Java Web利用poi导出Excel2003、2007完整解决方案
1997-2003版行列数量限制:行-65535,列-256
2007-2010版行列数量限制:行-1048576,列-16384根据自己的业务需求来选择版本,这里注意一下,03版本的后缀是.xls ,07版是.xlsx ,注意。本文以07版为例。
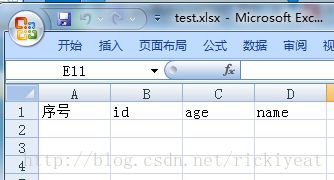
关于到导出策略,又有两种方式可供选择,一种是直接写代码来导出,但是每次都要去写表头,复制代码,这种方式的代码量比较大;另一种则是基于模板来导出,先写好表头,再填写内容,这种方式封装性比较好,代码量也较少,但会损失一部分性能。
项目是基于Maven的,下面直接上代码:
2、Maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poiartifactId>
<version>3.13version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxmlartifactId>
<version>3.13version>
dependency>3、ExcelUtil
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.catalina.servlet4preview.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCell;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFRow;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFSheet;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
/**
* Excel导出封装类
*
* @author yezhiyuan
* @param
*/
public class ExcelUtil<T> {
/**
* 基于Excel 2007模板写入数据
*
* @Title: writeExcel
* @param:@param file 模板文件
* @param:@param dataSet 数据集
* @param:@throws IOException
* @param:@throws NoSuchMethodException
* @param:@throws SecurityException
* @param:@throws InvocationTargetException
* @return:void
* @author yezhiyuan
* @date 2017-3-14 下午3:13:12
* @throws
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public void writeExcel(File file,Collection dataSet)
throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException,SecurityException,
InvocationTargetException {
XSSFWorkbook workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(new FileInputStream(file));
XSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 写入内容
Iterator iterator = dataSet.iterator();
int index = 1;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
XSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(index);
T t = (T) iterator.next();
// 利用反射,根据javabean属性的先后顺序,动态调用getXxx()方法得到属性值
Field[] fields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (short i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(index);
cell = row.createCell(i + 1);
fields[i].setAccessible(true);
try {
String fieldName = fields[i].getName();
String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
Object valueObject = fields[i].get(t);
Classextends Object> tCls = t.getClass();
Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName,new Class[]{});
Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[]{});
if (valueObject instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject + "");
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
XSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i + 1);
fields[i].setAccessible(true);
try {
String fieldName = fields[i].getName();
String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
Object valueObject = fields[i].get(t);
Classextends Object> tCls = t.getClass();
Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName,new Class[]{});
Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[]{});
if (valueObject instanceof String) {
if (valueObject == null) {
cell.setCellValue("");
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
}
} else if (valueObject instanceof BigDecimal) {
BigDecimal vDecimal = (BigDecimal) value;
cell.setCellValue(vDecimal.doubleValue());
} else if (valueObject instanceof Integer) {
cell.setCellValue((Integer) valueObject);
} else if (valueObject instanceof Double) {
cell.setCellValue((Double) valueObject);
} else {
if (valueObject == null) {
cell.setCellValue("");
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
}
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
index++;
}
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(outputStream);
outputStream.close();
}
/**
* 下载Excel
*
* @param request
* @param response
* @param list 要导出的数据
* @param model 模板名称
* @param name 导出Excel文件名
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public void download(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response,
List list,String model,String name) throws IOException {
ServletOutputStream out = null;
FileInputStream inputStream = null;
try {
response.setContentType("multipart/form-data");
String path = ExcelUtil.class.getResource("").getPath();// 获取模板路径
path += model + ".xlsx";//excel模板
String fileName = name +"_" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx";
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition","attachment;fileName=" + URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"));
FileUtils.Copy(path, path + fileName);
File file = new File(path + fileName);
writeExcel(file, list);//组装数据
out = response.getOutputStream();
inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
int b = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
while ((b = inputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
out.write(buffer, 0, b);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
inputStream.close();
out.close();
out.flush();
}
}
/**
* 基于Excel 2003模板写入数据
*
* @Title: writeExcelContent
* @param:@param file
* @param:@param dataSet
* @param:@throws IOException
* @param:@throws NoSuchMethodException
* @param:@throws SecurityException
* @param:@throws InvocationTargetException
* @return:void
* @Description:TODO()
* @date
* @throws
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public void writeExcel2003(File file, Collection dataSet)
throws IOException, NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException,
InvocationTargetException {
HSSFWorkbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(new FileInputStream(file));
HSSFSheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 写入内容
Iterator iterator = dataSet.iterator();
int index = 1;
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(index);
T t = (T) iterator.next();
// 利用反射,根据javabean属性的先后顺序,动态调用getXxx()方法得到属性值
Field[] fields = t.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (short i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) {
if (i == 0) {
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(index);
cell = row.createCell(i + 1);
fields[i].setAccessible(true);
try {
String fieldName = fields[i].getName();
String getMethodName = "get"
+ fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
Object valueObject = fields[i].get(t);
Classextends Object> tCls = t.getClass();
Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName,
new Class[]{});
Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[]{});
if (valueObject instanceof String) {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject + "");
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(i + 1);
fields[i].setAccessible(true);
try {
String fieldName = fields[i].getName();
String getMethodName = "get"
+ fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()
+ fieldName.substring(1);
Object valueObject = fields[i].get(t);
Classextends Object> tCls = t.getClass();
Method getMethod = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName,
new Class[]{});
Object value = getMethod.invoke(t, new Object[]{});
if (valueObject instanceof String) {
if (valueObject == null) {
cell.setCellValue("");
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
}
} else if (valueObject instanceof BigDecimal) {
BigDecimal vDecimal = (BigDecimal) value;
cell.setCellValue(vDecimal.doubleValue());
} else if (valueObject instanceof Integer) {
cell.setCellValue((Integer) valueObject);
} else if (valueObject instanceof Double) {
cell.setCellValue((Double) valueObject);
} else {
if (valueObject == null) {
cell.setCellValue("");
} else {
cell.setCellValue(valueObject.toString());
}
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
index++;
}
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
workbook.write(outputStream);
outputStream.close();
}
} 4、FileUtils
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class FileUtils {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FileUtils.class);
/**
* Construct a file from the set of name elements.
*
* @param directory
* the parent directory
* @param names
* the name elements
* @return the file
*/
public static File getFile(File directory, String... names) {
if (directory == null) {
throw new NullPointerException(
"directorydirectory must not be null");
}
if (names == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("names must not be null");
}
File file = directory;
for (String name : names) {
file = new File(file, name);
}
return file;
}
public static void Copy(String oldPath, String newPath)throws IOException {
int byteread = 0;
File oldfile = new File(oldPath);
if (oldfile.exists()) {
InputStream inStream = new FileInputStream(oldPath);
FileOutputStream fs = new FileOutputStream(newPath);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1444];
while ((byteread = inStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fs.write(buffer, 0, byteread);
}
inStream.close();
} else {
logger.error("文件不存在:{}",oldPath);
}
}
/**
* Construct a file from the set of name elements.
*
* @param names
* the name elements
* @return the file
*/
public static File getFile(String... names) {
if (names == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("names must not be null");
}
File file = null;
for (String name : names) {
if (file == null) {
file = new File(name);
} else {
file = new File(file, name);
}
}
return file;
}
/**
* Opens a {@link FileInputStream} for the specified file, providing better
* error messages than simply calling new FileInputStream(file)
* .
*
* At the end of the method either the stream will be successfully opened,
* or an exception will have been thrown.
*
* An exception is thrown if the file does not exist. An exception is thrown
* if the file object exists but is a directory. An exception is thrown if
* the file exists but cannot be read.
*
* @param file
* the file to open for input, must not be {@code null}
* @return a new {@link FileInputStream} for the specified file
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* if the file does not exist
* @throws IOException
* if the file object is a directory
* @throws IOException
* if the file cannot be read
*/
public static FileInputStream openInputStream(File file) throws IOException {
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException("File '" + file
+ "' exists but is a directory");
}
if (file.canRead() == false) {
throw new IOException("File '" + file + "' cannot be read");
}
} else {
throw new FileNotFoundException("File '" + file
+ "' does not exist");
}
return new FileInputStream(file);
}
/**
* 创建文件
*
* @param path
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
public static File createFile(String path, String fileName) {
File file = new File(path);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdir();
}
file = new File(path, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return file;
}
/**
* Opens a {@link FileOutputStream} for the specified file, checking and
* creating the parent directory if it does not exist.
