LintCode线段树/扫描线/查询题总结
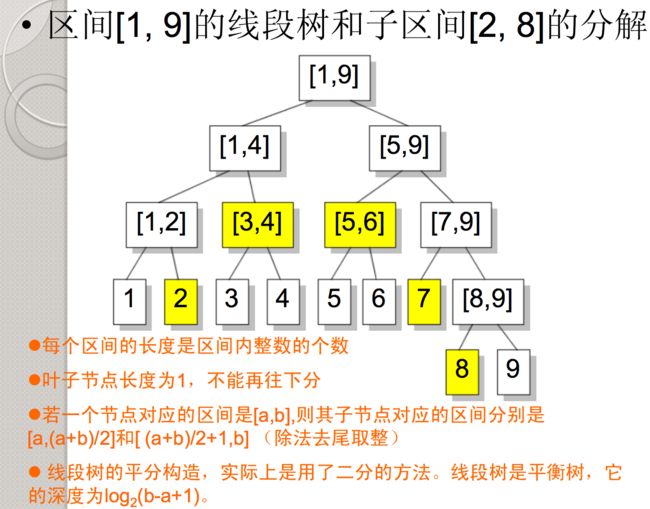
线段树(Segment Tree)又叫区间树(Interval Tree),它实际上是一颗二叉树,树种的每一个节点表示一个区间[a, b],左儿子的区间是[a, (a+b)/2],右儿子的区间是[(a+b)/2+1, b]。
线段树常用于区间统计/查询相关的问题:比如某些数据可以按区间进行划分,按区间动态进行修改,而且还需要按区间多次进行查询,那么使用线段树可以达到较快查询速度。动态的求/更新区间和、区间最值就适用于用线段树来求解。
由于线段树的深度不会超过logL,所以查询的时间复杂度也是O(logL)。
北大的POJ上有关于这个高级数据结构的介绍:http://poj.org/summerschool/1_interval_tree.pdf
LintCode上线段树专题下有这些题目:
201. Segment Tree Build
创建线段树,利用递归的方式:
/**
* Definition of SegmentTreeNode:
* public class SegmentTreeNode {
* public int start, end;
* public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
* public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end) {
* this.start = start, this.end = end;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*@param start, end: Denote an segment / interval
*@return: The root of Segment Tree
*/
public SegmentTreeNode build(int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTreeNode node = new SegmentTreeNode(start, end);
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = build(start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = build( (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
return node;
}
return null;
}
}439. Segment Tree Build II
跟上题类似,多了一个要求,需要每个节点还要保存最大值的信息。
/**
* Definition of SegmentTreeNode:
* public class SegmentTreeNode {
* public int start, end, max;
* public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
* public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end, int max) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* this.max = max
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*@param A: a list of integer
*@return: The root of Segment Tree
*/
public SegmentTreeNode buildHelper(int[] A, int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTreeNode node = new SegmentTreeNode(start, end, A[start]);
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = buildHelper(A, start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = buildHelper(A, (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
node.max = Math.max(node.left.max, node.right.max);
return node;
}
return null;
}
public SegmentTreeNode build(int[] A) {
return buildHelper(A, 0, A.length - 1);
}
}202. Segment Tree Query
对线段树进行查询,要求找到给定区间(start, end)内的最大值
/**
* Definition of SegmentTreeNode:
* public class SegmentTreeNode {
* public int start, end, max;
* public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
* public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end, int max) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* this.max = max
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*@param root, start, end: The root of segment tree and
* an segment / interval
*@return: The maximum number in the interval [start, end]
*/
public int query(SegmentTreeNode root, int start, int end) {
// 查询区间在当前节点的范围之内
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.max;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// 查询区间和左子树有交集
if (start <= mid) {
ans = Math.max(ans, query(root.left, start, end));
}
// 查询区间和右子树有交集
if (end >= mid + 1) {
ans = Math.max(ans, query(root.right, start, end));
}
return ans;
}
}247. Segment Tree Query II
每个节点存了一个count,代表当前区间有多少个元素。给定一个区间,要查询该区间内有多少个元素存在。
/**
* Definition of SegmentTreeNode:
* public class SegmentTreeNode {
* public int start, end, count;
* public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
* public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end, int count) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* this.count = count;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*@param root, start, end: The root of segment tree and
* an segment / interval
*@return: The count number in the interval [start, end]
*/
public int helper(SegmentTreeNode root, int start, int end) {
// 查询区间在当前节点的范围之内
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.count;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
int leftSum = 0, rightSum = 0;
// 查询区间和左子树有交集
if (start <= mid) {
