爬虫进阶:验证码突破--6、机器学习识别简单图片字母验证码
一、生成验证码图片作为测试样本:
#coding:utf-8
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFont
import random
class ValidCodeImg:
def __init__(self, width=150, height=30, code_count=5, font_size=32, point_count=20, line_count=3,
img_format='png'):
'''
可以生成一个经过降噪后的随机验证码的图片
:param width: 图片宽度 单位px
:param height: 图片高度 单位px
:param code_count: 验证码个数
:param font_size: 字体大小
:param point_count: 噪点个数
:param line_count: 划线个数
:param img_format: 图片格式
:return 生成的图片的bytes类型的data
'''
self.width = width
self.height = height
self.code_count = code_count
self.font_size = font_size
self.point_count = point_count
self.line_count = line_count
self.img_format = img_format
@staticmethod
def getRandomColor():
'''获取一个随机颜色(r,g,b)格式的'''
c1 = random.randint(0, 255)
c2 = random.randint(0, 255)
c3 = random.randint(0, 255)
return (c1, c2, c3)
@staticmethod
def getRandomStr():
'''获取一个随机字符串,每个字符的颜色也是随机的'''
random_num = str(random.randint(0, 9))
random_low_alpha = chr(random.randint(97, 122))
random_upper_alpha = chr(random.randint(65, 90))
random_char = random.choice([random_num, random_low_alpha, random_upper_alpha])
return random_char
def getValidCodeImg(self):
# 获取一个Image对象,参数分别是RGB模式。宽150,高30,随机颜色
image = Image.new('RGB', (self.width, self.height), self.getRandomColor())
# 获取一个画笔对象,将图片对象传过去
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
# 获取一个font字体对象参数是ttf的字体文件的目录,以及字体的大小
font = ImageFont.truetype("londrina-solid.ttf", size=self.font_size)
temp = []
for i in range(self.code_count):
# 循环5次,获取5个随机字符串
random_char = self.getRandomStr()
# 在图片上一次写入得到的随机字符串,参数是:定位,字符串,颜色,字体
draw.text((10 + i * 30, -2), random_char, self.getRandomColor(), font=font)
# 保存随机字符,以供验证用户输入的验证码是否正确时使用
temp.append(random_char)
valid_str = "".join(temp)
# 噪点噪线
# 划线
for i in range(self.line_count):
x1 = random.randint(0, self.width)
x2 = random.randint(0, self.width)
y1 = random.randint(0, self.height)
y2 = random.randint(0, self.height)
draw.line((x1, y1, x2, y2), fill=self.getRandomColor())
# 画点
for i in range(self.point_count):
draw.point([random.randint(0, self.width), random.randint(0, self.height)], fill=self.getRandomColor())
x = random.randint(0, self.width)
y = random.randint(0, self.height)
draw.arc((x, y, x + 4, y + 4), 0, 90, fill=self.getRandomColor())
# 在内存生成图片
from io import BytesIO
f = BytesIO()
image.save(f, self.img_format)
data = f.getvalue()
f.close()
return data, valid_str
if __name__ == '__main__':
filePath = r"D:/CapCha/Test/"
n=0
m = 1500 #生成1500个验证码
while n<1500:
img = ValidCodeImg()
data, valid_str = img.getValidCodeImg()
f = open(filePath+valid_str+'.png', 'wb')
print(filePath+valid_str+'.png'+" Generated")
f.write(data)
f.close()
n+=1
本段代码主要是使用PIL模块,来进行识别,生成的样本数据,见如下截图:

在实际的运用中,验证码往往是从要爬取的网站上通过验证码页面获取的图片,一般是不可能有验证码的值的,只能人工标识。这一操作消耗大量人工。本人是基于学习机器学习的兴趣,才从网络中找到这一块的代码段。
参考网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/6324TV/p/8811249.html
二:图片处理,包含转化为灰度图,二值化处理,去除噪点,图片分割等
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFile
import cv2
import imagehash
import time
import os
import pytesseract
from collections import defaultdict
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.externals import joblib
# tesseract.exe所在的文件路径
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = 'C://Program Files (x86)/Tesseract-OCR/tesseract.exe'
def ReadFileList(rootdir):
#尝试直接识别
list = os.listdir(rootdir)
for i in range(0,len(list))[0:10]:
path = os.path.join(rootdir,list[i])
print(path)
if os.path.isfile(path):
print(os.path.basename(path))
image = Image.open(path)
code = pytesseract.image_to_string(image)
print(code)
def splitimage(rownum, colnum, dstpath,img_name,outpath):
'''
图片分割
:param rownum: 切割行数
:param colnum: 切割列数
:param dstpath: 图片文件路径
:param img_name: 要切割的图片文件
:param outpath: 输出文件路径
:return:
'''
img = Image.open(img_name)
w, h = img.size
if rownum <= h and colnum <= w:
print('Original image info: %sx%s, %s, %s' % (w, h, img.format, img.mode))
print('开始处理图片切割, 请稍候...')
