LinkedList用法及源码解析
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/github_39430101/article/details/76861393
LinkedList简介
LinkedList是由双向链表实现的,对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList优于LinkedList,因为LinkedList要移动指针。对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。另外LinkedList实现了Deque接口,可以实现栈和队列的功能。
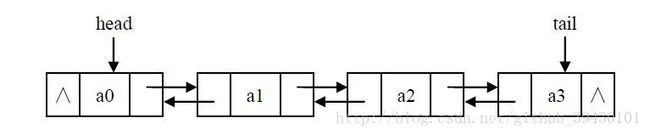
LinkedList结构
常见用法
package com.code.LinkedList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class TestLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
/**
* 基本方法
*/
list.add("关羽");
list.add("张飞");
list.add("刘备");
list.add("曹操");
//addFirst(E e)将指定元素添加到此列表的开头
list.addFirst("诸葛亮");
//addLast(E e)将指定元素添加到此列表的尾部
list.addLast("rank");
//contains()
if(list.contains("郭嘉")) {
System.out.println("若郭嘉在世");
}else System.out.println("岂有赤壁之败");
//get(int index)
System.out.println(list.get(4));
//getFirst()返回此列表中第一个元素
System.out.println("此列表的老大是:"+list.getFirst());
System.out.println("此列表中老末是:"+list.getLast());
System.out.println(list);
// peek() peekFirst() peekLast()获取但不移除
// poll() pollFirst() pollLast()获取且移除
//它们与remove的区别是遇到为空的链表会报异常
/**
* 实现栈和队列的功能
*/
list.clear();
list.removeFirst();//会报异常 java.util.NoSuchElementException
//栈特点:先进后出,后进先出 push进栈 pop出栈
TestStack tl = new TestLinkedList().new TestStack();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
tl.push(i);
}
System.out.println(tl.pop());
TestQueue tq = new TestLinkedList().new TestQueue();
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
tq.put(i);
}
System.out.println(tq.get());
//队列特点:先进先出,后进后出 put入列 get出列
}
class TestStack{
LinkedList 源码
package java.util;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
//实现了Deque接口,可以实现栈和队列的功能 LinkedList是通过prev和next两个指针串联的
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List, Deque, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//LinkedList中元素的个数
transient int size = 0;
//first指向链表的头结点
transient Node first;
//last指向链表的尾节点
transient Node last;
/**
* 空的构造函数
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
//将c中元素添加到LinkedList中
public LinkedList(Collectionextends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
/**
* 添加头结点
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node f = first;//f向头节点
final Node newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); //新建一个节点
first = newNode;//first指向新的节点,f保存着之前first的节点
if (f == null)
last = newNode;//当节点为空时尾节点指向新的节点
else
f.prev = newNode;//赋给头节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 添加尾节点
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 在一个非空节点之前加入一个节点
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/*
* 删除一个非空的头(first)节点,把指向该节点的指针都移除,同时把first指向它的next,如果next节点为空,说明这个节点是List中的最后一个节点,那么first和last都指向空
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item; //把节点中的值赋给element
final Node next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next; //把f元素的next值
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 同理,删除一个非空的尾(last)节点
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node next = x.next;
final Node prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//返回此列表的第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//返回此列表的最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
//移除并且返回此列表的第一个元素
public E removeFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Removes and returns the last element from this list.
*
* @return the last element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this list contains the specified element.
* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this list contains
* at least one element {@code e} such that
* (o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e)).
*
* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this list contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return indexOf(o) != -1;
}
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Appends all of the elements in the specified collection to the end of
* this list, in the order that they are returned by the specified
* collection's iterator. The behavior of this operation is undefined if
* the specified collection is modified while the operation is in
* progress. (Note that this will occur if the specified collection is
* this list, and it's nonempty.)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collectionextends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* Inserts all of the elements in the specified collection into this
* list, starting at the specified position. Shifts the element
* currently at that position (if any) and any subsequent elements to
* the right (increases their indices). The new elements will appear
* in the list in the order that they are returned by the
* specified collection's iterator.