*
* At the end of the method either the stream will be successfully opened,
* or an exception will have been thrown.
*
* The parent directory will be created if it does not exist. The file will
* be created if it does not exist. An exception is thrown if the file
* object exists but is a directory. An exception is thrown if the file
* exists but cannot be written to. An exception is thrown if the parent
* directory cannot be created.
*
* @param file
* the file to open for output, must not be {@code null}
* @param append
* if {@code true}, then bytes will be added to the end of the
* file rather than overwriting
* @return a new {@link FileOutputStream} for the specified file
* @throws IOException
* if the file object is a directory
* @throws IOException
* if the file cannot be written to
* @throws IOException
* if a parent directory needs creating but that fails
*/
public static FileOutputStream openOutputStream(File file, boolean append)
throws IOException {
if (file.exists()) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException("File '" + file
+ "' exists but is a directory");
}
if (file.canWrite() == false) {
throw new IOException("File '" + file
+ "' cannot be written to");
}
} else {
File parent = file.getParentFile();
if (parent != null) {
if (!parent.mkdirs() && !parent.isDirectory()) {
throw new IOException("Directory '" + parent
+ "' could not be created");
}
}
}
return new FileOutputStream(file, append);
}
public static FileOutputStream openOutputStream(File file)
throws IOException {
return openOutputStream(file, false);
}
/**
* Cleans a directory without deleting it.
*
* @param directory
* directory to clean
* @throws IOException
* in case cleaning is unsuccessful
*/
public static void cleanDirectory(File directory) throws IOException {
if (!directory.exists()) {
String message = directory + " does not exist";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
if (!directory.isDirectory()) {
String message = directory + " is not a directory";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
File[] files = directory.listFiles();
if (files == null) { // null if security restricted
throw new IOException("Failed to list contents of " + directory);
}
IOException exception = null;
for (File file : files) {
try {
forceDelete(file);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
exception = ioe;
}
}
if (null != exception) {
throw exception;
}
}
/**
* 创建目录
*
* @Title: createDirectory
* @param:@param directoryPath
* @param:@return
* @return:boolean
* @Description:TODO(这里用一句话描述这个方法的作用)
* @author liuping
* @date 2016-9-9 上午11:31:37
* @throws
*/
public static boolean createDirectory(String directoryPath) {
boolean bFlag = false;
try {
File file = new File(directoryPath.toString());
if (!file.exists()) {
bFlag = file.mkdir();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bFlag;
}
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* Deletes a directory recursively.
*
* @param directory
* directory to delete
* @throws IOException
* in case deletion is unsuccessful
*/
public static void deleteDirectory(File directory) throws IOException {
if (!directory.exists()) {
return;
}
cleanDirectory(directory);
if (!directory.delete()) {
String message = "Unable to delete directory " + directory + ".";
throw new IOException(message);
}
}
/**
* Deletes a file. If file is a directory, delete it and all
* sub-directories.
*
* The difference between File.delete() and this method are:
*
* - A directory to be deleted does not have to be empty.
* - You get exceptions when a file or directory cannot be deleted.
* (java.io.File methods returns a boolean)
*
*
* @param file
* file or directory to delete, must not be {@code null}
* @throws NullPointerException
* if the directory is {@code null}
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* if the file was not found
* @throws IOException
* in case deletion is unsuccessful
*/
public static void forceDelete(File file) throws IOException {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
deleteDirectory(file);
} else {
boolean filePresent = file.exists();
if (!file.delete()) {
if (!filePresent) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("File does not exist: "
+ file);
}
String message = "Unable to delete file: " + file;
throw new IOException(message);
}
}
}
/**
* Deletes a file, never throwing an exception. If file is a directory,
* delete it and all sub-directories.
