官方文档:https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth-le
前言
前面写过一篇文章关于使用传统蓝牙的聊天demo实现,后续因为继续研究了一下蓝牙的另外一种形式:低功耗蓝牙(Bluetooth low energy,简称 BLE,后文使用蓝牙 BLE 指代低功耗蓝牙)。所以在这里再写一篇文章记录一下。正好完善关于蓝牙的总结。
前面说过,经典蓝牙就像是 Socket 一样,有接口提供 Socket 实现端对端的连接和数据交互。而低功耗蓝牙在概念和使用都和经典蓝牙较为不同。蓝牙BLE是在Android 4.3 及以上引入的,换而言之低功耗蓝牙的APP至少要运行在 4.3 的系统上。低功耗蓝牙的优点是低功耗,延迟短,范围更短,但随之相伴的是传输速度慢,数据量小等的缺点。瑕不掩瑜,如今穿戴式设备和车载系统上都广泛应用蓝牙BLE技术。
基础概念
译文:Key terms and concepts
通用属性配置文件(GATT)
GATT配置文件是通过BLE链路发送和接收称为“属性”的短数据的通用规范。目前所有低能耗应用配置文件均基于GATT。
Bluetooth SIG 为低能耗设备定义了许多 配置文件。配置文件是设备在特定应用程序中的工作方式的规范。请注意,设备可以实现多个配置文件。例如,设备可以包含心率监测器和电池水平检测器。
属性协议(ATT) -GATT建立在属性协议(ATT)之上。这也称为GATT / ATT。ATT经过优化,可在BLE设备上运行。为此,它使用尽可能少的字节。每个属性由通用唯一标识符(UUID)唯一标识,UUID是用于唯一标识信息的字符串ID的标准化128位格式。ATT传输的属性被格式化为特征和服务。
Characteristic(特征) - 特征包含单个值和描述特征值的0-n描述符。特征可以被认为是类型,类似于类。
Descriptor(描述符) -Descriptors是定义特征值的已定义属性。例如,描述符可以指定人类可读的描述,特征值的可接受范围,或特征值特定的度量单位。
Service(服务) -服务是一系列特征。例如,您可以使用名为“心率监测器”的服务,其中包括“心率测量”等特征。您可以在bluetooth.org上找到基于GATT的现有配置文件和服务的列表 。
以上是官网的翻译,实际上我对此还处于一知半解状态。相对而言我还是简述一下我在应用中所接触到的几个概念和我对上面个别概念的理解。
service 和 Characteristic
service 就像是航道上的一艘船,一个蓝牙连接就是一条航道,这条船就是保证交流的通道,或者说是传输方式。特征(Characteristic)就像是船上的集装箱,装载了数据。这个集装箱分成了好几个区,里面有 value、descriptor、size等。我们常常就会把自己的数据丢到 value 里面,然后让船(service)带着集装箱(Characteristic,里面装了 value 等数据),沿着航道(蓝牙BLE连接),从大陆的一头驶向另一头(从一个设备到另一个设备)。这样,就完成数据交互。
同一条航道上(一条BLE连接),有很多的船(service),他们往往是只能明确的,比如某条船用于发送消息,某条船用于接收消息。
要注意的是,蓝牙BLE 中要打开 notify 的服务,才会收到信息。不然接收不到返回的信息。
Characteristic 定义了数值和操作。操作可以操作读写通知权限。
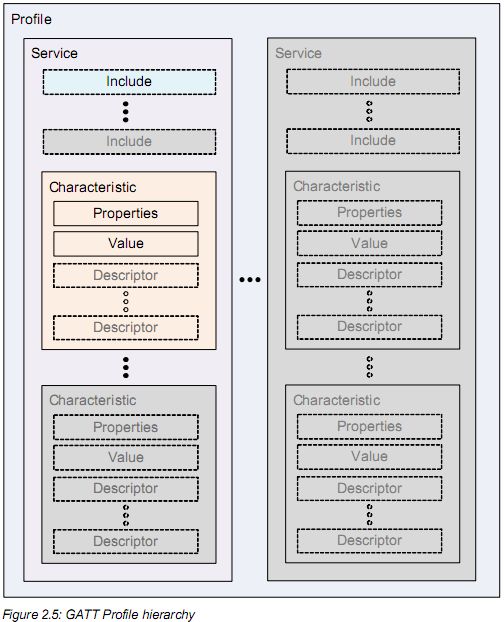
我们说的 BLE 通信,其实就是对 Characteristic 的读写或者订阅通知。还有最外面一层,Profile配置文件,把若干个相关的 Service 组合在一起,就成为了一个 Profile,Profile 就是定义了一个实际的应用场景。
从图中可以看出,GATT 最上层是 Profile,Profile 由一个或多个服务(Service)组成。服务是由 Characteristic 组成,或者是其他服务的引用组成。Characteristic 包含一个 Characteristic 声明、Characteristic 属性、值、值的描述(Descriptor)。
Ble 连接流程
前置准备
前置准备和传统蓝牙基本一致。需要申请好权限,设备支持蓝牙,并且已经开启蓝牙。详细内容可以查看上一篇博客Android-蓝牙聊天demo
扫描蓝牙设备
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP) {
mScanner.startScan(filters, scanSettings, mScanCallback);
} else {
mBtAdapter.startLeScan(leScanCallback);
}
API 21 以后提供了新的扫描方法,可以通过 ScanFilter 配置扫描的过滤项,如特定的UUID,或者是广播中制造商的定制的数据 setManufacturerData。另外还可以配置 ScanSettings,配置扫描的设置,如 setScanMode 扫描的功耗模式等。通过这些设置可以使得 BLE 扫描更高效节能。另外一个参数就是扫描设备的回调,他会返回改设备的基本信息。
若没有精确定位权限,则可能会扫描蓝牙设备无结果
获取 BLE 设备
扫描出来后,一般会根据 MAC 地址获取一个蓝牙设备对象
BluetoothDevice device = mBtAdapter.getRemoteDevice(mac);
连接 BLE 设备的 GATT 服务
mBluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(context, autoConnect, mGattCallback);
connectGatt() 可以连接由 BLE 设备托管的 GATT 服务,并且返回一个 BluetoothGatt 实例,该实例可以用来执行 gatt 客户端操作,如读写数据等。
监听 BluetoothGattCallback 回调
1、连接状态回调
onConnectionStateChange 是连接状态监听,连接成功,断开连接都会触发这个方法,在这里面也可以进行重连操作。
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {
String intentAction = null;
if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) {
intentAction = ACTION_GATT_CONNECTED;
gatt.discoverServices();
} else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) {
intentAction = ACTION_GATT_DISCONNECTED;
mConnectState = STATE_DISCONNECTED;
}
}
2、获取服务,特征等等
onConnectionStateChange 连接成功之后,还需要调用 gatt.discoverServices() 去获取服务,特性等。一个 BLE 设备可以有多个 BluetoothGattService,每个服务也可以有多个 BluetoothGattCharacterstic 特征。