if (end <= mid) { // 包含
leftSum = query(root.left, start, end);
} else { // 分裂
leftSum = query(root.left, start, mid);
}
}
// 查询区间和右子树有交集
if (end >= mid + 1) {
if (start >= mid + 1) { // 包含
rightSum = query(root.right, start, end);
} else { // 分裂
rightSum = query(root.right, mid + 1, end);
}
}
return leftSum + rightSum;
}
public int query(SegmentTreeNode root, int start, int end) {
if (root == null || start > root.end || end < root.start) {
return 0;
}
return helper(root, start, end);
}
}203. Segment Tree Modify
对线段树进行更新,更新了一个节点上的值后,所有对应的节点都要更新:
/**
* Definition of SegmentTreeNode:
* public class SegmentTreeNode {
* public int start, end, max;
* public SegmentTreeNode left, right;
* public SegmentTreeNode(int start, int end, int max) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* this.max = max
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
/**
*@param root, index, value: The root of segment tree and
*@ change the node's value with [index, index] to the new given value
*@return: void
*/
public void modify(SegmentTreeNode root, int index, int value) {
// Find the leaf node that needs modifying
if (root.start == index && root.end == index) {
root.max = value;
return;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
if (index <= mid) { // target leaf node is in the left
modify(root.left, index, value);
root.max = Math.max(root.left.max, root.right.max);
} else { // target leaf node is in the right
modify(root.right, index, value);
root.max = Math.max(root.left.max, root.right.max);
}
return;
}
}205. Interval Minimum Number
给定一个数组,要求对它进行多次区间查询,每次区间查询都是返回数组在查询区间范围内的最小值。这是一道典型的应用线段树来进行查询的问题。首先建立区间树,然后每次查询都用区间查询,这样每次查询的时间复杂度都是O(logL)。
/**
* Definition of Interval:
* public classs Interval {
* int start, end;
* Interval(int start, int end) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* }
*/
class SegmentTree {
public int start, end, min;
public SegmentTree left, right;
public SegmentTree(int start, int end, int min) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.min = min;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
*@param A, queries: Given an integer array and an query list
*@return: The result list
*/
public SegmentTree build(int[] A, int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTree node = new SegmentTree(start, end, A[start]);
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = build(A, start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = build(A, (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
node.min = Math.min(node.left.min, node.right.min);
return node;
}
return null;
}
public int query(SegmentTree root, int start, int end) {
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.min;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (start <= mid) {
ans = Math.min(ans, query(root.left, start, end));
}
if (end > mid) {
ans = Math.min(ans, query(root.right, start, end));
}
return ans;
}
public ArrayList intervalMinNumber(int[] A,
ArrayList queries) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList();
SegmentTree root = build(A, 0, A.length - 1);
for (Interval in: queries) {
res.add(query(root, in.start, in.end));
}
return res;
}
} 206. Interval Sum
给定一个数组,要求对它进行多次区间查询,每次区间查询都是返回数组在查询区间范围内的sum和。这是一道典型的应用线段树来进行查询的问题。首先建立区间树,然后每次查询都用区间查询,这样每次查询的时间复杂度都是O(logL)。
/**
* Definition of Interval:
* public classs Interval {
* int start, end;
* Interval(int start, int end) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* }
*/
class SegmentTree {
public int start, end;
public long sum;
public SegmentTree left, right;
public SegmentTree(int start, int end, long sum) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.sum = sum;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
*@param A, queries: Given an integer array and an query list
*@return: The result list
*/
public SegmentTree build(int[] A, int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTree node = new SegmentTree(start, end, Long.valueOf(A[start]));
