谈一款MOBA类游戏的服务端架构设计
一、前言
《码神联盟》是一款为技术人做的开源情怀游戏,每一种编程语言都是一位英雄。客户端和服务端均使用C#开发,客户端使用Unity3D引擎,数据库使用MySQL。这个MOBA类游戏是笔者在学习时期和客户端美术策划的小伙伴一起做的游戏,笔者主要负责游戏服务端开发,客户端也参与了一部分,同时也是这个项目的发起和负责人。这次主要分享这款游戏的服务端相关的设计与实现,从整体的架构设计,到服务器网络通信底层的搭建,通信协议、模型定制,再到游戏逻辑的分层架构实现。同时这篇博客也沉淀了笔者在游戏公司实践五个月后对游戏架构与设计的重新审视与思考。
这款游戏自去年完成后笔者曾多次想写篇博客来分享,也曾多次停笔,只因总觉得灵感还不够积淀还不够思考还不够,现在终于可以跨过这一步和大家分享,希望可以带来的是干货与诚意满满。由于目前关于游戏服务端相关的介绍文章少之又少,而为数不多的几篇也都是站在游戏服务端发展历史和架构的角度上进行分享,很少涉及具体的实现,这篇文章我将尝试多从实现的层面上加以介绍,所附的代码均有详尽注释,篇幅较长,可以关注收藏后再看。学习时期做的项目可能无法达到工业级,参考了github上开源的C#网络框架,笔者在和小伙伴做这款游戏时农药还没有现在这般火。 : )
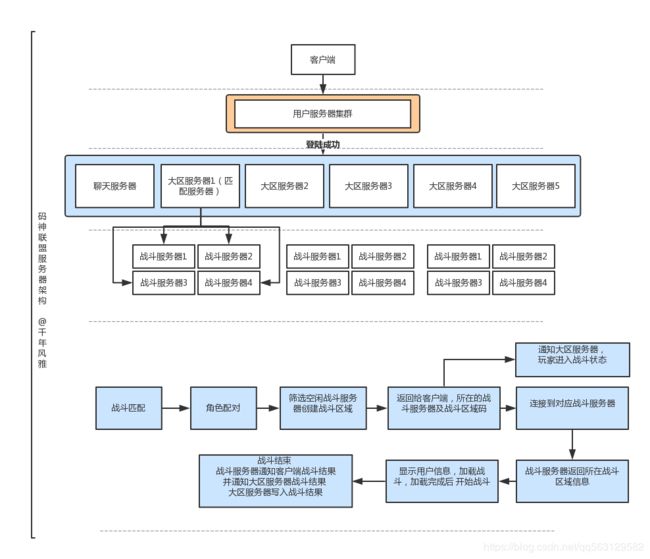
上图为这款游戏的服务器架构和主要逻辑流程图,笔者将游戏的代码实现分为三个主要模块:Protocol通信协议、NetFrame服务器网络通信底层的搭建以及LOLServer游戏的具体逻辑分层架构实现,下面将针对每个模块进行分别介绍。
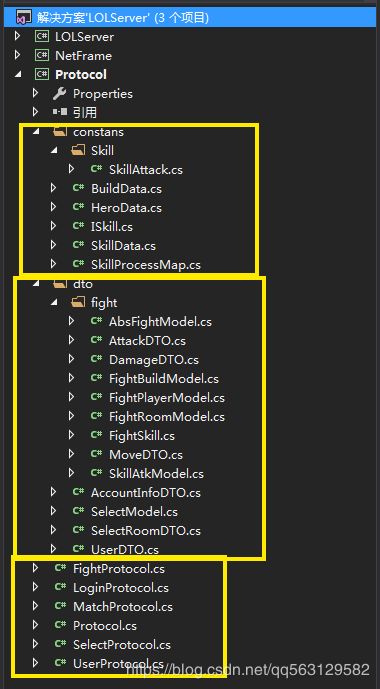
先从最简单也最基本的通信协议部分说起,我们可以看到这部分代码主要分为xxxProtocol、xxxDTO和xxxModel、以及xxxData四种类型,让我们来对它们的作用一探究竟。
1.Protocol协议
LOLServer\Protocol\Protocol.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace GameProtocol
{
public class Protocol
{
public const byte TYPE_LOGIN = 0;//登录模块
public const byte TYPE_USER = 1;//用户模块
public const byte TYPE_MATCH = 2;//战斗匹配模块
public const byte TYPE_SELECT = 3;//战斗选人模块
public const byte TYPE_FIGHT = 4;//战斗模块
}
}
从上述的代码举例可以看到,在Protocol协议部分,我们主要是定义了一些常量用于模块通信,在这个部分分别定义了用户协议、登录协议、战斗匹配协议、战斗选人协议以及战斗协议。
2.DTO数据传输对象
DTO即数据传输对象,表现层与应用层之间是通过数据传输对象(DTO)进行交互的,需要了解的是,数据传输对象DTO本身并不是业务对象。数据传输对象是根据UI的需求进行设计的,而不是根据领域对象进行设计的。比如,User领域对象可能会包含一些诸如name, level, exp, email等信息。但如果UI上不打算显示email的信息,那么UserDTO中也无需包含这个email的数据。
简单来说Model面向业务,我们是通过业务来定义Model的。而DTO是面向界面UI,是通过UI的需求来定义的。通过DTO我们实现了表现层与Model之间的解耦,表现层不引用Model,如果开发过程中我们的模型改变了,而界面没变,我们就只需要改Model而不需要去改表现层中的东西。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace GameProtocol.dto
{
[Serializable]
public class UserDTO
{
public int id;//玩家ID 唯一主键
public string name;//玩家昵称