*
* The difference between File.delete() and this method are:
*
* - A directory to be deleted does not have to be empty.
* - No exceptions are thrown when a file or directory cannot be deleted.
*
*
* @param file
* file or directory to delete, can be {@code null}
* @return {@code true} if the file or directory was deleted, otherwise
* {@code false}
*
*/
public static boolean deleteQuietly(File file) {
if (file == null) {
return false;
}
try {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
cleanDirectory(file);
}
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
try {
return file.delete();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
return false;
}
}
/**
* Makes a directory, including any necessary but nonexistent parent
* directories. If a file already exists with specified name but it is not a
* directory then an IOException is thrown. If the directory cannot be
* created (or does not already exist) then an IOException is thrown.
*
* @param directory
* directory to create, must not be {@code null}
* @throws NullPointerException
* if the directory is {@code null}
* @throws IOException
* if the directory cannot be created or the file already exists
* but is not a directory
*/
public static void forceMkdir(File directory) throws IOException {
if (directory.exists()) {
if (!directory.isDirectory()) {
String message = "File " + directory + " exists and is "
+ "not a directory. Unable to create directory.";
throw new IOException(message);
}
} else {
if (!directory.mkdirs()) {
// Double-check that some other thread or process hasn't made
// the directory in the background
if (!directory.isDirectory()) {
String message = "Unable to create directory " + directory;
throw new IOException(message);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Returns the size of the specified file or directory. If the provided
* {@link File} is a regular file, then the file's length is returned. If
* the argument is a directory, then the size of the directory is calculated
* recursively. If a directory or subdirectory is security restricted, its
* size will not be included.
*
* @param file
* the regular file or directory to return the size of (must not
* be {@code null}).
*
* @return the length of the file, or recursive size of the directory,
* provided (in bytes).
*
* @throws NullPointerException
* if the file is {@code null}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the file does not exist.
*
*/
public static long sizeOf(File file) {
if (!file.exists()) {
String message = file + " does not exist";
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
if (file.isDirectory()) {
return sizeOfDirectory(file);
} else {
return file.length();
}
}
/**
* Counts the size of a directory recursively (sum of the length of all
* files).
*
* @param directory
* directory to inspect, must not be {@code null}
* @return size of directory in bytes, 0 if directory is security
* restricted, a negative number when the real total is greater than
* {@link Long#MAX_VALUE}.
* @throws NullPointerException
* if the directory is {@code null}
*/
public static long sizeOfDirectory(File directory) {
checkDirectory(directory);
final File[] files = directory.listFiles();
if (files == null) { // null if security restricted
return 0L;
}
long size = 0;
for (final File file : files) {
size += sizeOf(file);
if (size < 0) {
break;
}
}
return size;
}
/**
* Checks that the given {@code File} exists and is a directory.
*
* @param directory
* The {@code File} to check.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the given {@code File} does not exist or is not a
* directory.
*/
private static void checkDirectory(File directory) {
if (!directory.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(directory + " does not exist");
}
if (!directory.isDirectory()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(directory
+ " is not a directory");
}
}
}6、实体类User
public class User {
private Integer id;
private Integer age;
private String name;
//省略get、set方法
}
7、Controller的写法
@RequestMapping(value = "/excel")
@ResponseBody
public void excelTest(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
ExcelUtil<User> vExcelUtil = new ExcelUtil<User>();//导出类初始化
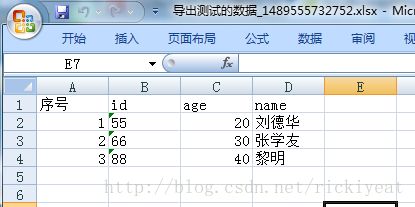
List<User> list = new ArrayList<>();
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(55);
user1.setAge(20);
user1.setName("刘德华");
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(66);
user2.setAge(30);
user2.setName("张学友");
User user3 = new User();
user3.setId(88);
user3.setAge(40);
user3.setName("黎明");
list.add(user1);
list.add(user2);
list.add(user3);
vExcelUtil.download(request, response, list,"test","导出测试的数据");
}8、浏览器输入:http://localhost:8080/excel