DGL框架之 message function 和 reduce function 相关介绍
文章目录
- DGL
- 两个API
- Builtin message passing functions
- MultiGraphs
- Reference
DGL
两个API
- message function(消息函数)
消息函数通过边获取变量:
(1)用 e.src.data 获得这条边出发节点的特征信息
(2)用 e.dst.data 获得这条边目标节点的特征信息
(3)用 e.data 获得这条边的特征信息
消息函数可以获得出发节点和目标节点的特征信息,描述了需要发给目标节点做下一步计算的信息。
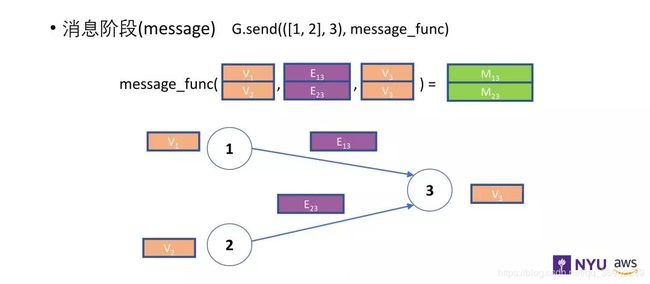
如上图,消息函数把节点1和节点2的信息都发送给节点3,可以发送的信息包括 v1、v2 和 v3 以及每条边上的消息。
- reduce function(累和函数)
目标节点在获得其他节点以及边的特征信息之后,通过累和函数计算出一个新的表示。

如上图,累和函数获得了消息函数传递过来的信息 M13、M23 同时还有自身的节点信息。
- 图神经网络案例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class GCNMessage(nn.Module):
"""消息函数"""
def forward(self, edges):
"""
:param: edges, a batch of edges
:return: This computes a (batch of) message called 'msg'
using the source node's feature 'h'
"""
# 源点的批量特征向量
return {"h": edges.src["h"]}
class GCNReduce(nn.Module):
"""累和函数"""
def __init__(self, in_feats, out_feats):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(in_feats, out_feats)
self.activation = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, nodes):
"""
:param: nodes, a batch of nodes
:return: This computes the new 'h' features
by summing received 'msg' in each node's mailbox
"""
# 批量消息张量, nodes.mailbox["h"]
accum = torch.sum(nodes.mailbox["h"], dim=1)
h = self.linear(accum)
h = self.activation(h)
return {"h": h}
class GCN(nn.Module):
"""GCN Layer"""
def __init__(self, in_feats, out_feats):
self.msg_func = GCNMessage()
self.reduce_func = GCNReduce(in_feats, out_feats)
def forward(self, g, inputs):
"""
:param: g, the graph
:param: inputs, the input node features
"""
# first set the node features
g.ndata["h"] = inputs
# 全局更新
g.update_all(self.msg_func, self.reduce_func)
"""
Or
g.send(g.edges(), gcn_message)
g.recv(g.nodes(), gcn_reduce)
And there the gcn_message and gcn_reduce are functions.
"""
# Get the 'h' features and remove the node/edge states from the graph
return g.ndata.pop("h")
这里的累和函数:
h i n e w = f ( Σ j ≠ i N h j ) h^{new}_i = f ( \Sigma_{j \neq i}^N h_j ) hinew=f(Σj=iNhj)
Builtin message passing functions
DGL 的消息传递主要使用两个 API:
send(edges, message_func)用于计算沿着给定边的消息recv(nodes, reduce_func)用于收集进入节点的消息,执行聚集等操作
使用 u,v 和 e分别表示 source nodes,destination nodes 和 edges
消息传递使用案例:
import dgl
import dgl.function as fn
import torch
# create a DGL Graph
g = ...
# each node has feature size 10
g.ndata['h'] = torch.randn((g.number_of_nodes(), 10))
# each edge has feature size 1
g.edata['w'] = torch.randn((g.number_of_edges(), 1))
# collect features from source nodes and aggregate them in destination nodes
g.update_all(fn.copy_u('h', 'm'), fn.sum('m', 'h_sum'))
# multiply source node features with edge weights and aggregate them in destination nodes
g.update_all(fn.u_mul_e('h', 'w', 'm'), fn.max('m', 'h_max'))
# compute edge embedding by multiplying source and destination node embeddings
g.apply_edges(fn.u_mul_v('h', 'h', 'w_new'))
对于一元消息函数(e.g. copy_u)需要一个输入的特征名和一个输出的消息名;对于二元消息函数(e.g. u_mul_e)需要两个输入特征名和一个输出消息名。对于 fn.u_mul_e('h', 'w', 'm') 是按如下函数定义:
def udf_u_mul_e(edges):
return {'m': edges.src['h'] * edges.data['w']}
对于 reduce function,需要给出一个输入消息名和一个输出节点特征名,例如,fn.max('m', 'h_max') 是按如下定义:
def udf_max(nodes):
return {'h_max': torch.max(nodes.mailbox['m'], 1)[0]}
MultiGraphs
创建图时需要设置 multigraph=True
g_multi = dgl.DGLGraph(multigraph=True)
g_multi.add_nodes(10)
g_multi.ndata['x'] = torch.randn(10, 2)
# edges, [(1, 0), (2, 0), (3, 0), ..., (9, 0), (1, 0)]
# two edges on 1->0
g_multi.add_edges(list(range(,, 10)), 0)
g_multi.add_edges(1, 0)
g_multi.edata['w'] = torch.randn(10, 2)
# set the first 1->0 edge's data
g_multi.edges[1].data['w'] = torch.zeros(1, 2)
MultiGraph 中的边没法通过节点 u u u 和 v v v 唯一确定,需要使用 edge_id 获取边的 id
# tensor([0, 9])
eid_10 = g_multi.edge_id(1, 0)
g_multi.edges[eid_10].data['w'] = torch.ones(len(eid_10), 2)
Reference
DGL at a Glance
DGL Basics
Builtin message passing functions
DGL 作者答疑!关于 DGL 你想知道的都在这里