public int level;//玩家等级
public int exp;//玩家经验
public int winCount;//胜利场次
public int loseCount;//失败场次
public int ranCount;//逃跑场次
public int[] heroList;//玩家拥有的英雄列表
public UserDTO() { }
public UserDTO(string name, int id, int level, int win, int lose, int ran,int[] heroList)
{
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.winCount = win;
this.loseCount = lose;
this.ranCount = ran;
this.level = level;
this.heroList = heroList;
}
}
}
3.Data属性配置表
这部分的实现主要是为了将程序功能与属性配置分离,后面可以由策划来配置这部分内容,由导表工具自动生成配表,从而减轻程序的开发工作量,扩展游戏的功能。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace GameProtocol.constans
{
/// 四、服务器通信底层搭建
这部分为服务器的网络通信底层实现,也是游戏服务器的核心内容,下面将结合具体的代码以及代码注释一一介绍底层的实现,可能会涉及到一些C#的网络编程知识,对C#语言不熟悉没关系,笔者对C#的运用也仅仅停留在使用阶段,只需通过C#这门简单易懂的语言来窥探整个服务器通信底层搭建起来的过程,来到我们的NetFrame网络通信框架,这部分干货很多,我将用完整的代码和详尽的注释来阐明其意。
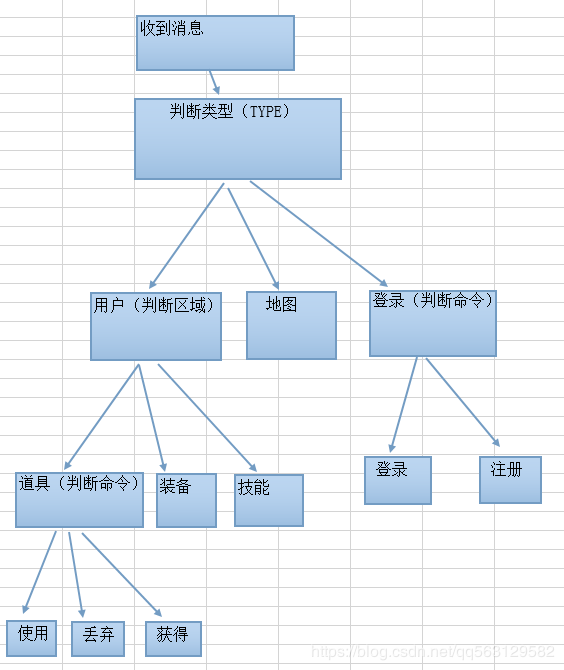
1.四层Socket模型

将SocketModel分为了四个层级,分别为:
(1)type:一级协议 用于区分所属模块,如用户模块
(2)area:二级协议 用于区分模块下的所属子模块,如用户模块的子模块为道具模块1、装备模块2、技能模块3等
(3)command:三级协议 用于区分当前处理逻辑功能,如道具模块的逻辑功能有“使用(申请/结果),丢弃,获得”等,技能模块的逻辑功能有“学习,升级,遗忘”等;
(4)message:消息体 当前需要处理的主体数据,如技能书
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame.auto
{
public class SocketModel
{
/// 2.对象序列化与反序列化为对象
序列化: 将数据结构或对象转换成二进制串的过程。
反序列化:将在序列化过程中所生成的二进制串转换成数据结构或者对象的过程。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
public class SerializeUtil
{
/// 3.消息体序列化与反序列化
相应的,我们利用上面写好的序列化和反序列化方法将我们再Socket模型中定义的message消息体进行序列化与反序列化
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame.auto
{
public class MessageEncoding
{
/// 4.将数据写入成二进制
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NetFrame
{
/// 5.粘包长度编码与解码
粘包出现原因:在流传输中出现(UDP不会出现粘包,因为它有消息边界)
1 发送端需要等缓冲区满才发送出去,造成粘包
2 接收方不及时接收缓冲区的包,造成多个包接收
所以这里我们需要对粘包长度进行编码与解码,具体的代码如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame.auto
