树莓派:传感器安装与测试
树莓派:传感器安装与测试
准备
烧录完系统的 raspberryPi 3
python 2.7
传感器:
- 树莓派专用摄像头 v2.1
- 四位数码管
- 温湿度传感器
摄像头
官方文档 1(简略版)
官方文档2 (完整版)
安装picamera
sudo apt-get install python3-picamera
使用示例,in python3.4:
camera = picamera.PiCamera()
camera.capture('image.jpg',resize=(320,240)) # 在 在当前文件夹下将截取图像存为image.jpg, 320*240大小
camera.close() # 使用完后一定要关闭, 否则因为端口被占用,下次调用会出错没有关闭camera对象在下次调用会出现以下错误
mmal: mmal_vc_port_enable: failed to enable port vc.null_sink:in:0(OPQV): ENOSPC
mmal: mmal_port_enable: failed to enable connected port (vc.null_sink:in:0(OPQV))0x1324250 (ENOSPC)
mmal: mmal_connection_enable: output port couldn't be enabled
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/picamera/camera.py", line 433, in __init__
self._init_preview()
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/picamera/camera.py", line 513, in _init_preview
self, self._camera.outputs[self.CAMERA_PREVIEW_PORT])
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/picamera/renderers.py", line 558, in __init__
self.renderer.inputs[0].connect(source).enable()
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/picamera/mmalobj.py", line 2212, in enable
prefix="Failed to enable connection")
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/picamera/exc.py", line 184, in mmal_check
raise PiCameraMMALError(status, prefix
picamera.exc.PiCameraMMALError: Camera component couldn't be enabled: Out of resources (other than memory) 四位数码管
常见的输出显示,四个数字+四个数点,总共 4*7+4=32个led灯管。如果采用一一对应的输入方式,至少需要32个针脚,但是实际上只有12个针脚。
所以我们采用动态方法:每一时刻只亮四个数字中的一个,并以足够快的速度在四个数字中循环,看起来就像一起亮着。
树莓派的针脚分布编号如下图:
我们这里采用BCM编码。
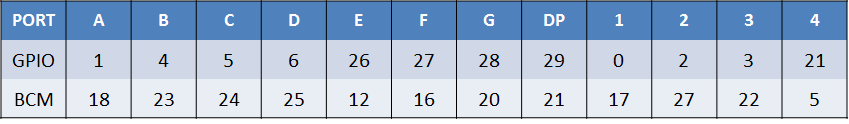
四位数码管的针脚与树莓派针脚的连接:
其中PORT表示数码管的编码(下图上半部分):
下方的table中写出了各个要显示的数字所需要的A-G各个针脚的电平。由于这款3461BS四位数码管是共阳极的,所以当A-G针脚对应的输入电平为负的时候,对应的led灯管亮起。
结合GPIO模块,用python实现按照输入的参数数字字符串输出数字到数码管上:
3461BS.py(python2.7)
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
import sys
mode0=[0,0,0,0,0,0,1]
mode1=[1,0,0,1,1,1,1]
mode2=[0,0,1,0,0,1,0]
mode3=[0,0,0,0,1,1,0]
mode4=[1,0,0,1,1,0,0]
mode5=[0,1,0,0,1,0,0]
mode6=[0,1,0,0,0,0,0]
mode7=[0,0,0,1,1,1,1]
mode8=[0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
mode9=[0,0,0,0,1,0,0]
PORT_TABLE=[mode0,mode1,mode2,mode3,mode4,mode5,mode6,mode7,mode8,mode9]
BCM_PORT=[17,27,22,5]
BCM_VALUE=[18,23,24,25,12,16,20,21]
def init():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
for port in BCM_PORT:
GPIO.setup(port,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(port,GPIO.HIGH)
for value in BCM_VALUE:
GPIO.setup(value,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(value,GPIO.LOW)
for port in BCM_PORT:
GPIO.output(port,GPIO.LOW)
def light_off():
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
for port in BCM_PORT:
GPIO.setup(port,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(port,GPIO.LOW)
for value in BCM_VALUE:
GPIO.setup(value,GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(value,GPIO.HIGH)
def dp_allume(dp_index):
light_off()
GPIO.setup(BCM_PORT[dp_index],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_PORT[dp_index],GPIO.HIGH)
GPIO.setup(BCM_VALUE[7],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_VALUE[7],GPIO.LOW)
def val_allume(value,led_index):
light_code=PORT_TABLE[value]
light_off()
for lc in range(7):
if light_code[lc]==0:
GPIO.setup(BCM_VALUE[lc],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_VALUE[lc],GPIO.LOW)
else:
GPIO.setup(BCM_VALUE[lc],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_VALUE[lc],GPIO.HIGH)
for li in range(4):
if li==led_index:
GPIO.setup(BCM_PORT[li],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_PORT[li],GPIO.HIGH)
else:
GPIO.setup(BCM_PORT[li],GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(BCM_PORT[li],GPIO.LOW)
def value_to_list(val):
num_list=[-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]
if val<10:
num_list[0]=int(val//1)
val=val-num_list[0]
num_list[2]=int(val//0.1)
val=val-num_list[2]*0.1
num_list[3]=int(val//0.01)
val=val-num_list[3]*0.01
num_list[4]=int(val//0.001)
elif val<100:
num_list[0]=int(val//10)
val=val-num_list[0]*10
num_list[1]=int(val//1)
val=val-num_list[1]
num_list[3]=int(val//0.1)
val=val-num_list[3]*0.1
num_list[4]=int(val*100)
elif val<1000:
num_list[0]=int(val//100)
val=val-num_list[0]*100
num_list[1]=int(val//10)
val=val-num_list[1]*10
num_list[2]=int(val//1)
val=val-num_list[2]
num_list[4]=int(val*10)
elif val<10000:
num_list[0]=int(val//1000)
val=val-num_list[0]*1000
num_list[1]=int(val//100)
val=val-num_list[1]*100
num_list[2]=int(val//10)
val=val-num_list[2]*10
num_list[3]=int(val)
else:
pass
return num_list
def show(number=0,show_time=5):
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
light_off()
num_list=value_to_list(number)
for itr in range(5):
if num_list[itr]==-1:
dp_itr=itr
break
del(num_list[dp_itr])
tmp=time.clock()
while time.clock()-tmpfor itr in range(4):
val_allume(num_list[itr],itr)
dp_allume(dp_itr-1)
light_off()
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv)==1:
show(number=float(sys.argv[1]))
GPIO.cleanup()
elif len(sys.argv)==2:
show(number=float(sys.argv[1]))
GPIO.cleanup()
elif len(sys.argv)==3:
show(number=float(sys.argv[1]),show_time=float(sys.argv[2]))
GPIO.cleanup()
else:
print "Usage: 3461BS.py [SHOW_NUMBER][SHOW_TIME]" 由于针脚较多,建议用面包板进行扩展:
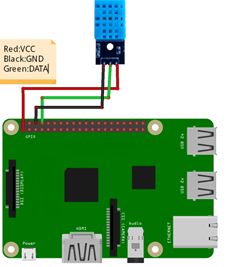
温湿度传感器
用高低电平的变化序列来表示温度和湿度数字
每一份温湿度数据的传输大约会需要4毫秒,包括
- 8位的湿度整数部分
- 8位的湿度小数部分
- 8位的温度整数部分
- 8位的温度小数部分
- 8位的校验和
每一位数据大约持续100微秒
传感器的通路连接分为两部分
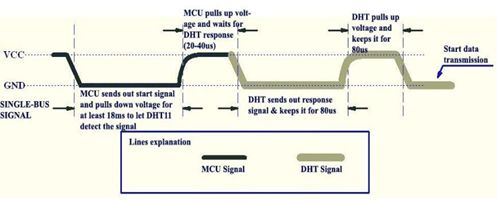
1. 握手阶段
- 树莓派向传感器发送一个开始信号:传感器默认为高电平,树莓派输出一个至少持续18毫秒的低电平后重新拉回高电平,持续20-40微秒
- 传感器向树莓派回复:传感器将电平降为低电平,持续80微秒后重新将电平拉回高电平,持续80微秒
2. 数据传输阶段
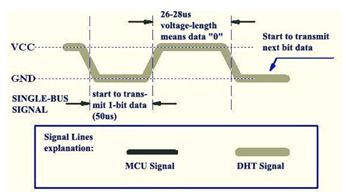
每一位数据(0或1)都以50微秒的低电平开始,并以高电平结束。
其中表示0的高电平持续26-28微秒,表示1的高电平持续70微秒。
解码python(2.7)文件:
dht11.py
#! /usr/bin/python*
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
class DHT11Result:
'DHT11 sensor result returned by DHT11.read() method'
ERR_NO_ERROR = 0
ERR_MISSING_DATA = 1
ERR_CRC = 2
error_code = ERR_NO_ERROR
temperature = -1
humidity = -1
def __init__(self, error_code, temperature, humidity):
self.error_code = error_code
self.temperature = temperature
self.humidity = humidity
def is_valid(self):
return self.error_code == DHT11Result.ERR_NO_ERROR
class DHT11:
'DHT11 sensor reader class for Raspberry'
__pin = 0
def __init__(self, pin):
self.__pin = pin
def read(self):
GPIO.setup(self.__pin, GPIO.OUT)
# send initial high
self.__send_and_sleep(GPIO.HIGH, 0.05)
# pull down to low
self.__send_and_sleep(GPIO.LOW, 0.02)
# change to input using pull up
GPIO.setup(self.__pin, GPIO.IN, GPIO.PUD_UP)
# collect data into an array
data = self.__collect_input()
# parse lengths of all data pull up periods
pull_up_lengths = self.__parse_data_pull_up_lengths(data)
# if bit count mismatch, return error (4 byte data + 1 byte checksum)
if len(pull_up_lengths) != 40:
return DHT11Result(DHT11Result.ERR_MISSING_DATA,0,0)
# calculate bits from lengths of the pull up periods
bits = self.__calculate_bits(pull_up_lengths)
# we have the bits, calculate bytes
the_bytes = self.__bits_to_bytes(bits)
