TensorFlow2.0——模型构建
模型构建:
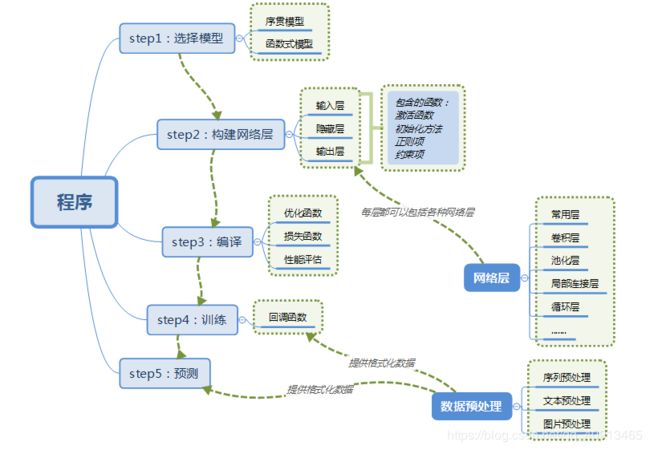
Keras有两种类型的模型,序贯模型(Sequential)和函数式模型(Model),函数式模型应用更为广泛,序贯模型是函数式模型的一种特殊情况。
a)序贯模型(Sequential):单输入单输出,一条路通到底,层与层之间只有相邻关系,没有跨层连接。这种模型编译速度快,操作也比较简单
b)函数式模型(Model):多输入多输出,层与层之间任意连接。这种模型编译速度慢。
引用:https://blog.csdn.net/zjw642337320/article/details/81204560
代码示例:
引用必要的函数库:
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
#为了能在notebook中显示图像
import numpy as np
import sklearn #注意
import pandas as pd
import os
import sys
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
1.选择模型并构建网络
#使用序贯模型Sequential tf.keras.models.sequential()
'''第一种写法
model = keras.models.Sequential()#注意要大写,选择模型
#构建网络
model.add(keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape = [28,28])) #序贯模型的第一层需要输入数据的shape
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(300, activation = "relu"))#Dense 全连接层
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(100, activation = "relu"))
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(10, activation = "softmax"))
'''
#第二种写法
model = keras.models.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape = [28, 28]), #注意逗号
keras.layers.Dense(300, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Dense(100, activation="relu"),
keras.layers.Dense(10, activation="softmax")
])
#softmax将向量变成概率分布 x = [xl, x2,x3].
# y = [e^x1/sum, e^x2/sum, e^x3/sum] sum = e^x1 + e^x2 + e^x3
2.编译
#编译compile
model.compile(loss = "sparse_categorical_crossentropy",
optimizer = "adam", #优化函数,不直接使用梯度下降
metrics = ["accuracy"])
loss 为损失函数;
sparse_categorical_crossentropy或者categorical_crossentropy,这两者都是多分类交差熵,区别在于:
sparse_categorical_crossentropy:tagets 是数字编码;
categorical_crossentropy:targets 是 one-hot 编码;
optimizer:优化函数,例如 AdamOptimizer、RMSPropOptimizer 或 GradientDescentOptimizer
metrics:性能评估,用于监控训练,它们是 tf.keras.metrics 模块中的字符串名称或可调用对象
查看模型信息:
model.layers #查看一下网络的层次
运行结果:
[
,
,
,
]
model.summary() # num = [none,784] * w + b -> [none,300] W.shape[300,784] , b = [300]
Model: “sequential_1”
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
===============================================================
flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 784) 0
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 300) 235500
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 100) 30100
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 10) 1010
===============================================================
Total params: 266,610
Trainable params: 266,610
Non-trainable params: 0
3.训练模型
#训练模型
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, validation_data=(x_valid, y_valid))
#会返回一个结果保存在history中
‘’’
model.fit的一些参数,参考官方API
batch_size:对总的样本数进行分组,每组包含的样本数量
epochs :训练次数
shuffle:是否把数据随机打乱之后再进行训练
validation_split:拿出百分之多少用来做交叉验证
verbose:屏显模式 0:不输出 1:输出进度 2:输出每次的训练结果
查看history的类型
type(history)
tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History
history.history
{‘loss’: [2.456370598454909,
0.6194203653292223,
0.5326741259748285,
0.4874053767854517,
0.4296531865163283,
0.4044668952768499,
0.39407426077669316,
0.372555995017832,
0.36333005535169083,
0.35417791644118046],
‘accuracy’: [0.72492725,
0.7869091,
0.8126,
0.8274182,
0.8468909,
0.8547091,
0.8584727,
0.86585456,
0.8695273,
0.87316364],
‘val_loss’: [0.6873663679599762,
0.5281977466583252,
0.47626469302177427,
0.43247376172542573,
0.4234978169679642,
0.4271171735525131,
0.3985502668261528,
0.4447905594587326,
0.42555881497859954,
0.38597796664237977],
‘val_accuracy’: [0.783,
0.8132,
0.8464,
0.851,
0.863,
0.851,
0.8708,
0.8616,
0.859,
0.8706]}
绘制图形查看
def plot_learning_curves(history):
pd.DataFrame(history.history).plot(figsize=(8,5))
plt.grid(True)
plt.show
plot_learning_curves(history)