{
public class LengthEncoding
{
/// 6.delegate委托声明
delegate 是表示对具有特定参数列表和返回类型的方法的引用的类型。 在实例化委托时,可以将其实例与任何具有兼容签名和返回类型的方法相关联。通过委托实例调用方法。委托相当于将方法作为参数传递给其他方法,类似于 C++ 函数指针,但它们是类型安全的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
public delegate byte[] LengthEncode(byte[] value);
public delegate byte[] LengthDecode(ref List<byte> value);
public delegate byte[] encode(object value);
public delegate object decode(byte[] value);
}
7.用户连接对象UserToken
SocketAsyncEventArgs介绍
SocketAsyncEventArgs是微软提供的高性能异步Socket实现类,主要为高性能网络服务器应用程序而设计,主要是为了避免在在异步套接字 I/O 量非常大时发生重复的对象分配和同步。使用此类执行异步套接字操作的模式包含以下步骤:
(1)分配一个新的 SocketAsyncEventArgs 上下文对象,或者从应用程序池中获取一个空闲的此类对象。
(2)将该上下文对象的属性设置为要执行的操作(例如,完成回调方法、数据缓冲区、缓冲区偏移量以及要传输的最大数据量)。
(3)调用适当的套接字方法 (xxxAsync) 以启动异步操作。
(4)如果异步套接字方法 (xxxAsync) 返回 true,则在回调中查询上下文属性来获取完成状态。
(5)如果异步套接字方法 (xxxAsync) 返回 false,则说明操作是同步完成的。可以查询上下文属性来获取操作结果。
(6)将该上下文重用于另一个操作,将它放回到应用程序池中,或者将它丢弃。
SocketAsyncEventArgs.UserToken 属性
获取或设置与此异步套接字操作关联的用户或应用程序对象。
命名空间: System.Net.Sockets
public object UserToken { get; set; }
备注:
此属性可以由应用程序相关联的应用程序状态对象与 SocketAsyncEventArgs 对象。 首先,此属性是一种将状态传递到应用程序的事件处理程序(例如,异步操作完成方法)的应用程序的方法。
此属性用于所有异步套接字 (xxxAsync) 方法。
UserToken类的完整实现代码如下,可以结合代码注释加以理解:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
/// 8.连接池UserTokenPool
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
public class UserTokenPool
{
private Stack<UserToken> pool;
public UserTokenPool(int max) {
pool = new Stack<UserToken>(max);
}
/// 9.抽象处理中心AbsHandlerCenter
在这里我们定义了客户端连接、收到客户端消息和客户端断开连接的抽象类,标记为抽象或包含在抽象类中的成员必须通过从抽象类派生的类来实现。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
public abstract class AbsHandlerCenter
{
/// 10.HandlerCenter实现类
接下来具体实现客户端连接、断开连接以及收到消息后的协议分发到具体的逻辑处理模块,代码如下:
using GameProtocol;
using LOLServer.logic;
using LOLServer.logic.fight;
