《JMX in action》学习笔记(一)——简单的JMX agent编写
书是从这里下载的https://download.csdn.net/download/fangzhilong/1594446
本文是《JMX in action》Chapter 2的学习笔记,原书是英文版,且本人水平有限,如有错误请指教
1 MBean的编写
每一个MBean都需要实现接口,因为JMX 通过接口来描述MBean需要暴露的属性和操作。
package com.tuan.JMXLearn.hello;
public interface helloWorldMBean {
void setGreeting(String greeting);
String getGreeting();
void printGreeting();
}
再写一个实现
package com.tuan.JMXLearn.hello;
public class helloWorld implements helloWorldMBean{
private String greeting = null;
public helloWorld() {
this.greeting = "Hello World! I am a Standard MBean";
}
public helloWorld(String greeting ) {
this.greeting = greeting;
}
public void setGreeting(String greeting) {
this.greeting = greeting;
}
public String getGreeting() {
return greeting;
}
public void printGreeting() {
System.out.println( greeting );
}
}
2 JMX Agent编写
接下来编写JMX agent,一共需要完成以下三个目标:
-
创建MBean Server
-
创建HTML适配器与HTML客户端连接
-
注册helloWorld这个MBean
注意这里需要引用jmxtools和jmxri两个jar包,这两个jar包直接通过maven添加dependency,仍然找不到类,打开本地maven库查看对应的文件夹里面,发现根本没有jar包
后来查了一下因为某些原因这两个包要去oracle的网站下载
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javasebusiness/downloads/java-archive-downloads-java-plat-419418.html#7657-jmx-1.2.1-oth-JPR
下载后把jar包分别放进对应的文件夹里面,改一下名字,在Idea里面Reimport一下即可
Agent类主要就是创建MBean Server,以及MBean的注册
package com.tuan.JMXLearn.hello;
import com.sun.jdmk.comm.HtmlAdaptorServer;
import javax.management.*;
public class helloAgent {
public helloAgent() {
MBeanServer mbs = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer("helloAgent"); //工厂模式创建MBean Server,通过domain属性区分不同Server
helloWorld hw = new helloWorld();
HtmlAdaptorServer adapter = new HtmlAdaptorServer();
ObjectName adapterName = null;
ObjectName helloWorldName = null;
try {
adapterName = new ObjectName("helloAgent:name=htmladapter,port=9092"); //字符串前缀为domain值,一般与Server的domain相同
helloWorldName = new ObjectName("helloAgent:name=helloWorld1");
mbs.registerMBean(hw, helloWorldName); //注册MBean
mbs.registerMBean(adapter, adapterName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
adapter.setPort(9092);
adapter.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
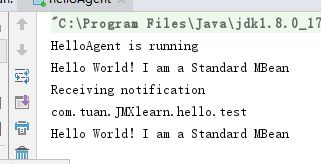
System.out.println("HelloAgent is running");
helloAgent agent = new helloAgent();
}
}
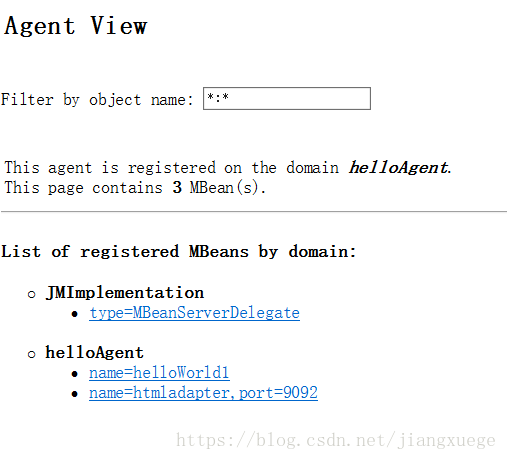
运行后,在浏览器访问http://你的IP:9092/
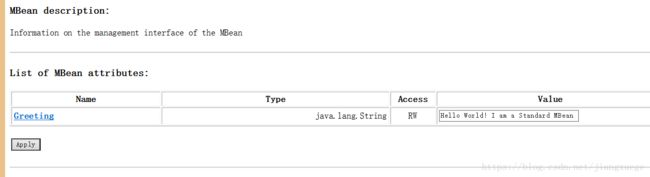
点开helloWorld1,可以在这里修改Greeting字符串的值,也可以执行方法printGreeting()
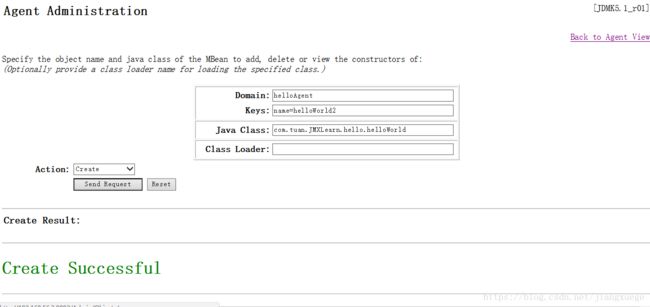
在Agent界面还可以通过网页,创建一个MBean并注册
3 MBean Notification的使用
Notification需要和一个Listener类配合使用,为了简单这里用Agent类作为Listener类,需要修改helloWorld和helloAgent两个类,代码如下
package com.tuan.JMXLearn.hello;
import javax.management.Notification;
import javax.management.NotificationBroadcasterSupport;
public class helloWorld extends NotificationBroadcasterSupport implements helloWorldMBean{
private String greeting = null;
public helloWorld() {
this.greeting = "Hello World! I am a Standard MBean";
}
public helloWorld(String greeting ) {
this.greeting = greeting;
}
public void setGreeting(String greeting) {
this.greeting = greeting;
}
public String getGreeting() {
return greeting;
}
public void printGreeting() {
System.out.println( greeting );
Notification notification = new Notification("com.tuan.JMXlearn.hello.test", this, 0, greeting); //新建Notification
sendNotification(notification);
}
}
package com.tuan.JMXLearn.hello;
import com.sun.jdmk.comm.HtmlAdaptorServer;
import javax.management.*;
