最近在使用opengl做学校的大作业,在读取模型时遇到了无法显示材质的问题,在通过研究obj与mtl文件格式时发现了原因。
由于之前一直是使用别人做好的读取类,对于有贴图的模型可以正常处理,但是这次的模型没有贴图,材质都是用属性直接指定的,如
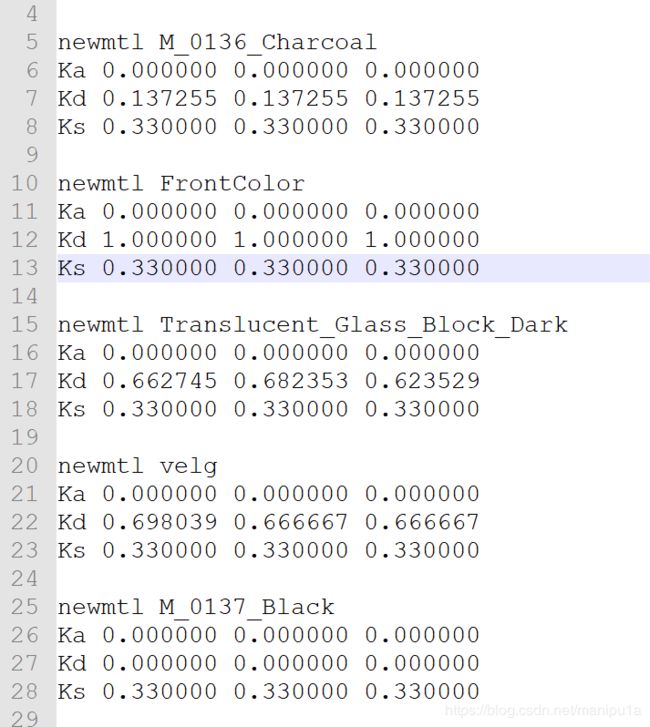
其中,Ka代表环境光,Kd代表漫反射光,Ks代表镜面高光。
为了读取这些数据,在已有的代码中进行了修改(代码在最下)。assimp中其实提供了方法读取这些数据,我们只要保存在mesh信息中,并传入着色器即可使用。
aiMaterial* material = scene->mMaterials[mesh->mMaterialIndex];
Material mat;
aiColor3D color;
//读取mtl文件顶点数据
material->Get(AI_MATKEY_COLOR_AMBIENT, color);
mat.Ka = glm::vec4(color.r, color.g, color.b,1.0);
其中AI_MATKEY_COLOR_AMBIENT即对应了环境光的信息。
在将数据传入着色器时,使用了ubo对象,因为vbo中已经保存了模型的顶点和法线等信息,所以单独处理材质。
代码如下:
mesh.h
#pragma once
#ifndef MESH_H
#define MESH_H
#include // holds all OpenGL type declarations
#include
#include
#include "shader_m.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Vertex {
// position
glm::vec3 Position;
// normal
glm::vec3 Normal;
// texCoords
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
// tangent
glm::vec3 Tangent;
// bitangent
glm::vec3 Bitangent;
};
struct Material {
//材质颜色光照
glm::vec4 Ka;
//漫反射
glm::vec4 Kd;
//镜反射
glm::vec4 Ks;
};
struct Texture {
unsigned int id;
string type;
string path;
};
class Mesh {
public:
/* Mesh Data */
vector vertices;
vector indices;
vector textures;
Material mats;
unsigned int VAO;
unsigned int uniformBlockIndex;
/* Functions */
// constructor
Mesh(vector vertices, vector indices, vector textures, Material mat)
{
this->vertices = vertices;
this->indices = indices;
this->textures = textures;
this->mats = mat;
// now that we have all the required data, set the vertex buffers and its attribute pointers.
