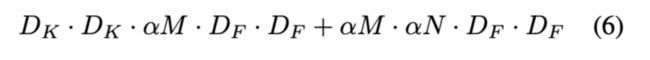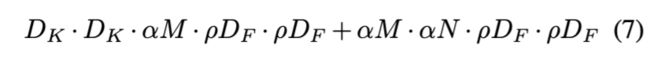MobileNet-v1算法详解
MobileNetv1
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.04861.pdf
谷歌出品的一种深度学习加速模型,在基本不影响准确率的前提下大大减少计算时间和参数数量
深度学习网络广泛应用在图像分类、检测中,但是网络结构复杂,参数过多,计算时间过长使其不容易在移动端应用。因此模型压缩、模型加速在未来是一个比较活跃的领域。
mobileNets主要将传统的卷积结构改造成两层卷积结构的网络,这种新的结构可以在基本不影响准确率的前提下大大减少计算时间(约为原来的1/9)和参数量(约为原来的1/7)
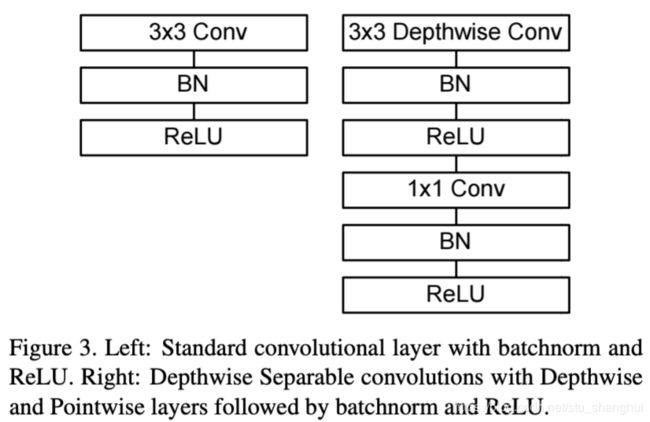
结构图:
算法详解
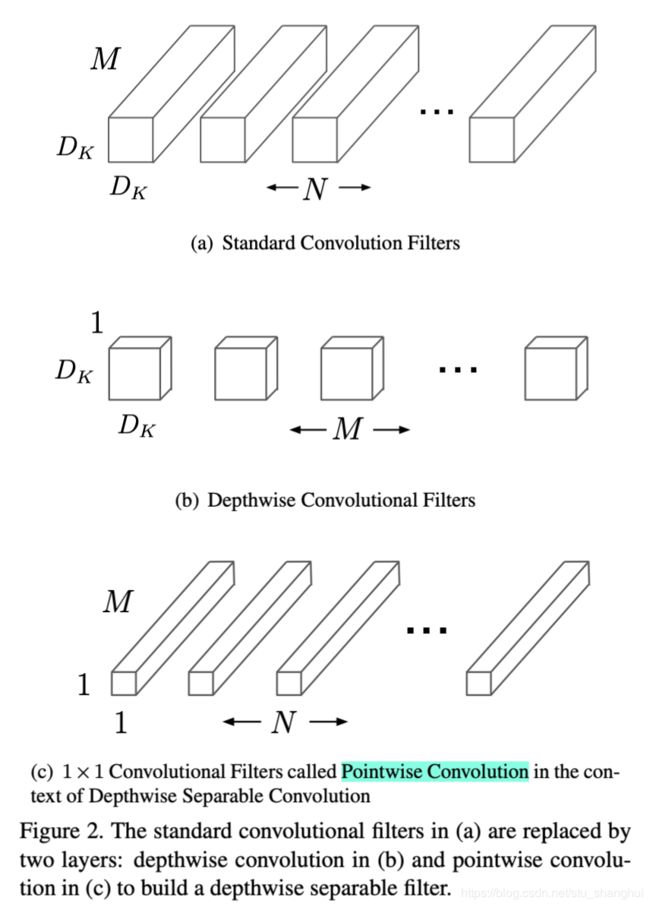
核心:将标准的卷积操作因式分解成一个depthwise convolution和一个1*1卷积(文中叫pointwise convolution) depthwise convolution卷积层之和每个channel进行卷积,pointwise convolution负责combining, 即将上一层卷积的结果进行合并。
M表示输入特征通道数,N表示输出特征通道数(也是本层的卷积核个数),因此如果卷积核大小是DK*DK*M*N, 输出是DF*DF*N,那么标准卷积的计算量是DK*DK*M*N*DF*DF,这个式子可以怎么理解:如果去掉M*N,那么就变成了一个二维卷积核去卷积一个二维输入feature map,输入feature map的大小是DF*DF,特征图的每个点都是由卷积操作生成的,而每卷积一次就会有DK*DK个计算量,因此一个二维卷积核去卷积一个二维特征图就会有DF*DF*DK*Dk个计算量;如果有M个输入,N个卷积核,那么计算量就是DF*DF*DK*DK*M*N个计算量。
计算过程:(设有N个卷积核,每个卷积核的维度是DK*DK*M,输出是DF*DF*N)
- 用M个维度为DK*DK*1的卷积核对应输入的M个feature map,得到M个结果,而且这M个结果不累加(传统的卷积是用N个卷积核卷积输入的所有feature map,然后累加这M个结果,最终得到N个累加后的结果)注意:使用的是M个卷积核不是N。计算量为:DK*DK*M*DF*DF
- 使用N个维度为1*1*M的卷积核卷积图(b)的结果,即输入是DF*DF*M,最终得到DF*DF*N的feature map。计算量为:DF*DF*1*1*M*N
所以计算量减少了:(如果卷积核大小为3*3,差不多卷积操作的时间能降到原来的1/9)
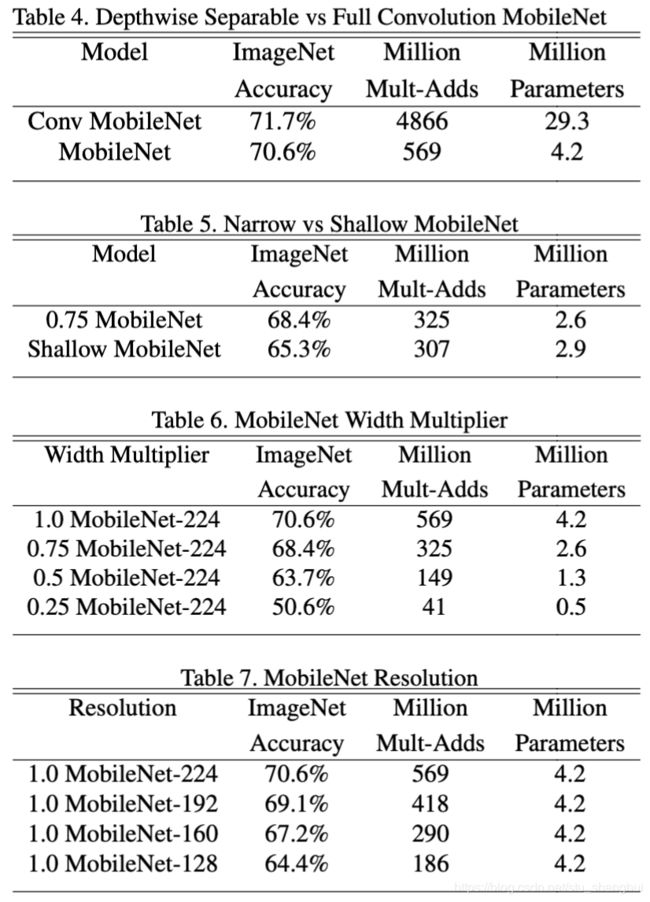
Width multiplier和Resolution multiplier.
为了得到更小和更快的模型,作者介绍了两个概念:width multiplier和resolution multiplier.width multiplier表示输入channel数变成baseline的多少倍,引入了参数![]() ------结果如table6所示。
------结果如table6所示。
width multiplier表示对输入图像做缩放-----结果如table7所示
Detail
实际中L2正则项的系数要设置的比较小,因为本身参数已经减少了许多
Tensorflow实现:(参考:https://github.com/xiaohu2015/DeepLearning_tutorials/tree/master/CNNs)
class MobileNet(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, num_classes=1000, is_training=True,
width_multiplier=1, scope="MobileNet"):
"""
The implement of MobileNet(ref:https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861)
:param inputs: 4-D Tensor of [batch_size, height, width, channels]
:param num_classes: number of classes
:param is_training: Boolean, whether or not the model is training
:param width_multiplier: float, controls the size of model
:param scope: Optional scope for variables
"""
self.inputs = inputs
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.is_training = is_training
self.width_multiplier = width_multiplier
# construct model
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
