神奇的分形图像(一)-Fractal Image-Mandelbrot And Julia
- 分析学原理不做过多阐述:这里以举例子的方式加以阐述,更能通俗的理解其概念。
分形几何学是一门以不规则几何形态为研究对象的几何学
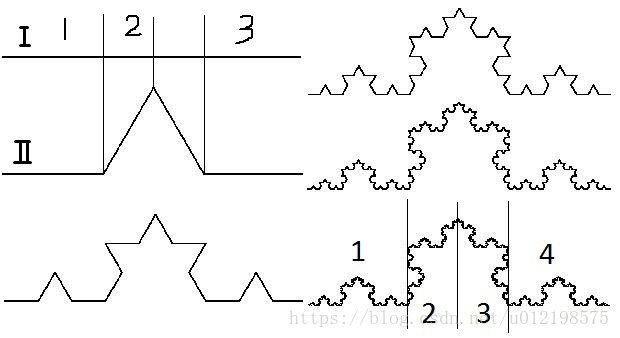
从上图,你能很清晰的回答出它们是直线、矩形、长方体、维度分别是1、2、3维
但是如下图形呢我们通常引入豪斯多夫维度来衡量该图像的维度
这张图像来源是:https://www.zhihu.com/question/19931652
可能你不好理解为什么是n^3 = 4,其实你可以想象成Ⅰ图变成Ⅱ图是
一、首先分割成均等的三分
二、将中间(1/3长度的直线)变成尖角(总长度2/3长度的直线)
所以3 * length(Ⅱ) = 4 * length(Ⅰ)
则![]() 维度
维度
- 今天要介绍的是Mandelbrot And Julia 曼德勃罗集 和 朱丽叶集 的代码实现
曼德勃罗集 和 朱丽叶集 都是利用 公式![]() 迭代
迭代
相同的是迭代初值均为![]() 而不同的迭代的参数
而不同的迭代的参数
曼德勃罗集选用![]() 继续迭代,而朱丽叶集采用固定参数迭代
继续迭代,而朱丽叶集采用固定参数迭代
其次需要理解一个知识点、迭代的条件是必须要收敛,否则结果无意义
这里参与迭代的参数是复数,如果对复数不了解请自行百度,复数表达方式为![]()
定义迭代结束的条件是![]() 等价于
等价于![]()
其中flag = 0实现曼德勃罗集 flag = 1实现 朱丽叶集,参数c由滑条TrackBar调节。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const int trackbar_val_max = 200;
class CMandelbrot
{
public:
CMandelbrot(): x1(0), y1(), ScaleX(), ScaleY(),image(Mat()){}
/*explicit CMandelbrot(int) : x1(0), y1(0), ScaleX(0), ScaleY(0)
{}*/
CMandelbrot(float x1,float y1,float ScaleX,float ScaleY, Mat image)
{
this->x1 = x1;
this->y1 = y1;
this->ScaleX = ScaleX;
this->ScaleY = ScaleY;
this->image = image;
}
public:
Mat getImage(){return image;}
float getX1(){return x1;}
float getY1(){return y1;}
float getScaleX(){return ScaleX;}
float getScaleY(){return ScaleY;}
private:
float x1;
float y1;
float ScaleX;
float ScaleY;
Mat image;
};
//逃逸时间算法实现
int mandelbrot(const complex &z0, const int max,const complex &z1)
{
complex z = z0;
for(int t = 0; t < max; t++)
{
if(z.real() * z.real() + z.imag() * z.imag()> 4.0f) return t;
z = z * z + z1;
}
return max;
}
int mandelbrotFormula(const complex &z0,const complex &z1, const int maxIter=255) {
int value = mandelbrot(z0, maxIter, z1);
if(maxIter - value == 0)//if value == maxIter, set pixel = 0
{
return 0;
}
return cvRound(sqrt(value / (float) maxIter) * 255);// in order to overcome linear scaling is make no sense to change of gray
}
void sequentialManelbrot(Mat &img, const float x1, const float y1, const float scaleX, const float scaleY, complex & c = complex(0, 0) ,int flag = 0)
{
if(flag == 0)
{
if(img.channels() == 1)
{
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
float x0 = j / scaleX + x1;//img x point convert to Mandelbrot set
float y0 = i / scaleY + y1;//img y point convert to Mandelbrot set
complex z0(x0,y0);
uchar value = (uchar)mandelbrotFormula(z0,z0);
img.ptr(i)[j] = value;
}
}
}
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
float x0 = j / scaleX + x1;//img x point convert to Mandelbrot set
float y0 = i / scaleY + y1;//img y point convert to Mandelbrot set
complex z0(x0,y0);
uchar value = (uchar)mandelbrotFormula(z0,z0);
if(value > 150)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, value);
else if(value > 75)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, saturate_cast(value + 75), saturate_cast(value+150));
else if(value > 50)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, value+50, 100);
else if(value > 10)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(value+25, value+50, 100);