setupMesh();
}
// render the mesh
void Draw(Shader shader)
{
// bind appropriate textures
unsigned int diffuseNr = 1;
unsigned int specularNr = 1;
unsigned int normalNr = 1;
unsigned int heightNr = 1;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < textures.size(); i++)
{
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + i); // active proper texture unit before binding
// retrieve texture number (the N in diffuse_textureN)
string number;
string name = textures[i].type;
if (name == "texture_diffuse")
number = std::to_string(diffuseNr++);
else if (name == "texture_specular")
number = std::to_string(specularNr++); // transfer unsigned int to stream
else if (name == "texture_normal")
number = std::to_string(normalNr++); // transfer unsigned int to stream
else if (name == "texture_height")
number = std::to_string(heightNr++); // transfer unsigned int to stream
// now set the sampler to the correct texture unit
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shader.ID, (name + number).c_str()), i);
// and finally bind the texture
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textures[i].id);
}
// draw mesh
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBufferRange(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER,0, uniformBlockIndex,0,sizeof(Material));
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, indices.size(), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
glBindVertexArray(0);
// always good practice to set everything back to defaults once configured.
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
}
private:
/* Render data */
unsigned int VBO, EBO;
/* Functions */
// initializes all the buffer objects/arrays
void setupMesh()
{
// create buffers/arrays
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &uniformBlockIndex);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
// load data into vertex buffers
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
// A great thing about structs is that their memory layout is sequential for all its items.
// The effect is that we can simply pass a pointer to the struct and it translates perfectly to a glm::vec3/2 array which
// again translates to 3/2 floats which translates to a byte array.
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex)+ sizeof(mats), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER, uniformBlockIndex);
glBufferData(GL_UNIFORM_BUFFER,sizeof(mats),(void*)(&mats), GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(unsigned int), &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// set the vertex attribute pointers
// vertex Positions
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)0);
// vertex normals
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, Normal));
// vertex texture coords
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, TexCoords));
// vertex tangent
glEnableVertexAttribArray(3);
glVertexAttribPointer(3, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, Tangent));
// vertex bitangent
glEnableVertexAttribArray(4);
glVertexAttribPointer(4, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, sizeof(Vertex), (void*)offsetof(Vertex, Bitangent));
}
};
#endif
model.h
#pragma once
#ifndef MODEL_H
#define MODEL_H
#include
#include
#include
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include "mesh.h"
#include "shader_m.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
顶点着色器:
#version 330 core
layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 aNormal;
uniform Mat{
vec4 aAmbient;
vec4 aDiffuse;
vec4 aSpecular;
};
out vec3 FragPos;
out vec3 Normal;
out vec4 Ambient;
out vec4 Diffuse;
out vec4 Specular;
uniform mat4 model;
uniform mat4 view;
uniform mat4 projection;
void main()
{
FragPos = vec3( model * vec4(aPos, 1.0));
//Normal =vec3(projection * vec4(mat3(transpose(inverse(view * model))) * aNormal,0.0));
Normal = mat3(transpose(inverse(model))) * aNormal;
Ambient = aAmbient;
Diffuse = aDiffuse;
Specular = aSpecular;
gl_Position = projection * view * vec4(FragPos, 1.0);
}
片段着色器:
#version 330 core
out vec4 FragColor;
struct Light {
vec3 position;
vec3 ambient;
vec3 diffuse;
vec3 specular;
float constant;
float linear;
float quadratic;
};
in vec3 FragPos;
in vec3 Normal;
in vec2 TexCoords;
//从Mtl中读取的数据
//Material
in vec4 Ambient;
in vec4 Diffuse;
in vec4 Specular;
uniform vec3 viewPos;
uniform Light light;
uniform float shininess;
void main()
{
// ambient
vec3 ambient = light.ambient * Diffuse.rgb;
// diffuse
vec3 norm = normalize(Normal);
vec3 lightDir = normalize(light.position - FragPos);
float diff = max(dot(norm, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse =light.diffuse * diff *Diffuse.rgb;
// attenuation
float distance = length(light.position - FragPos);
float attenuation = 1.0 / (light.constant + light.linear * distance + light.quadratic * (distance * distance));
// specular
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - FragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, norm);
float spec = pow(max(dot(viewDir, reflectDir), 0.0), shininess);
vec3 specular = light.specular * spec * Specular.rgb;
//ambient *= attenuation;
diffuse *= attenuation;
specular *= attenuation;
vec3 result = ambient + diffuse +specular;
FragColor = vec4(result ,1.0);
}