using LOLServer.logic.login;
using LOLServer.logic.match;
using LOLServer.logic.select;
using LOLServer.logic.user;
using NetFrame;
using NetFrame.auto;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LOLServer
{
public class HandlerCenter:AbsHandlerCenter
{
HandlerInterface login;
HandlerInterface user;
HandlerInterface match;
HandlerInterface select;
HandlerInterface fight;
public HandlerCenter() {
login = new LoginHandler();
user = new UserHandler();
match = new MatchHandler();
select = new SelectHandler();
fight = new FightHandler();
}
public override void ClientClose(UserToken token, string error)
{
Console.WriteLine("有客户端断开连接了");
select.ClientClose(token, error);
match.ClientClose(token, error);
fight.ClientClose(token, error);
//user的连接关闭方法 一定要放在逻辑处理单元后面
//其他逻辑单元需要通过user绑定数据来进行内存清理
//如果先清除了绑定关系 其他模块无法获取角色数据会导致无法清理
user.ClientClose(token, error);
login.ClientClose(token, error);
}
public override void ClientConnect(UserToken token)
{
Console.WriteLine("有客户端连接了");
}
public override void MessageReceive(UserToken token, object message)
{
SocketModel model = message as SocketModel;
switch (model.type) {
case Protocol.TYPE_LOGIN:
login.MessageReceive(token, model);
break;
case Protocol.TYPE_USER:
user.MessageReceive(token, model);
break;
case Protocol.TYPE_MATCH:
match.MessageReceive(token, model);
break;
case Protocol.TYPE_SELECT:
select.MessageReceive(token, model);
break;
case Protocol.TYPE_FIGHT:
fight.MessageReceive(token, model);
break;
default:
//未知模块 可能是客户端作弊了 无视
break;
}
}
}
}
11.启动服务器
启动服务器->监听IP(可选)->监听端口,服务器处理流程如下图:
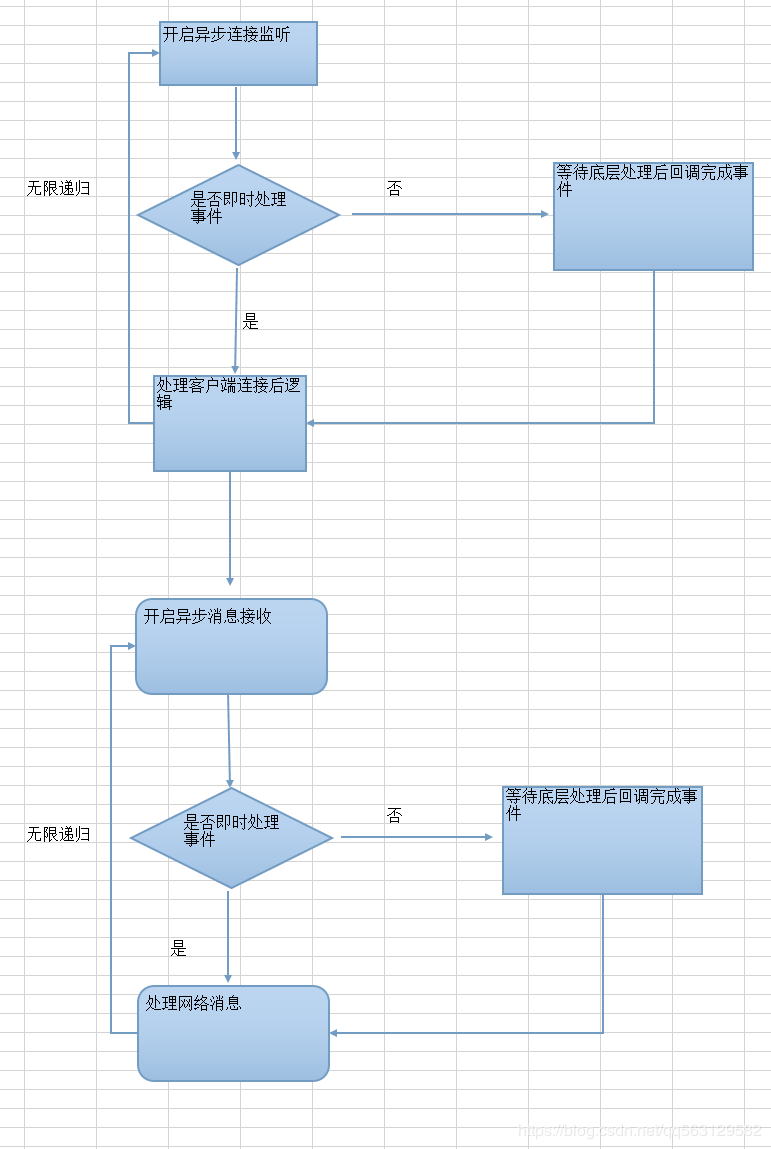
让我们来具体看看代码实现,均给了详细的注释:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace NetFrame
{
public class ServerStart
{
Socket server;//服务器socket监听对象
int maxClient;//最大客户端连接数
Semaphore acceptClients;
