基于springboot的Mybatis源码分析 -----------------1 Mybatis初始化
直接找到MybatisAutoConfiguration这个类,至于为什么要找这个类,可以看下我springboot源码相关的文章。
这个类上有一个注解
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)说明在这之前会优先去解析DataSourceAutoConfiguration这个类,从名字也能看出这个和数据源有关系找到MybatisAutoConfiguration其中一个被标注了@Bean的方法
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
。。。。
return factory.getObject();
}看到最后一句话,返回了SqlSessionFactoryBean的getObject方法,由于SqlSessionFactoryBean是继承了FacotoryBean的。看SqlSessionFacotryBean的getObject方法
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
this.afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}进入afterPropertiesSet之后再进入
this.sqlSessionFactory = this.buildSqlSessionFactory();这个方法中整体都是给Configuration对象的一些属性赋值,采用了建造者模式。我们先来看下Configuration这个类
protected Environment environment;
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class logImpl;
protected Class vfsImpl;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" }));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory();
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL
protected String databaseId;
/**
* Configuration factory class.
* Used to create Configuration for loading deserialized unread properties.
*
* @see Issue 300 (google code)
*/
protected Class configurationFactory;
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = new TypeHandlerRegistry();
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
protected final LanguageDriverRegistry languageRegistry = new LanguageDriverRegistry();
protected final Map mappedStatements = new StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection");
protected final Map caches = new StrictMap("Caches collection");
protected final Map resultMaps = new StrictMap("Result Maps collection");
protected final Map parameterMaps = new StrictMap("Parameter Maps collection");
protected final Map keyGenerators = new StrictMap("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set loadedResources = new HashSet();
protected final Map sqlFragments = new StrictMap("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
protected final Collection incompleteStatements = new LinkedList();
protected final Collection incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList();
protected final Collection incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList();
protected final Collection incompleteMethods = new LinkedList();
/*
* A map holds cache-ref relationship. The key is the namespace that
* references a cache bound to another namespace and the value is the
* namespace which the actual cache is bound to.
*/
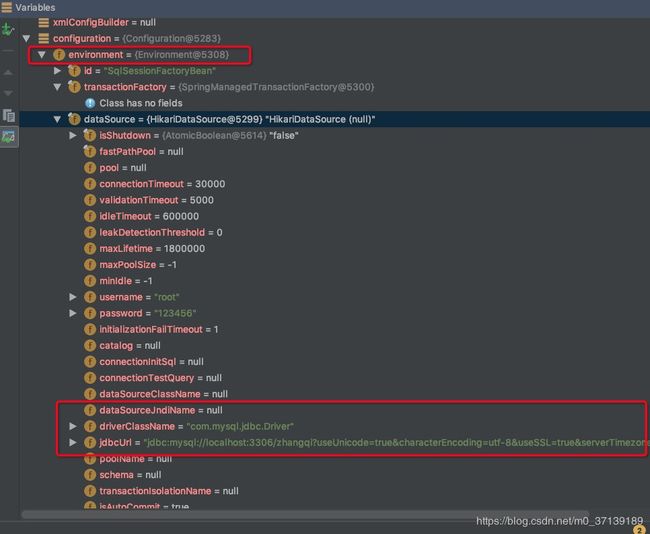
protected final Map cacheRefMap = new HashMap(); 上面列举了Configuration的所有的成员变量,挑几个讲一下,首先是Evironment,这个变量其实就是挂载了一些数据源信息,如果你的项目需要根据不同环境配置不同的数据源,那么这个Evnroment就是根据不同环境来执行不同的数据源。
public final class Environment {
private final String id;
private final TransactionFactory transactionFactory;
private final DataSource dataSource;
//这个就是注册mapper文件和接口
protected final MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
//插件
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
//这个是sql语句和id之间的关系
protected final Map mappedStatements = new StrictMap("Mapped Statements collection");
//resultMap相关
protected final Map resultMaps = new StrictMap("Result Maps collection");
这段代码相当长,挑重点讲:”
如果配置了xml相关的配置,会读取xml中的配置,这可能是为一些还配置xml的springboot项目准备的
(this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), (String)null, this.configurationProperties);
configuration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();这里就是设置数据源了
configuration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment, this.transactionFactory, this.dataSource));接下去就是解析mapper。xml文件了,。也就是我们写sql的那个xml,
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();一开始是初始化一个解析器。
然后重点是
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();点击进去
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();会从mapper节点开始解析
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));这里我们会看到很多熟悉的节点,缓存、入参,结果以及sql,重点看下最后一句=
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}private void buildStatementFromContext(List list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
} ------------->
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);-------->
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);MappedStatement中记录了所有和sql相关的信息,最后会向configuration的
mappedStatements中加入这个MappedStatement,可以理解成id和sql的关系//随后会绑定mapper和接口
bindMapperForNamespace();
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}这里在configuration的loadedResources中加入xml资源
mapperRegistry中加入接口类整个parse执行完之后看一下configuration对象
首先是数据源对象
mappedStatements,可以看到一mappedstatment对应了两个k,一个全类名,一个是id,至于为什么,我也不知道。。。
this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration);---------------.>
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);其实就是创建了一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory的对象。
最后我们来看下这个对象:
很简单,就是包含了一个configuration对象。
--------------------
这边还有个问题,spring是如何做到把Mapper自动注入的呢?因为我们在mapper不需要加上@Service,但是Mapper却可以被spring管理。这里就涉及到一个注解
@MapperScan这个注解上有@Import({MapperScannerRegistrar.class})
找到MapperScannerRegistrar的registerBeanDefinitions方法
其实就是这个方法内部会根据MapperScan中的包,然后把这个包中的mapper加入到BeanDefinationMap中
可以找到
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#doScan方法返回的
return beanDefinitions;就是扫描包中定义的mapper接口
们在写service的时候注入mapper会加1@Autowired,例如
@Autowired UserMapper userMapper;
这里的注入@Autowired实际上就是调用
MapperFactoryBean的getObject方法
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return this.getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
这个sqlSession我上一篇说过是DefaultSqlSession。其实最终会调用到
publicT getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) { return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession); }
------------->
publicT getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory ) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }
上面代码可以看到会根据接口去获取到一个MapperProxyFactory,然后调用它的
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
点进去发现最终会根据接口去创建一个代理类
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
这也就解释了为何mapperRegistry中保存了接口和mapper文件的关系。。