s = os.path.split(img_name)
if dstpath == '':
dstpath = s[0]
fn = s[1].split('.')
basename = fn[0]
ext = fn[-1]
num = 1
rowheight = h // rownum
colwidth = w // colnum
file_list = []
for r in range(rownum):
index = 0
for c in range(colnum):
# (left, upper, right, lower)
# box = (c * colwidth, r * rowheight, (c + 1) * colwidth, (r + 1) * rowheight)
if index < 1:
colwid = colwidth + 6
elif index < 2:
colwid = colwidth + 1
elif index < 3:
colwid = colwidth
box = (c * colwid, r * rowheight, (c + 1) * colwid, (r + 1) * rowheight)
newfile = os.path.join(dstpath, basename[num - 1] + '_' + basename + "_" + str(num - 1) + '.' + ext)
file_list.append(newfile)
img.crop(box).save(
os.path.join(outpath, basename[num - 1] + '_' + basename + "_" + str(num - 1) + '.' + ext), ext)
num = num + 1
index += 1
for f in file_list:
print(f)
print('图片切割完毕,共生成 %s 张小图片。' % (num - 1))
def get_threshold(image):
# 获取图片中像素点数量最多的像素
pixel_dict = defaultdict(int)
# 像素及该像素出现次数的字典
rows, cols = image.size
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
pixel = image.getpixel((i, j))
pixel_dict[pixel] += 1
count_max = max(pixel_dict.values()) # 获取像素出现出多的次数
pixel_dict_reverse = {v:k for k,v in pixel_dict.items()}
threshold = pixel_dict_reverse[count_max] # 获取出现次数最多的像素点
return threshold
def get_bin_table(threshold):
# 按照阈值进行二值化处理
# threshold: 像素阈值
# 获取灰度转二值的映射table
table = []
for i in range(256):
#rate = 0.01 # 在threshold的适当范围内进行处理,由于rate设置为0.1时,有一个字母灰度太接近这个阈值,导致映射为0
#if threshold*(1-rate)<= i <= threshold*(1+rate):
if i == threshold:
table.append(1)
else:
table.append(0)
return table
def cut_noise(image):
# 去掉二值化处理后的图片中的噪声点
rows, cols = image.size # 图片的宽度和高度
change_pos = [] # 记录噪声点位置
# 遍历图片中的每个点,除掉边缘
for i in range(1, rows-1):
for j in range(1, cols-1):
# pixel_set用来记录该店附近的黑色像素的数量
pixel_set = []
# 取该点的邻域为以该点为中心的九宫格
for m in range(i-1, i+2):
for n in range(j-1, j+2):
if image.getpixel((m, n)) != 1: # 1为白色,0位黑色
pixel_set.append(image.getpixel((m, n)))
# 如果该位置的九宫内的黑色数量小于等于4,则判断为噪声
if len(pixel_set) <= 4:
change_pos.append((i,j))
# 对相应位置进行像素修改,将噪声处的像素置为1(白色)
for pos in change_pos:
image.putpixel(pos, 1)
return image # 返回修改后的图片
def OCR_lmj(img_path):
# 识别图片中的数字加字母
# 传入参数为图片路径,返回结果为:识别结果
image = Image.open(img_path) # 打开图片文件
imgry = image.convert('L') # 转化为灰度图
# 获取图片中的出现次数最多的像素,即为该图片的背景
max_pixel = get_threshold(imgry)
# 将图片进行二值化处理
table = get_bin_table(threshold=max_pixel)
out = imgry.point(table, '1')
# 去掉图片中的噪声(孤立点)
out = cut_noise(out)
#保存图片
# out.save('E://figures/img_gray.jpg')
# 仅识别图片中的数字
#text = pytesseract.image_to_string(out, config='digits')
# 识别图片中的数字和字母
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(out)
# 去掉识别结果中的特殊字符
exclude_char_list = ' .:\\|\'\"?![],()~@#$%^&*_+-={};<>/¥'
text = ''.join([x for x in text if x not in exclude_char_list])
return text
def main():
# pytesseract识别指定文件目录下的图片
# 图片存放目录figures
dir = 'E://figures'
correct_count = 0 # 图片总数