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
broadcastUpdate(ACTION_GATT_SERVICES_DISCOVERED);
mConnectState = STATE_CONNECTED;
} else {
broadcastUpdate(ACTION_GATT_SERVICES_FAIL);
}
}
一般来说我们只会与几个特定的 Service 和 Characterstic 进行数据读写,依赖的识别标志就是 UUID_SERVICE和UUID_CHARACTERSTIC,这两个UUID 一般是设备厂商提供。
要注意的是,只有当
onServicesDiscovered回调返回status=success,BLE 才算是连接成功,可以进行数据交互。
3、开启通知
想要收到 BLE 特征变化的数据,还需要开启通知。开启后就能监听 Characterstic 的数据变化了。
public boolean setCharacteristicNotification(BluetoothDevice device,
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, boolean enable) {
BluetoothGatt gatt = getBluetoothGatt(device);
BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor = characteristic.getDescriptor(UUID.fromString(UUID_DESCRIPTOR));
if (enable) {
descriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.ENABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
} else {
descriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.DISABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
}
gatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, enable);
return gatt.writeDescriptor(descriptor);
}
4、监听数据变化
经过以上设置,就可以在 onCharacteristicChanged 回调中获取 BLE 设备发过来的数据了。
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
//todo 解析数据
parseData(characteristic.getValue());
}
而发送数据,可以使用获取到的 GATT 对象来向 BLE 设备发送数据。
//根据UUID找到对应的service和characteristic
characteristic.setValue(sendValue);
gatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);
注意,由于 BLE 低功耗的特性,传输数据量较低,限制为20字节以内。尽管 Android 可以通过设置 MTU 扩大收发帧,但是不同平台无法统一,且 iOS 无法这样设置,所以需要对 20 字节的收发做分包处理。这里一般会定义好交互的协议,通过协议头,尾标识符以及长度域,对发送接收的数据分包,并包。并定义好失败重传机制。在本文中就不做累述,我们只在 demo 中对发送的数据做简易的分包处理
public void writeValue(String serviceUuid, String characteristicUuid, byte[] value) {
if (mBleService == null || mDevice == null) {
return;
}
List supportedGattServices = mBleService.getSupportedGattServices(mDevice);
if (supportedGattServices == null) {
return;
}
for (BluetoothGattService bluetoothGattService : supportedGattServices) {
String gattServiceUUID = Long.toHexString(
bluetoothGattService.getUuid().getMostSignificantBits())
.substring(0, 4);
for (BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic : bluetoothGattService.getCharacteristics()) {
String gattCharacteristicUUID = Long.toHexString(
characteristic.getUuid().getMostSignificantBits())
.substring(0, 4);
//找到对应的uuid
if (gattServiceUUID.equals(serviceUuid)
&& gattCharacteristicUUID.equals(characteristicUuid)) {
int length = value.length;
int index = 0;
int sendLength = 0;
while (length > 0) {
if (length > mBleService.getMTU()) {
sendLength = mBleService.getMTU();
} else {
sendLength = length;
}
byte sendValue[] = new byte[sendLength];
System.arraycopy(value, index, sendValue, 0, sendLength);
//发完一帧需要sleep一下
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
characteristic.setValue(sendValue);
characteristic
.setWriteType(BluetoothGattCharacteristic.WRITE_TYPE_NO_RESPONSE);
this.writeValue(characteristic);
length -= sendLength;
index += sendLength;
}
}
}
}
}
demo
在这里 demo 使用 《信驰达低功耗蓝牙(ble)模块及协议-标准透传 v2.31u(cc2540)180802》文档与蓝牙模块进行展示,在代码里面的搜索蓝牙的过滤器请按实际进行修改。展示效果如下所示:
Demo 地址:BLE-demo
1、搜索蓝牙
2、数据交互