else if(value > 0)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(value+25, 0, 100);
else
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
}
}
}
else
{
if(img.channels() == 1)
{
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
float x0 = j / scaleX + x1;//img x point convert to Mandelbrot set
float y0 = i / scaleY + y1;//img y point convert to Mandelbrot set
complex z0(x0,y0);
uchar value = (uchar)mandelbrotFormula(z0,c);
img.ptr(i)[j] = value;
}
}
}
else
{
for(int i = 0; i < img.rows; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < img.cols; j++)
{
float x0 = j / scaleX + x1;//img x point convert to Mandelbrot set
float y0 = i / scaleY + y1;//img y point convert to Mandelbrot set
complex z0(x0,y0);
uchar value = (uchar)mandelbrotFormula(z0,c);
if(value > 150)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, value);
else if(value > 75)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, value, saturate_cast(value+150));
else if(value > 50)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, value, 50);
else if(value > 10)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(value+25, value, 50);
else if(value > 0)
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(value+25, 0, 50);
else
img.at(i, j) = Vec3b(0, 0, 0);
}
}
}
}
}
static float CalibrateRate(int pos)
{
float rate = pos * 1.0f / trackbar_val_max;
if(rate < 0.5)
rate = -2 * rate;
else
rate = 2 * rate;
return rate;
}
static void on_trackbar_Real(int pos, void * userdata)
{
int im_pos = getTrackbarPos("imaginary", "fractal");
CMandelbrot *mm = (CMandelbrot *)userdata;
float re_rate = CalibrateRate(pos);
float im_rate = CalibrateRate(im_pos);
#ifdef _DEBUG
cout << "re_rate" << re_rate << endl;
cout << "im_rate" << im_rate << endl;
#endif
sequentialManelbrot(mm->getImage(),mm->getX1(),mm->getY1(),mm->getScaleX(),mm->getScaleY(),complex(re_rate,im_rate),1);
imshow("fractal",mm->getImage());
}
static void on_trackbar_Imaginary(int pos , void * userdata)
{
int re_pos = getTrackbarPos("real", "fractal");
CMandelbrot *mm = (CMandelbrot *)userdata;
float re_rate = CalibrateRate(re_pos);
float im_rate = CalibrateRate(pos);
#ifdef _DEBUG
cout << "re_rate" << re_rate << endl;
cout << "im_rate" << im_rate << endl;
#endif
sequentialManelbrot(mm->getImage(),mm->getX1(),mm->getY1(),mm->getScaleX(),mm->getScaleY(),complex(re_rate,im_rate),1);
imshow("fractal",mm->getImage());
}
int main()
{
namedWindow("fractal",1);
Mat mandelbrotImg2(800,600,CV_8UC3);
float x1 = -1.4f, x2 = 1.16f;
float y1 = -1.2f, y2 = 1.2f;
float scaleX = mandelbrotImg2.cols / (x2 - x1);
float scaleY = mandelbrotImg2.rows / (y2 - y1);
CMandelbrot mm(x1,y1,scaleX,scaleY,mandelbrotImg2);
int re = 40,im = 40;
createTrackbar("real","fractal",&re,trackbar_val_max,on_trackbar_Real,&mm);
createTrackbar("imaginary","fractal",&im,trackbar_val_max,on_trackbar_Imaginary,&mm);
waitKey();
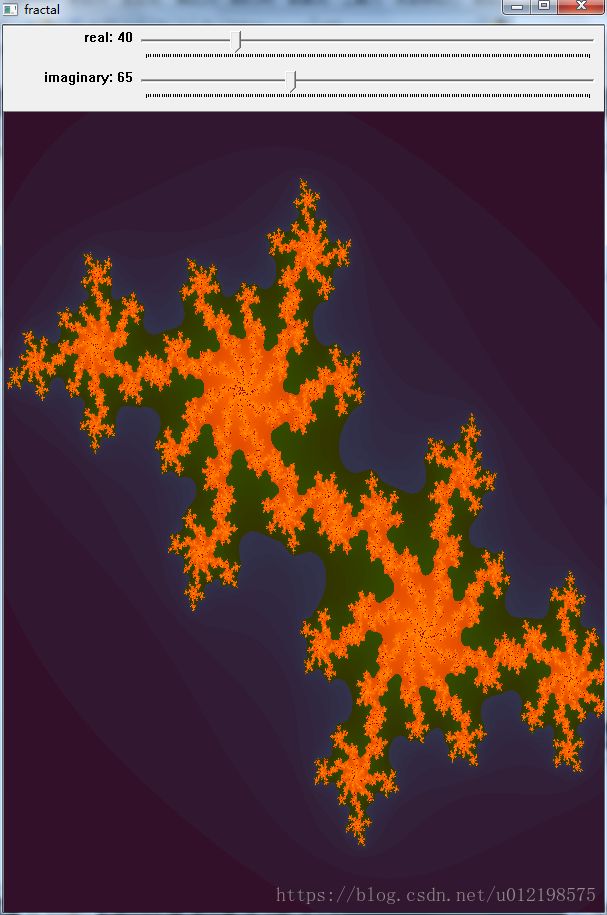
} 实现结果
Re = -0.4 Im = 0.65
调的颜色有点丑,大家请见谅。