total_count = 0 # 识别正确的图片数量
# 遍历figures下的png,jpg文件
for file in os.listdir(dir):
if file.endswith('.png') or file.endswith('.jpg'):
# print(file)
image_path = '%s/%s'%(dir,file) # 图片路径
answer = file.split('.')[0] # 图片名称,即图片中的正确文字
recognizition = OCR_lmj(image_path) # 图片识别的文字结果
print((answer, recognizition))
if recognizition == answer: # 如果识别结果正确,则total_count加1
correct_count += 1
total_count += 1
print('Total count: %d, correct: %d.'%(total_count, correct_count))
def GenPngByCap(img_name):
rownum = 1
colnum = 5
dstpath = "D:/CapCha/Test/"
outpath = "D:/CapCha/outdir"
grypath = "D:/CapCha/grydir/"
fileName = dstpath + img_name
image = Image.open(fileName) # 打开图片文件
imgry = image.convert('L') # 转化为灰度图L
# 获取图片中的出现次数最多的像素,即为该图片的背景
max_pixel = get_threshold(imgry)
# 将图片进行二值化处理
table = get_bin_table(threshold=max_pixel)
out = imgry.point(table, '1')
# 去掉图片中的噪声(孤立点)
out = cut_noise(out)
out.save(grypath + img_name)
splitimage(rownum, colnum, dstpath, grypath + img_name, outpath)
def genby_pytesseract():
dstpath = "D:/CapCha/grydir"
correct_count = 0 # 图片总数
total_count = 0 # 识别正确的图片数量
list = os.listdir(dstpath)
for i in range(0, len(list)):
path = os.path.join(dstpath, list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
# GenPngByCap(os.path.basename(path))
answer = os.path.basename(path).split('.')[0]
text = pytesseract.image_to_string(path)
# 去掉识别结果中的特殊字符
exclude_char_list = ' .:\\|\'\"?![],()~@#$%^&*_+-={};<>/¥'
recognizition = ''.join([x for x in text if x not in exclude_char_list])
print(path, recognizition, answer)
if recognizition == answer: # 如果识别结果正确,则total_count加1
correct_count += 1
total_count += 1
print('Total count: %d, correct: %d.' % (total_count, correct_count))
# 二值化的图片,识别通过率Total count: 1000, correct: 59.
def GenPngByCap2(img_name):
rownum = 1
colnum = 5
dstpath = "D:/test/Test/"
outpath = "D:/test/outdir"
grypath = "D:/test/grydir/"
fileName = dstpath + img_name
image = Image.open(fileName) # 打开图片文件
imgry = image.convert('L') # 转化为灰度图L
# 获取图片中的出现次数最多的像素,即为该图片的背景
max_pixel = get_threshold(imgry)
# 将图片进行二值化处理
table = get_bin_table(threshold=max_pixel)
out = imgry.point(table, '1')
# 去掉图片中的噪声(孤立点)
out = cut_noise(out)
out.save(grypath + img_name)
splitimage(rownum, colnum, dstpath, grypath + img_name, outpath)
if __name__ == '__main__':
list = os.listdir(r"D:\CapCha\Test")
for i in range(0, len(list)):
path = os.path.join(r"D:\CapCha\Test", list[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
GenPngByCap2(list[i])
在这个处理的过程中,由于尝试了使用OCR直接识别,或者图片转化后在OCR识别,依然成功率太低,所以尝试从深度学习上进行训练。
分割后的图片示例:
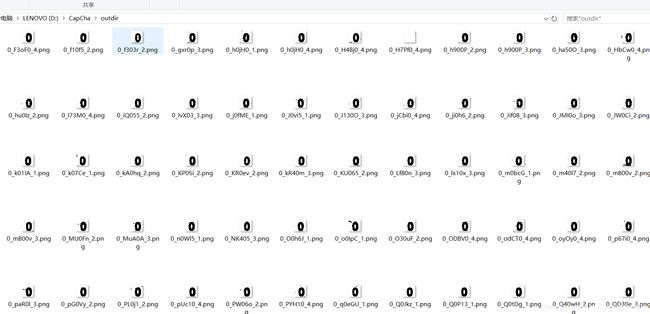
由于我本身生成的验证码是有标识的,所以在作为数据集时,可以直接作为Y值使用,而X值则需要进行转化
图片处理参考网址:
https://blog.csdn.net/icamera0/article/details/50843172
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38641983/article/details/80899354
三:模型训练:
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image,ImageDraw,ImageFile
import cv2
import imagehash
