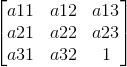RANSAC算法以及图像算法中的应用
Ransac的缩写是Random Sample Consensus。
Ransac算法的直线拟合算法大致步骤如下:
k是迭代次数,n是每次采样点个数,t是拟合的阈值,如果是直线拟合,可以理解为check的点到拟合出的直线距离,小于则是inliner否则为outliner。
如果迭代过程中,发现有合适的足够的点满足,那么就认为这个模型是比较优良的模型,将优良的模型中的内点以及可能的内点,重新进行拟合。如果拟合的误差小于最大误差,那么就更新最优化的模型,一直到迭代结束。
算法的步骤:
Given:
data – a set of observed data points
model – a model that can be fitted to data points
n – minimum number of data points required to fit the model
k – maximum number of iterations allowed in the algorithm
t – threshold value to determine when a data point fits a model
d – number of close data points required to assert that a model fits well to data
Return:
bestfit – model parameters which best fit the data (or nul if no good model is found)
iterations = 0
bestfit = nul
besterr = something really large
while iterations < k {
maybeinliers = n randomly selected values from data
maybemodel = model parameters fitted to maybeinliers
alsoinliers = empty set
for every point in data not in maybeinliers {
if point fits maybemodel with an error smaller than t
add point to alsoinliers
}
if the number of elements in alsoinliers is > d {
% this implies that we may have found a good model
% now test how good it is
bettermodel = model parameters fitted to all points in maybeinliers and alsoinliers
thiserr = a measure of how well model fits these points
if thiserr < besterr {
bestfit = bettermodel
besterr = thiserr
}
}
increment iterations
}
return bestfit
这是在知乎上找到的伪代码 ,我觉得讲的很到位了。文末有参考链接,不过他里面有一个ransac的matlab实现版本,那个版本没有进行获得最优模型之后refit。
下面在总结一下Ransac的详细算法流程:
(1)随机选择一些原始数据,叫作假设inliers子集
(2)建立模型拟合
(3)用其他数据来验证,根据模型特定的loss-function来计算是否符合该模型(如果模型是直线的话,lossfuction就是点到直线距离)
(4)如果足够的点都算是“一致性”设置(如果是直线模型,那么就是足够的点到直线的距离小于设定的最小阈值)里则该模型算是好模型A;基于好的模型A,我们在用找到该模型的样本点和检测符合A模型内点的所有点进行拟合,又出来一个模型,然后再比较这B模型和A模型的好坏,好外用内点的个数来衡量,选择一个较优的,此时继续进入步骤(1)
(5)比较所有的“一致性”设置(就是建立的所有模型)看看哪个inliers多就是我们要的。
RANSAC算法在图像中的应用有很多。
这里主要陈述一下关于单应矩阵的计算,其实在opencv里就一个函数,
Mat homo = findHomography(imagePoints1, imagePoints2, CV_RANSAC);
所谓的单应矩阵本质上就是2D平面到2D平面的投影关系
这里的两组点至少是四对,因为单应矩阵的自由度是四个
a11,a12,a21,a22表示旋转和缩放,a13和a23是平移向量,
a31和a32是非线性相关的向量,这个目前还没有深究。
单应矩阵和透视矩阵:
这里的解释是百度找不到,希望大家重视一下哈。
我们还知道有一个getPerspectiveTransform这个函数,这个函数是用于计算透视矩阵的。之前我好奇两者是否一样的,google一顿发现,是的。
但是区别是findHomography找单应矩阵的时候是利用了ransac,也就是说传进函数里的是一个点集而不是特定个数的点,算法通过ransac找出最佳的透视矩阵(单应矩阵)。而getPerspectiveTransform():计算4个二维点对之间的透射变换矩阵 H(3行x3列) 。
最近工作比较忙,先写成这样,有问题大家评论一起讨论啊。
参考文献:1. https://blog.csdn.net/lhanchao/article/details/52849446
2.https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/36301702
3.https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11237948/findhomography-getperspectivetransform-getaffinetransform