UserTokenPool pool;
public LengthEncode LE;
public LengthDecode LD;
public encode encode;
public decode decode;
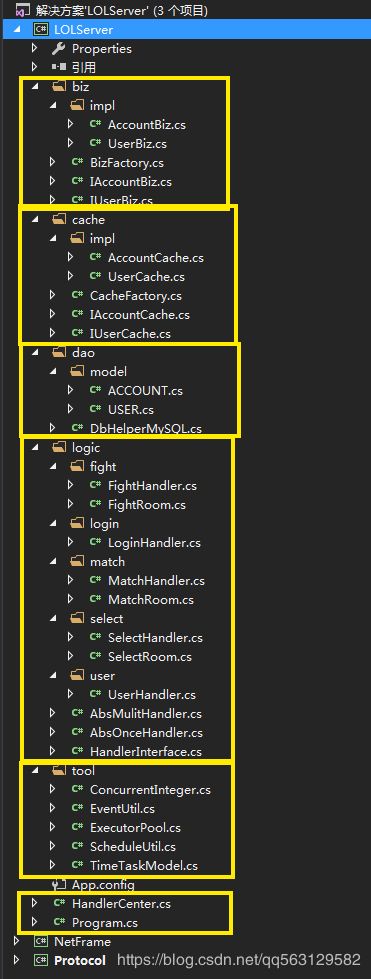
/// 至此,服务器的通信底层已经搭建完毕,可以进一步进行具体的游戏逻辑玩法开发了。
(1)logic逻辑层:逻辑处理模块,异步的逻辑处理,登录、用户处理、匹配、选人、战斗的主要逻辑都在这里,Moba类游戏是典型的房间服务器架构,AbsOnceHandler用于单体消息发送的处理,AbsMulitHandler用于群发;
AbsOnceHandler代码如下:
using LOLServer.biz;
using LOLServer.dao.model;
using NetFrame;
using NetFrame.auto;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LOLServer.logic
{
public class AbsOnceHandler
{
public IUserBiz userBiz = BizFactory.userBiz;
private byte type;
private int area;
public void SetArea(int area) {
this.area = area;
}
public virtual int GetArea() {
return area;
}
public void SetType(byte type)
{
this.type = type;
}
public new virtual byte GetType()
{
return type;
}
/// AbsMulitHandler继承自AbsOnceHandler,实现代码如下:
using NetFrame;
using NetFrame.auto;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace LOLServer.logic
{
public class AbsMulitHandler:AbsOnceHandler
{
public List<UserToken> list = new List<UserToken>();
/// (2)biz事务层:事务处理,保证数据安全的逻辑处理,如账号、用户信息相关的处理,impl是相关的实现类;
(3)cache缓存层:读取数据库中的内容放在内存中,加快访问速度;
(4)dao数据层:服务器和数据库之间的中间件;
(5)工具类:一些实用的工具类放在这里,如定时任务列表,用来实现游戏中的刷怪,buff等;
逻辑处理流程如下:

六、优化思路
思考了一些优化思路,自文章发布后也收到了许多来自朋友圈或留言评论中大神们给出的优化思路,大多数建议都质量很高,极具参考价值和学习意义,大概这就是开源的魅力所在吧。现在把这些思路整理出来分享给大家:
(1)在原有架构基础上,可以进一步考虑下:协议的自动化生成,托管内存的gc消耗控制,更小的网络延迟和更大的网络并发;
(2)如果用上异步消息机制和Nosql 单服承载人数或许还能够上升一些,目前Nosql中MongoDB在游戏服务端中有较多应用,Redis是笔者个人很喜欢的一个开源Nosql数据库,也有一些游戏项目已经在尝试集成;
(3).net 自带的二进制序列化性能偏差,文章中代码里数据接收发送时的内存拷贝次数偏多,序列化可以尝试Google开源的protobuf,目前很多线上游戏都在应用;
(4)用.net framework其实就把服务器绑定到windows上了,同时mono性能堪忧,如果非要用c#的话,可以尝试.net core + docker ,网络库可以libuv ,这个方案不管是从扩展还是性能监控管理上都比windows要优秀许多,业界的游戏服务器也确实大多在Linux上部署;
(5)收发消息部分太复杂,使用现成的RPC框架性能、安全性会更好。