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collectionextends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
/**
* Removes all of the elements from this list.
* The list will be empty after this call returns.
*/
public void clear() {
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for (Node x = first; x != null; ) {
Node next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;
size = 0;
modCount++;
}
// Positional Access Operations
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of an existing element.
*/
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index < size;
}
/**
* Tells if the argument is the index of a valid position for an
* iterator or an add operation.
*/
private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {
return index >= 0 && index <= size;
}
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
private void checkElementIndex(int index) {
if (!isElementIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {
if (!isPositionIndex(index))
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
// Search Operations
/**
* Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element
* in this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element.
* More formally, returns the lowest index {@code i} such that
* (o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i))),
* or -1 if there is no such index.
*
* @param o element to search for
* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in
* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
//返回最后一次出现该对象的索引
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
int index = size;
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (x.item == null)
return index;
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
index--;
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
}
}
return -1;
}
// Queue operations.
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of this list.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Adds the specified element as the tail (last element) of this list.
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @since 1.5
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
return add(e);
}
// Deque operations
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the front of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerFirst})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
addFirst(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the end of this list.
*
* @param e the element to insert
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Deque#offerLast})
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves, but does not remove, the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the first element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* Retrieves and removes the last element of this list,
* or returns {@code null} if this list is empty.
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, inserts the element at the front of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
/**
* Pops an element from the stack represented by this list. In other
* words, removes and returns the first element of this list.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #removeFirst()}.
*
* @return the element at the front of this list (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this list)
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element in this
* list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list
* does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
/**
* Removes the last occurrence of the specified element in this
* list (when traversing the list from head to tail). If the list
* does not contain the element, it is unchanged.
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Returns a list-iterator of the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list.
* Obeys the general contract of {@code List.listIterator(int)}.
*
* The list-iterator is fail-fast: if the list is structurally
* modified at any time after the Iterator is created, in any way except
* through the list-iterator's own {@code remove} or {@code add}
* methods, the list-iterator will throw a
* {@code ConcurrentModificationException}. Thus, in the face of
* concurrent modification, the iterator fails quickly and cleanly, rather
* than risking arbitrary, non-deterministic behavior at an undetermined
* time in the future.
*
* @param index index of the first element to be returned from the
* list-iterator (by a call to {@code next})
* @return a ListIterator of the elements in this list (in proper
* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @see List#listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator listIterator(int index) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
private Node lastReturned;
private Node next;
private int nextIndex;
private int expectedModCount = modCount;
ListItr(int index) {
// assert isPositionIndex(index);
next = (index == size) ? null : node(index);
nextIndex = index;
}
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex < size;
}
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasNext())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return nextIndex > 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
if (!hasPrevious())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
lastReturned = next = (next == null) ? last : next.prev;
nextIndex--;
return lastReturned.item;
}
public int nextIndex() {
return nextIndex;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return nextIndex - 1;
}
public void remove() {
checkForComodification();
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
Node lastNext = lastReturned.next;
unlink(lastReturned);
if (next == lastReturned)
next = lastNext;
else
nextIndex--;
lastReturned = null;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastReturned == null)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
lastReturned.item = e;
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
lastReturned = null;
if (next == null)
linkLast(e);
else
linkBefore(e, next);
nextIndex++;
expectedModCount++;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumersuper E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
while (modCount == expectedModCount && nextIndex < size) {
action.accept(next.item);
lastReturned = next;
next = next.next;
nextIndex++;
}
checkForComodification();
}
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
/**
* @since 1.6
*/
public Iterator descendingIterator() {
return new DescendingIterator();
}
/**
* Adapter to provide descending iterators via ListItr.previous
*/
private class DescendingIterator implements Iterator<E> {
private final ListItr itr = new ListItr(size());
public boolean hasNext() {
return itr.hasPrevious();
}
public E next() {
return itr.previous();
}
public void remove() {
itr.remove();
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private LinkedList superClone() {
try {
return (LinkedList) super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError(e);
}
}
/**
* Returns a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList}. (The elements
* themselves are not cloned.)
