
ljpeg_file = get_ljpeg(image_name)
# Convert the LJPEG file to PNM and delete the original LJPEG.
pnm_file = ljpeg_to_pnm(ljpeg_file, image_info)
File.delete(ljpeg_file)
# Now convert the PNM file to PNG and delete the PNG file.
target_png_file = image_name + '.png'
png_file = pnm_to_png(pnm_file, target_png_file)
File.delete(pnm_file)
# Test to see if we got something.
if !FileTest.exist?(png_file)
raise 'Could not create PNG file.'
exit(-1)
end
# Display the path to the file.
puts File.expand_path(png_file)
#write image name
write_image_names(image_name)
#exit(0)
end
end
exit(0)
end
# The help message
def get_help
<
(Note: the '\\' simply indicates that the above command should be on
one line.)
where:
* is the name of the DDSM image you want to get and
convert, for example: 'A_1141_1.LEFT_MLO'.
If successful, the program will print the path to the PNG file of
the requested mammogram to standard output and will return a status
code of 0. If unsuccessful, the program should display a
useful error message and return a non-zero status code.
END_OF_HELP
end
# Call the entry point.
main
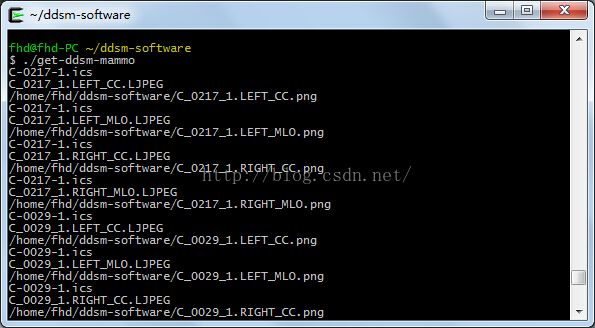
很麻烦的一点是,原程序运行需要手动依次输入图像名称,一次只能处理一张图像,一张图像处理完后才能处理下一张,很费时费力,所以在上面贴出的程序中我还做了一点修改,可以批量处理图像。方法是将要处理的图像的名称提前写在一个txt文件里,一行一个,命名为read_names,运行程序只需输入 ./get-ddsm-mammo即可。程序运行界面如下:
每处理完一张图像,程序会将图像的名称写在一个名为image_name的txt文件里,所以在运行程序前要先创建一个名为image_name的txt文件。
最后一点要说明的是,用户手册中提到在安装Cygwin时要同时安装Ruby,因为当时的Cygwin版本较低,Ruby已不在手册中所示位置,而是单独拿出来的,要安装如下图所示的Ruby和rubygems:
和
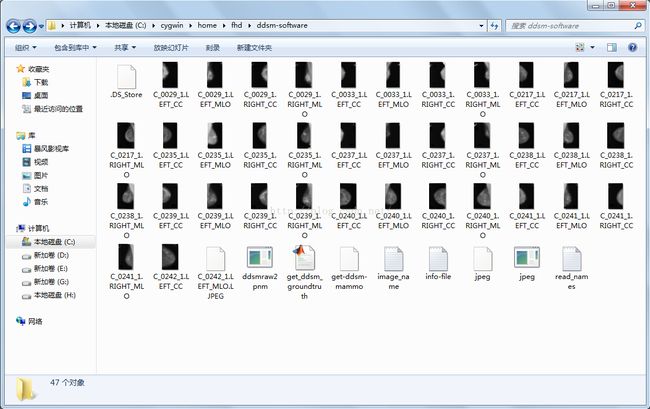
在ddsm-software文件夹下,会看到已经转为PNG格式的图像:
[1]http://marathon.csee.usf.edu/Mammography/software/heathusf_v1.1.0.html
[2]http://sourceforge.net/projects/xmedcon/