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = build(A, start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = build(A, (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
node.sum = node.left.sum + node.right.sum;
return node;
}
return null;
}
public long query(SegmentTree root, int start, int end) {
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.sum;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
long leftSum = 0L, rightSum = 0L;
if (start <= mid) {
if (end <= mid) {
leftSum = query(root.left, start, end);
} else {
leftSum = query(root.left, start, mid);
}
}
if (end > mid) {
if (start <= mid) {
rightSum = query(root.right, mid + 1, end);
} else {
rightSum = query(root.right, start, end);
}
}
return leftSum + rightSum;
}
public ArrayList intervalSum(int[] A,
ArrayList queries) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList();
SegmentTree root = build(A, 0, A.length - 1);
for (Interval in: queries) {
res.add(query(root, in.start, in.end));
}
return res;
}
}
207. Interval Sum II
与上题相比,多了一个modify函数,用于更新节点
class SegmentTree {
public int start, end;
public long sum;
public SegmentTree left, right;
public SegmentTree(int start, int end, long sum) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.sum = sum;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
/* you may need to use some attributes here */
private SegmentTree root;
public SegmentTree build(int[] A, int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTree node = new SegmentTree(start, end, Long.valueOf(A[start]));
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = build(A, start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = build(A, (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
node.sum = node.left.sum + node.right.sum;
return node;
}
return null;
}
public long queryHelper(SegmentTree root, int start, int end) {
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.sum;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
long leftSum = 0L, rightSum = 0L;
if (start <= mid) {
if (end <= mid) {
leftSum = queryHelper(root.left, start, end);
} else {
leftSum = queryHelper(root.left, start, mid);
}
}
if (end > mid) {
if (start <= mid) {
rightSum = queryHelper(root.right, mid + 1, end);
} else {
rightSum = queryHelper(root.right, start, end);
}
}
return leftSum + rightSum;
}
/**
* @param A: An integer array
*/
public Solution(int[] A) {
root = build(A, 0, A.length - 1);
}
/**
* @param start, end: Indices
* @return: The sum from start to end
*/
public long query(int start, int end) {
return queryHelper(root, start, end);
}
public void modifyHelper(SegmentTree root, int index, int value) {
if (root.start == index && root.end == index) {
root.sum = Long.valueOf(value);
return;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
if (index <= mid) {
modifyHelper(root.left, index, value);
} else {
modifyHelper(root.right, index, value);
}
root.sum = root.left.sum + root.right.sum;
return;
}
/**
* @param index, value: modify A[index] to value.
*/
public void modify(int index, int value) {
modifyHelper(root, index, value);
}
}
248. Count of Smaller Number
给定一个数组,和一些查询,每次查询都要返回数组中有多少个数是小于查询数字的。这道题最死板的方法是用循环枚举,稍微好一点的是排序+二分查找(二分查找方法已经在我之前的博客中有说明解法:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengkim/article/details/52103427)。时间复杂度取决于排序的最快速度:O(NlogN)
由于题目中已经说明了每个数字的值不会超过10000。所以每个数字的范围在0~10000之间。我们可以事先把线段树建好,然后叶子节点用于统计那个数字出现的次数。
更好的办法就是用线段树来做:http://www.jiuzhang.com/solutions/count-of-smaller-number/
但是我还有更快的方法来做这道题,由于每个数字的值在0~10000之间,那我完全可以用基数排序来统计。这样先用一轮loop (OlogN) 统计字数用于更新统计数组,然后一次性把所有的累加和求出来存到数组,用于查询。这样总共的时间复杂度就是O(n)。是线性的:
public ArrayList countOfSmallerNumber(int[] A, int[] queries) {
int[] countArr = new int[10001];
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
countArr[A[i]]++;
}
int[] res = new int[10001];
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < countArr.length; i++) {
res[i] = sum;
sum += countArr[i];
}
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
list.add(res[queries[i]]);
}
return list;
} 249. Count of Smaller Number before itself