public class helloAgent implements NotificationListener{
public helloAgent() {
MBeanServer mbs = MBeanServerFactory.createMBeanServer("helloAgent");
helloWorld hw = new helloWorld();
HtmlAdaptorServer adapter = new HtmlAdaptorServer();
ObjectName adapterName = null;
ObjectName helloWorldName = null;
try {
adapterName = new ObjectName("helloAgent:name=htmladapter,port=9092");
helloWorldName = new ObjectName("helloAgent:name=helloWorld1");
hw.addNotificationListener(this, null, null); //把Agent类设置为hw对象的Notification Listener
mbs.registerMBean(hw, helloWorldName);
mbs.registerMBean(adapter, adapterName);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
adapter.setPort(9092);
adapter.start();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("HelloAgent is running");
helloAgent agent = new helloAgent();
}
@Override
public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback) { //Notification处理
System.out.println("Receiving notification");
System.out.println(notification.getType());
System.out.println(notification.getMessage());
}
}
run起来之后,执行一下printGreeting(),控制台打印了Notification的相关信息
简单剖析一下Notification是如何做的
首先看一下Listener类,每个Listener类需要实现接口NotificationListener,这个接口只有一个方法,在每次接收到Notification的时候自动执行,notification对象包含MBean赋予的一些信息,例如type、message等,handback是一个回调对象
public void handleNotification(Notification notification, Object handback);其次看一下MBean,本例中的MBean继承NotificationBroadcasterSupport这个类,这个类是接口NotificationEmitter的一个实现,接口NotificationEmitter继承了NotificationBroadcaster,这个接口一共有三个方法,很显然一个是添加Listener一个是移除Listener,另外一个是获得所有的Notification信息
public void addNotificationListener(NotificationListener listener,
NotificationFilter filter,
Object handback)
throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException;
public void removeNotificationListener(NotificationListener listener)
throws ListenerNotFoundException;
public MBeanNotificationInfo[] getNotificationInfo();接口NotificationEmitter的removeNotificationListener方法升级了一下,参数变得和addNotificationListener一样多
public void removeNotificationListener(NotificationListener listener,
NotificationFilter filter,
Object handback)
throws ListenerNotFoundException;重点来看一下NotificationBroadcasterSupport这个类,添加、移除Listener其实就是在维护一个并发容器ListlistenerList,sendNotification()调用后,对每个存放在List中的Listener都执行发送(还有一些过滤等操作,现在先不管)
private List listenerList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
public void addNotificationListener(NotificationListener listener,
NotificationFilter filter,
Object handback) {
if (listener == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Listener can't be null") ;
}
listenerList.add(new ListenerInfo(listener, filter, handback));
}
public void removeNotificationListener(NotificationListener listener,
NotificationFilter filter,
Object handback)
throws ListenerNotFoundException {
ListenerInfo li = new ListenerInfo(listener, filter, handback);
boolean removed = listenerList.remove(li);
if (!removed) {
throw new ListenerNotFoundException("Listener not registered " +
"(with this filter and " +
"handback)");
}
}
public void sendNotification(Notification notification) {
if (notification == null) {
return;
}
boolean enabled;
for (ListenerInfo li : listenerList) {
try {
enabled = li.filter == null ||
li.filter.isNotificationEnabled(notification);
} catch (Exception e) {
if (logger.debugOn()) {
logger.debug("sendNotification", e);
}
continue;
}
if (enabled) {
executor.execute(new SendNotifJob(notification, li));
}
}
}