*
* @return a shallow copy of this {@code LinkedList} instance
*/
public Object clone() {
LinkedList clone = superClone();
// Put clone into "virgin" state
clone.first = clone.last = null;
clone.size = 0;
clone.modCount = 0;
// Initialize clone with our elements
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
clone.add(x.item);
return clone;
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence (from first to last element).
*
* The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are
* maintained by this list. (In other words, this method must allocate
* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.
*
*
This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based
* APIs.
*
* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list
* in proper sequence
*/
public Object[] toArray() {
Object[] result = new Object[size];
int i = 0;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
return result;
}
/**
* Returns an array containing all of the elements in this list in
* proper sequence (from first to last element); the runtime type of
* the returned array is that of the specified array. If the list fits
* in the specified array, it is returned therein. Otherwise, a new
* array is allocated with the runtime type of the specified array and
* the size of this list.
*
* If the list fits in the specified array with room to spare (i.e.,
* the array has more elements than the list), the element in the array
* immediately following the end of the list is set to {@code null}.
* (This is useful in determining the length of the list only if
* the caller knows that the list does not contain any null elements.)
*
*
Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between
* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows
* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,
* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.
*
*
Suppose {@code x} is a list known to contain only strings.
* The following code can be used to dump the list into a newly
* allocated array of {@code String}:
*
*
* String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);
*
* Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to
* {@code toArray()}.
*
* @param a the array into which the elements of the list are to
* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the
* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.
* @return an array containing the elements of the list
* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array
* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in
* this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T[] toArray(T[] a) {
if (a.length < size)
a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(
a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
int i = 0;
Object[] result = a;
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
result[i++] = x.item;
if (a.length > size)
a[size] = null;
return a;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 876323262645176354L;
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
// Write out any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in any hidden serialization magic
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size
int size = s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject());
}
/**
* Creates a late-binding
* and fail-fast {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this
* list.
*
* The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#SIZED} and
* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}. Overriding implementations should document
* the reporting of additional characteristic values.
*
* @implNote
* The {@code Spliterator} additionally reports {@link Spliterator#SUBSIZED}
* and implements {@code trySplit} to permit limited parallelism..
*
* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list
* @since 1.8
*/
@Override
public Spliterator spliterator() {
return new LLSpliterator(this, -1, 0);
}
/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */
static final class LLSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int BATCH_UNIT = 1 << 10; // batch array size increment
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final LinkedList list; // null OK unless traversed
Node current; // current node; null until initialized
int est; // size estimate; -1 until first needed
int expectedModCount; // initialized when est set
int batch; // batch size for splits
LLSpliterator(LinkedList list, int est, int expectedModCount) {
this.list = list;
this.est = est;
this.expectedModCount = expectedModCount;
}
final int getEst() {
int s; // force initialization
final LinkedList lst;
if ((s = est) < 0) {
if ((lst = list) == null)
s = est = 0;
else {
expectedModCount = lst.modCount;
current = lst.first;
s = est = lst.size;
}
}
return s;
}
public long estimateSize() { return (long) getEst(); }
public Spliterator trySplit() {
Node p;
int s = getEst();
if (s > 1 && (p = current) != null) {
int n = batch + BATCH_UNIT;
if (n > s)
n = s;
if (n > MAX_BATCH)
n = MAX_BATCH;
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int j = 0;
do { a[j++] = p.item; } while ((p = p.next) != null && j < n);
current = p;
batch = j;
est = s - j;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, j, Spliterator.ORDERED);
}
return null;
}
public void forEachRemaining(Consumersuper E> action) {
Node p; int n;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if ((n = getEst()) > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
current = null;
est = 0;
do {
E e = p.item;
p = p.next;
action.accept(e);
} while (p != null && --n > 0);
}
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumersuper E> action) {
Node p;
if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (getEst() > 0 && (p = current) != null) {
--est;
E e = p.item;
current = p.next;
action.accept(e);
if (list.modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
return true;
}
return false;
}
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.SIZED | Spliterator.SUBSIZED;
}
}
}