给定一个数组,对于数组中的每个数字,求出该数字左边有多少个数小于该数。题目条件说明了每个数字的范围在0到1W之间。
要查询当前数字左边共有多少个数比当前数字小,其实也就是统计下标从0到k-1的书里面有几个是小于A[k]的,相当于对前k-1个数字变相求和。那么可以先按照区间[0, 10000]建立一棵线段树。每个叶子节点的count都先记为1。那么查询的时候,就可以边更新边查询了。从左往右扫描数组,遇到当前的数字就把对应到的线段树更新自增,然后查询。查询的时候就是进行统计,找到线段树中所有小于当前数字的区间的count sum。由于每次只会把当前访问过的数字更新,这样就保证了查询是正确的。
举个栗子,比如数组是[1,2,9,8,5]。那如果对8进行查询,看左边有多少个数字小于8的话,其实就统计区间[0, 7]的count sum。而且要保证8右边的数字不出现在区间内。怎么样做到在query查询的时候,8右边的数字不出现在区间统计里面呢?我们可以通过从左到右扫描数组的方式进行。扫描数组的过程中,只有访问到了该数字,才把对应的线段树更新。这样一来,8左边比它大的数字并不会出现在线段树查询的区间中,故自然不会影响到结果。二来,8右边的比它小的数字由于还没被访问到,所以也不会影响查询结果。这一来二去就保证了用线段树的查询是正确的:
class SegmentTree {
public int start, end;
public int count;
public SegmentTree left, right;
public SegmentTree(int start, int end, int count) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.count = count;
this.left = this.right = null;
}
}
public class Solution {
/**
* @param A: An integer array
* @return: Count the number of element before this element 'ai' is
* smaller than it and return count number array
*/
public SegmentTree build(int[] A, int start, int end) {
if (start <= end) {
SegmentTree node = new SegmentTree(start, end, 0);
if (start == end) {
return node;
}
node.left = build(A, start, (start + end) / 2);
node.right = build(A, (start + end) / 2 + 1, end);
node.count = 0;
return node;
}
return null;
}
public int query(SegmentTree root, int start, int end) {
if (start <= root.start && root.end <= end) {
return root.count;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
int leftSum = 0, rightSum = 0;
if (start <= mid) {
if (end <= mid) {
leftSum = query(root.left, start, end);
} else {
leftSum = query(root.left, start, mid);
}
}
if (end > mid) {
if (start <= mid) {
rightSum = query(root.right, mid + 1, end);
} else {
rightSum = query(root.right, start, end);
}
}
return leftSum + rightSum;
}
public void modify(SegmentTree root, int index, int value) {
if (root.start == index && root.end == index) {
root.count += value;
return;
}
int mid = (root.start + root.end) / 2;
if (index <= mid) {
modify(root.left, index, value);
} else {
modify(root.right, index, value);
}
root.count = root.left.count + root.right.count;
return;
}
public ArrayList countOfSmallerNumberII(int[] A) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList();
SegmentTree root = build(A, 0, 10000);
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) {
if (A[i] > 0) {
res.add(query(root, 0, A[i] - 1));
} else {
res.add(0);
}
modify(root, A[i], 1);
}
return res;
}
}
扫描线则是另外一种类型的区间求解的方法。一般遇到如下的几种类型的题目就适用扫描线Sweep Line来解题。扫描线就是模拟用一根线去扫描区间,然后获取每个时间点的信息来解题。
a. 告诉你一些飞机的起飞和降落时间,问你最多能有几架飞机在同时在天上飞。
b. 给你一些会议的开始和结束时间,问你至少需要多少个会议室才能满足需求。
c. 告诉你火车的起始和到达时间,问你需要多少铁轨才能容纳所有的火车。
391. Number of Airplanes in the Sky
告诉你飞机的起飞和降落时间,问你最多有多少个飞机同时在天上飞。典型的扫描线问题。本来给定的是类似于[2, 4], [1, 10]这样的区间代表起飞和结束时间,但是仅仅用这样的数据结构是无法解题的。得把区间拆分成点。而我们其实只需要记录起点和终点就行了。
我们用一个新的数据结构Point来记录,Point的time代表那个时间点,Point的flag代表那个点是起飞还是降落。比如flag为1就是起飞,flag为0就是降落。这样我们就可以把原始数据转化成Point的数据了,并且由于Point只有一个时间点,我们可以对之进行排序。得到按时间有序的Point集合。然后再扫描Point集合,用count标记天上的飞机数目。如果遇到flag为1的Point就增加count数,如果flag为0就减少count。
/**
* Definition of Interval:
* public classs Interval {
* int start, end;
* Interval(int start, int end) {
* this.start = start;
* this.end = end;
* }
*/
class Point {
public int time;
public int flag;
public Point(int time, int flag) {
this.time = time;
this.flag = flag;
}
}
class PointComparator implements Comparator {
public int compare(Point a, Point b) {
if (a.time == b.time) {
return a.flag - b.flag;
}
return a.time - b.time;
}
}
class Solution {
/**
* @param intervals: An interval array
* @return: Count of airplanes are in the sky.
*/
public int countOfAirplanes(List airplanes) {
List list = new ArrayList();
for (Interval in: airplanes) {
list.add(new Point(in.start, 1));
list.add(new Point(in.end, 0));
}
Collections.sort(list, new PointComparator());
int count = 0, res = 0;
for (Point p: list) {
if (p.flag == 1) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
res = Math.max(res, count);
}
return res;
}
}