# conv1
net = conv2d(inputs, "conv_1", round(32 * width_multiplier),
filter_size=3,strides=2) # ->[N, 112, 112, 32]
net = tf.nn.relu(bacthnorm(net, "conv_1/bn",
is_training=self.is_training))
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 64, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_2") # ->[N, 112, 112, 64]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 128, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_3", downsample=True) # ->[N, 56, 56, 128]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 128, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_4") # ->[N, 56, 56, 128]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 256, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_5", downsample=True) # ->[N, 28, 28, 256]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 256, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_6") # ->[N, 28, 28, 256]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_7", downsample=True) # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_8") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_9") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_10") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_11") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 512, self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_12") # ->[N, 14, 14, 512]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 1024,self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_13", downsample=True) # ->[N, 7, 7, 1024]
net = self._depthwise_separable_conv2d(net, 1024,self.width_multiplier,
"ds_conv_14") # ->[N, 7, 7, 1024]
net = avg_pool(net, 7, "avg_pool_15")
net = tf.squeeze(net, [1, 2], name="SpatialSqueeze")
self.logits = fc(net, self.num_classes, "fc_16")
self.predictions = tf.nn.softmax(self.logits)
def _depthwise_separable_conv2d(self, inputs, num_filters, width_multiplier,
scope, downsample=False):
"""depthwise separable convolution 2D function"""
num_filters = round(num_filters * width_multiplier)
strides = 2 if downsample else 1
with tf.variable_scope(scope):
# depthwise conv2d
dw_conv = depthwise_conv2d(inputs, "depthwise_conv", strides=strides)
# batchnorm
bn = bacthnorm(dw_conv, "dw_bn", is_training=self.is_training)
# relu
relu = tf.nn.relu(bn)
# pointwise conv2d (1x1)
pw_conv = conv2d(relu, "pointwise_conv", num_filters)
# bn
bn = bacthnorm(pw_conv, "pw_bn", is_training=self.is_training)
return tf.nn.relu(bn)