【TensorFlow2.0】实现ResNet
深度残差网络(Deep residual network, ResNet)的提出是CNN图像史上的一件里程碑事件,ResNet取得了5项第一,并又一次刷新了CNN模型在ImageNet上的历史。
本文介绍如何用 TensorFlow2.0 来实现 ResNet18,并用其训练 cifar100 的分类模型。
ResNet 的实现
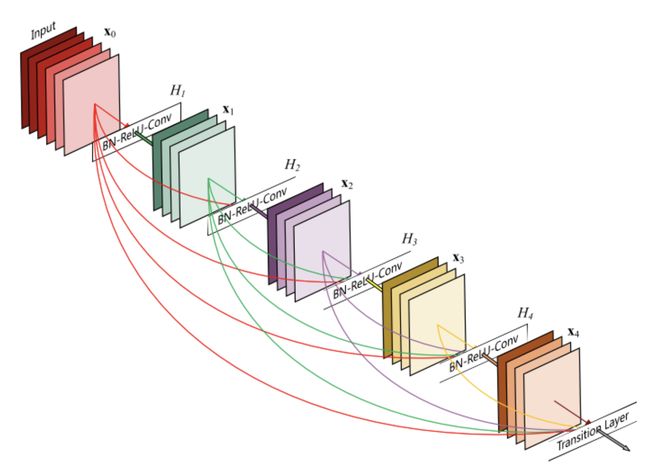
ResNet 的基本结构如上图所示,为了解决网络层次过深而导致的退化问题(Degradation problem)。ResNet 设计了一种短路连接(shortcut connection)来解决这个问题。
在编程实现的角度来看,首先我们要建一个 BasicBlock ,它包括两个 layer,以及一个 shortcut connection。ResNet 则是由多个 BasicBlock 堆叠而成。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers, Sequential
class BasicBlock(layers.Layer):
def __init__(self, filter_num, stride=1):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (3, 3), strides=stride, padding='same')
self.bn1 = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.relu = layers.Activation('relu')
self.conv2 = layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (3, 3), strides=1, padding='same')
self.bn2 = layers.BatchNormalization()
if stride != 1:
self.downsample = Sequential()
self.downsample.add(layers.Conv2D(filter_num, (1, 1), strides=stride))
else:
self.downsample = lambda x:x
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# [b, h, w, c]
out = self.conv1(inputs)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
identity = self.downsample(inputs)
output = layers.add([out, identity])
output = tf.nn.relu(output)
return output
class ResNet(keras.Model):
def __init__(self, layer_dims, num_classes=100): # [2, 2, 2, 2]
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.stem = Sequential([layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1)),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.Activation('relu'),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')
])
self.layer1 = self.build_resblock(64, layer_dims[0])
self.layer2 = self.build_resblock(128, layer_dims[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self.build_resblock(256, layer_dims[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self.build_resblock(512, layer_dims[3], stride=2)
# output: [b, 512, h, w],
self.avgpool = layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()
self.fc = layers.Dense(num_classes)
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
x = self.stem(inputs)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
# [b, c]
x = self.avgpool(x)
# [b, 100]
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def build_resblock(self, filter_num, blocks, stride=1):
res_blocks = Sequential()
# may down sample
res_blocks.add(BasicBlock(filter_num, stride))
for _ in range(1, blocks):
res_blocks.add(BasicBlock(filter_num, stride=1))
return res_blocks
def resnet18():
return ResNet([2, 2, 2, 2])
def resnet34():
return ResNet([3, 4, 6, 3])
使用 ResNet
ResNet 的使用和一般的模型使用没有什么区别,如果不清楚可以看这篇文章:【TensorFlow2.0】手撕前向传播算法。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, optimizers, datasets, Sequential
import os
from resnet1 import resnet18
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
tf.random.set_seed(2345)
def preprocess(x, y):
# [-1~1]
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255. - 0.5
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
(x,y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.cifar100.load_data()
y = tf.squeeze(y, axis=1)
y_test = tf.squeeze(y_test, axis=1)
print(x.shape, y.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
train_db = train_db.shuffle(1000).map(preprocess).batch(512)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test))
test_db = test_db.map(preprocess).batch(512)
sample = next(iter(train_db))
print('sample:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape,
tf.reduce_min(sample[0]), tf.reduce_max(sample[0]))
def main():
# [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 1, 1, 512]
model = resnet18()
model.build(input_shape=(None, 32, 32, 3))
model.summary()
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-3)
for epoch in range(500):
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(train_db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 100]
logits = model(x)
# [b] => [b, 100]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=100)
# compute loss
loss = tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, logits, from_logits=True)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step %50 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss))
total_num = 0
total_correct = 0
for x,y in test_db:
logits = model(x)
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
total_correct += int(correct)
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'acc:', acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()