import time
import os
import pytesseract
from collections import defaultdict
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.externals import joblib
train_data_path = "D:/CapCha/outdir"
def read_train_data(train_data_path):
"""
读取训练集文件夹下的单字母/数字图像文件
:return:image_array, image_label:图像list、图像label list """
files = os.listdir(train_data_path)
image_array = []
image_label = []
for capt_per_char_file in files:
image_label += list(capt_per_char_file.split("_")[0])
for capt_per_char_file in files:
path = os.path.join(train_data_path, capt_per_char_file)
image = Image.open(path)
image_array.append(image)
print(capt_per_char_file + " 读取成功")
return image_array, image_label
#feature generated
def feature_transfer(image):
"""
生成特征矩阵
计算每副图像的行和、列和,共image_width + image_height个特征
:param image:图像list
:return:
"""
image_width, image_height=(30,30)
image = image.resize((image_width, image_height)) #标准化图像格式
feature = []#计算特征
for x in range(image_width):#计算行特征
feature_width = 0
for y in range(image_height):
if image.getpixel((x, y)) == 0:
feature_width += 1
feature.append(feature_width)
for y in range(image_height): #计算列特征
feature_height = 0
for x in range(image_width):
if image.getpixel((x, y)) == 0:
feature_height += 1
feature.append(feature_height)
# print('feature length :',len(feature))
return feature
def main():
image_array, image_label = read_train_data(train_data_path)
image_feature = []
for num, image in enumerate(image_array):
feature = feature_transfer(image)
image_feature.append(feature)
return image_feature, image_label
if __name__ == '__main__':
'''
train_table, train_labels = main()
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
clf.fit(train_table, train_labels)
joblib.dump(clf, 'rf.model')
print("训练完成")
'''
clf = joblib.load("rf.model")
test_labels=[]
CAPT_PATH = r"D:/test/outdir"
capt_per_char_list = os.listdir(CAPT_PATH)
image_array, image_label = read_train_data(CAPT_PATH)
image_feature = []
for num, image in enumerate(image_array):
feature = feature_transfer(image)
image_feature.append(feature)
print(capt_per_char_list)
print(clf.predict(image_feature))
如下代码段是训练模型的逻辑,使用joblib保存训练好的模型,之后就可以通过 joblib.load重新拿出来使用了
train_table, train_labels = main()
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
clf.fit(train_table, train_labels)
joblib.dump(clf, 'rf.model')
print("训练完成")
测试结果:
…
T_2B5Td_3.png 读取成功
U_hxUzm_2.png 读取成功
x_hxUzm_1.png 读取成功
z_hxUzm_3.png 读取成功
[‘1_3q1fo_2.png’, ‘2_2B5Td_0.png’, ‘3_3q1fo_0.png’, ‘5_2B5Td_2.png’, ‘B_2B5Td_1.png’, ‘d_2B5Td_4.png’, ‘f_3q1fo_3.png’, ‘h_hxUzm_0.png’, ‘m_hxUzm_4.png’, ‘o_3q1fo_4.png’, ‘q_3q1fo_1.png’, ‘T_2B5Td_3.png’, ‘U_hxUzm_2.png’, ‘x_hxUzm_1.png’, ‘z_hxUzm_3.png’]
[‘1’ ‘2’ ‘3’ ‘5’ ‘B’ ‘d’ ‘f’ ‘h’ ‘m’ ‘o’ ‘q’ ‘T’ ‘U’ ‘x’ ‘z’]
显然成功率达到使用的要求啦。
本文中使用的机器学习是随机森林模型
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=None,min_samples_split=2, random_state=0)
其他分类模型也是可以使用的,比如KNN,SVM,CNN等