# calculate checksum and check
checksum = self.__calculate_checksum(the_bytes)
if the_bytes[4] != checksum:
return DHT11Result(DHT11Result.ERR_CRC, 0, 0)
# ok, we have valid data, return it
return DHT11Result(DHT11Result.ERR_NO_ERROR, the_bytes[2], the_bytes[0])
def __send_and_sleep(self, output, sleep):
GPIO.output(self.__pin, output)
time.sleep(sleep)
def __collect_input(self):
# collect the data while unchanged found
unchanged_count = 0
# this is used to determine where is the end of the data
max_unchanged_count = 100
last = -1
data = []
while True:
current = GPIO.input(self.__pin)
data.append(current)
if last != current:
unchanged_count = 0
last = current
else:
unchanged_count += 1
if unchanged_count > max_unchanged_count:
break
return data
def __parse_data_pull_up_lengths(self, data):
STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN = 1
STATE_INIT_PULL_UP = 2
STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN = 3
STATE_DATA_PULL_UP = 4
STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN = 5
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN
lengths = [] # will contain the lengths of data pull up periods
current_length = 0 # will contain the length of the previous period
for i in range(len(data)):
current = data[i]
current_length += 1
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_DOWN:
if current == 0:
# ok, we got the initial pull down
state = STATE_INIT_PULL_UP
continue
else:
continue
if state == STATE_INIT_PULL_UP:
if current == 1:
# ok, we got the initial pull up
state = STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN
continue
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_FIRST_PULL_DOWN:
if current == 0:
# we have the initial pull down, the next will be the data pull up
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
continue
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_UP:
if current == 1:
# data pulled up, the length of this pull up will determine whether it is 0 or 1
current_length = 0
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN
continue
else:
continue
if state == STATE_DATA_PULL_DOWN:
if current == 0:
# pulled down, we store the length of the previous pull up period
lengths.append(current_length)
state = STATE_DATA_PULL_UP
continue
else:
continue
return lengths
def __calculate_bits(self, pull_up_lengths):
# find shortest and longest period
shortest_pull_up = 1000
longest_pull_up = 0
for i in range(0, len(pull_up_lengths)):
length = pull_up_lengths[i]
if length < shortest_pull_up:
shortest_pull_up = length
if length > longest_pull_up:
longest_pull_up = length
# use the halfway to determine whether the period it is long or short
halfway = shortest_pull_up + (longest_pull_up - shortest_pull_up) / 2
bits = []
for i in range(0, len(pull_up_lengths)):
bit = False
if pull_up_lengths[i] > halfway:
bit = True
bits.append(bit)
return bits
def __bits_to_bytes(self, bits):
the_bytes = []
byte = 0
for i in range(0, len(bits)):
byte = byte << 1
if (bits[i]):
byte = byte | 1
else:
byte = byte | 0
if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0):
the_bytes.append(byte)
byte = 0
return the_bytes
def __calculate_checksum(self, the_bytes):
return the_bytes[0] + the_bytes[1] + the_bytes[2] + the_bytes[3] & 255 测量执行python程序:
TemHumSensor.py
import dht11
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
try:
while True:
instance=dht11.DHT11(pin=4)
result = instance.read()
print 'temperature'+str(result.temperature)
print 'humidity'+str(result.humidity)
time.sleep(2)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass