概述
Service 的启动过程和根 Activity 启动过程有部分相似的知识点,Service 的启动过程将分为两个部分来进行讲解,分别是 ContextImpl 到 ActivityManageService 的调用过程和 ActivityThread 启动 Service。
1. ContextImpl 到 AMS 的调用过程
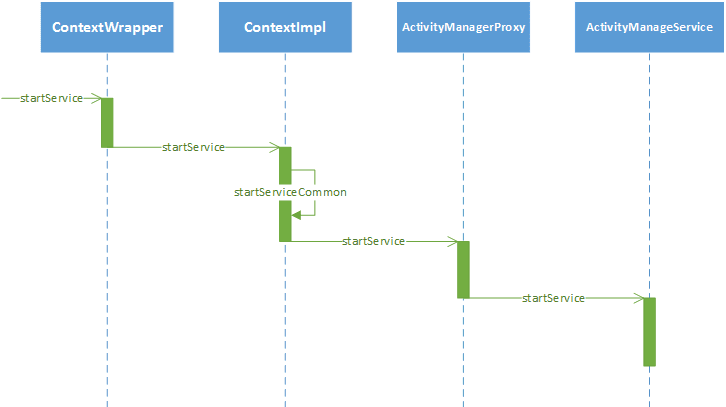
ContextImpl 到 AMS 的调用过程很简短,如图所示:
要启动Service,我们会调用 startService 方法,它在 ContextWrapper 中实现,代码如下所示:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/ContextWrapper.java
public class ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase;
...
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
return mBase.startService(service);
}
...
}
在 startService 方法中会调用 mBase 的 startService 方法,Context 类型的 mBase 对象具体指的是什么呢?通过学习根 Activity 启动过程我们知道,ActivityThead 启动 Activity 时会调用如下代码创建 Activity 的上下文环境:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
if (activity != null) {
Context appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r, activity); //1
...
}
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window);
...
}
return activity;
}
在注释 1 处创建上下文对象 appContext,并传入 Activity 的 attach 方法中,将 Activity 与上下文对象 appContext 关联起来,这个上下文对象 appContext 的具体类型是什么?我们接着查看 createBaseContextForActivity 方法,代码如下所示:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private Context createBaseContextForActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, final Activity activity) {
...
ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createActivityContext(
this, r.packageInfo, r.token, displayId, r.overrideConfig);
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
Context baseContext = appContext;
...
return baseContext;
}
上下文对象 appContext 的具体类型就是 ContextImpl,在 Activity 的 attach 方法中将 ContextImpl 赋值给 ContextWrapper 的成员变量 mBase,因此,上面提出的问题就得到了解答,mBase 具体指向的就是 ContextImpl。那么,紧接着来查看 ContextImpl 的 startService 方法,代码如下所示:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
/**
* 1
*/
ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
...
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
在 startService 方法中会返回 startServiceCommon 方法,在 startServiceCommon 方法中会在注释 1 处调用 AMS 的代理 IActivityManager 的 startService 方法,最终调用的是 AMS 的 startService 方法。
2. ActivityThread 启动 Service
ActivityThread 启动 Service 的时序图如图所示:
接下来我们来查看 AMS 的 startService 方法,如下所示:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
synchronized(this) {
...
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, userId); //1
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return res;
}
}
注释 1 处调用 mServices 的 startServiceLocked 方法,mServices 的类型是 ActiveServices,ActiveServices 的 startServiceLocked 方法代码如下所示:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
···
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false); //1
if (res == null) {
return null;
}
if (res.record == null) {
return new ComponentName("!", res.permission != null
? res.permission : "private to package");
}
ServiceRecord r = res.record; //2
···
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting); //3
return cmp;
}
注释 1 处的 retrieveServiceLocked 方法会查找是否有与参数 service 对应的 ServiceRecord,如果没有找到,就会调用 PackageManagerService 去获取参数 service 对应的 Service 信息,并封装到 ServiceRecord 中,最后将 ServiceRecord 封装为 ServiceLookupResult 返回。其中 ServiceRecord 用于描述一个 Service,和此前讲过的 ActivityRecord 类似,在注释 2 处通过注释 1 处返回的 ServiceLookupResult 得到参数 service 对应的 ServiceRecord,并传入到注释 3 处的 startServiceInnerLocked 方法中。
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
return startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
...
return r.name;
}
startServiceLocked 方法的末尾 return 了 startServiceInnerLocked 方法,而 startServiceInnerLocked 方法中又调用了 bringUpServiceLocked 方法,如下所示:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
...
final String procName = r.processName; //1
ProcessRecord app;
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false); //2
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) { //3
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode,
mAm.mProcessStats);
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg); //4
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
} else {
app = r.isolatedProc;
}
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) { //5
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
"service", r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) { //6
...
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
...
return null;
}
在注释 1 处得到 ServiceRecord 的 processName 的值赋值给 procName ,其中 processName 用来描述 Service 想要在哪个进程运行,默认是当前进程,我们也可以在 AndroidManifes 配置文件中设置 android:process 属性来新开启一个进程运行 Service。注释 2 处将 procName 和 Service 的 uid 传入到 AMS 的 getProcessRecordLocked 方法中,来查询是否存在一个与 Service 对应的 ProcessRecord 类型的对象 app,ProcessRecord 主要用来记录运行的应用程序进程的信息。注释 5 处判断 Service 对应的 app 为 null 则说明用来运行 Service 的应用程序进程不存在,则调用注释 6 处的 AMS 的 startProcessLocked 方法来创建对应的应用程序进程。注释 3 处判断如果用来运行 Service 的应用程序进程存在,则调用注释 4 处的 realStartServiceLocked 方法来启动 Service:
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActiveServices.java
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
...
try {
...
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
...
}
...
}
在 realStartServiceLocked 方法中调用了 app.thread 的 scheduleCreateService 方法。其中 app.thread 是 IApplicationThread 类型的,它的实现是 ActivityThread 的内部类 ApplicationThread。ApplicationThread 的 scheduleCreateService 方法如下所示:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
首先将要启动的信息封装成 CreateServiceData 对象并传给 sendMessage 方法,sendMessage 方法向 H 发送 CREATE_SERVICE 消息,sendMessage 方法有多个重载方法,最终调用的 sendMessage 方法如下所示:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private void sendMessage(int what, Object obj, int arg1, int arg2, boolean async) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(
TAG, "SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what)
+ ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = what;
msg.obj = obj;
msg.arg1 = arg1;
msg.arg2 = arg2;
if (async) {
msg.setAsynchronous(true);
}
mH.sendMessage(msg);
}
这里 mH 指的是 H,它是 ActivityThread 的内部类并继承自 Handler,是应用程序进程中主线程的消息管理类。我们接着查看 H 的handleMessage 方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private class H extends Handler {
public static final int LAUNCH_ACTIVITY = 100;
public static final int PAUSE_ACTIVITY = 101;
...
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog.v(TAG, ">>> handling: " + codeToString(msg.what));
switch (msg.what) {
···
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
...
}
handleMessage 方法根据消息类型为 CREATE_SERVICE,会调用 handleCreateService 方法:
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
unscheduleGcIdler();
//获取要启动 Service 的应用程序的 LoadedApk
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo); //1
Service service = null;
try {
//获取类加载器
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader(); //2
//创建 Service 实例
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance(); //3
} catch (Exception e) {
···
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
//创建 Service 的上下文环境 ContextImpl 对象
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo); //4
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//初始化 Service
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManager.getService()); //5
service.onCreate(); //6
mServices.put(data.token, service); //7
try {
ActivityManager.getService().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
···
}
}
在注释 1 处获取要启动 Service 的应用程序的 LoadedApk,LoadedApk 是一个 APK 文件的描述类。在注释 2 处通过调用 LoadedApk 的 getClassLoader 方法来获取类加载器。接着在注释 3 处根据 CreateServiceData 对象中储存的 Service 信息,创建 Service 实例。在注释 4 处创建 Service 的上下文环境 ContextImpl 对象。在注释 5 处通过 Service 的 attach 方法来初始化 Service。在注释 6 处调用 Service 的 onCreate 方法,这样 Service 就启动了。在注释 7 处启动的 Service 加入到 ActivityThread 的成员变量 mServices 中,其中 mServices 是 ArrayMap 类型。
Service 的启动过程就讲到这里,接下来我们学习 Service 的绑定过程。