《人工智能》机器学习 - 第4章 决策树算法【分类】(四 CART算法实现)
4.6 CART算法
CART(Classification and Regression Trees )是L. Breiman, J. Friedman, R. Olshen, C. Stone在1984年提出的。
前文介绍了ID3、C4.5生成决策树的算法。由于上文使用的测试数据以及建立的模型都比较简单,所以其泛化能力很好。但是,当训练数据量很大的时候,建立的决策树模型往往非常复杂,树的深度很大。此时虽然对训练数据拟合得很好,但是其泛化能力即预测新数据的能力并不一定很好,也就是出现了过拟合现象。这个时候我们就需要对决策树进行剪枝处理以简化模型。
CART,即分类与回归树(classification and regression tree),也是一种应用很广泛的决策树学习方法。但是CART算法比较强大,既可用作分类树,也可以用作回归树。作为分类树时,其本质与ID3、C4.5并有多大区别,只是选择特征的依据不同而已。另外,CART算法建立的决策树一般是二叉树,即特征值只有yes or no的情况(个人认为并不是绝对的,只是看实际需要)。当CART用作回归树时,以最小平方误差作为划分样本的依据。
CART有分类和回归,本文主要讲的是分类,也就是分类树。分类树采用基尼指数选择最优特征。假设有 K K K个类,样本点属于第 k k k类的概率为 p k p_k pk,则概率分布的基尼指数定义为
G a i n ( p ) = ∑ k = 1 K p k ( 1 − p k ) = 1 − ∑ k = 1 K p k 2 \color{red}Gain(p)=\sum_{k=1}^Kp_k(1-p_k)=1-\sum_{k=1}^Kp_k^2 Gain(p)=∑k=1Kpk(1−pk)=1−∑k=1Kpk2
对于二分类问题,若样本点属于第1类的概率为 p p p,则概率分布的基尼指数为
G a i n ( p ) = 2 p ( 1 − p ) \color{red}Gain(p)=2p(1-p) Gain(p)=2p(1−p)
对于给定的样本集合 D D D,其基尼指数为

这里, C k C_k Ck是 D D D中属于第 k k k类的样本子集, K K K是类的个数。
Python代码如下:
"""
函数说明:计算基尼指数
Parameters:
dataSet - 数据集
Returns:
计算结果
"""
def calcGini(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: # 遍历每个实例,统计标签的频数
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys():
labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1
Gini = 1.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key]) / numEntries
Gini -= prob * prob # 以2为底的对数
return Gini
如果样本集合 D D D根据特征集合 A A A是否去某一特征值 a a a被分割两个部分 D 1 D_1 D1、 D 2 D_2 D2,即
D 1 = { ( x , y ) ∈ D ∣ A ( x ) = a } , D 2 = D − D 1 D_1=\{(x,y)\in D|A(x)=a\},D_2=D-D_1 D1={(x,y)∈D∣A(x)=a},D2=D−D1
那么在给定特征A的条件下,集合D的基尼指数定义为
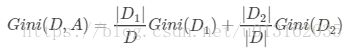
基尼指数 G i n i ( D ) Gini(D) Gini(D)表示集合 D D D的不确定性,基尼指数 G i n i ( D , A ) Gini(D,A) Gini(D,A)表示经 A = a A=a A=a分割后集合 D D D的不确定性。基尼指数值越大,样本集合的不确定性也就越大,这一点与熵相似。
Python代码如下:
"""
函数说明:计算给定特征下的基尼指数
Parameters:
dataSet - 数据集
feature - 特征维度
value - 该特征变量所取的值
Returns:
计算结果
"""
def calcGiniWithFeat(dataSet, feature, value):
D0 = []; D1 = []
# 根据特征划分数据
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[feature] == value:
D0.append(featVec)
else:
D1.append(featVec)
Gini = len(D0) / len(dataSet) * calcGini(D0) + len(D1) / len(dataSet) * calcGini(D1)
return Gini
算法(CART算法)
输入:训练数据集 D D D,停止计算的条件;
输出:CART决策树;
根据训练数据集,从根节点开始,递归地对每个特征进行操作,构建交叉二叉树。
- step.1设结点的训练数据集为 D D D,计算现有放入特征对该数据集的基尼指数,此时,对每个特征 A A A,对其可能有的 a a a个值,根据样本点 A = a A=a A=a 的测试为“是”或者“否”将 D D D分割成 D 1 D_1 D1和 D 2 D_2 D2两部分,计算 A = a A=a A=a的基尼指数。
- step.2 在所有的可能特征A以及他们所有的可能切分点a中,选择基尼指数最小的特征以及对应放入切分点最优特征与最优切分点,依最优特征与最优切分点,从现结点生成两个子结点,将训练数据集依特征分配到两个子结点中去;
- step.3对两个子结点递归调用step1和step2,直到满足停止条件;
- step.4生成CART决策树。
Python代码如下所示。
"""
函数说明:选择最优特征
Parameters:
dataSet - 数据集
Returns:
bestFeat - 最优特征
"""
def chooseBestSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0])-1
bestGini = 0; bestFeat = 0;newGini = 0
for i in range(numFeatures):
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featList)
for splitVal in uniqueVals:
newGini = calcGiniWithFeat(dataSet, i, splitVal)
if newGini < bestGini:
bestFeat = i
bestGini = newGini
return bestFeat
"""
函数说明:按照给定特征划分数据集
Parameters:
dataSet - 待划分的数据集
axis - 划分数据集的特征
value - 需要返回的特征的值
Returns:
无
"""
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
#创建返回的数据集列表
retDataSet = []
#遍历数据集
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
#去掉axis特征
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis]
#将符合条件的添加到返回的数据集
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
#返回划分后的数据集
return retDataSet
"""
函数说明:统计classList中出现此处最多的元素(类标签)
Parameters:
classList - 类标签列表
Returns:
sortedClassCount[0][0] - 出现此处最多的元素(类标签)
"""
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount = {}
for vote in classList:
#统计classList中每个元素出现的次数
if vote not in classCount.keys():
classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key = operator.itemgetter(1), reverse = True) #根据字典的值降序排序
#返回classList中出现次数最多的元素
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
"""
函数说明:创建决策树
Parameters:
dataSet - 训练数据集
labels - 分类属性标签
featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签
Returns:
myTree - 决策树
"""
def createTree(dataSet, labels,featLabels):
#取分类标签(是否放贷:yes or no)
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
#如果类别完全相同则停止继续划分
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]
#遍历完所有特征时返回出现次数最多的类标签
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1:
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat= chooseBestSplit(dataSet) #选择最优特征
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]#最优特征的标签
featLabels.append(bestFeatLabel)
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} #根据最优特征的标签生成树
del(labels[bestFeat]) #删除已经使用特征标签
#得到训练集中所有最优特征的属性值
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues) #去掉重复的属性值
#遍历特征,创建决策树。
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:]
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value), subLabels,featLabels)
return myTree
"""
函数说明:使用决策树分类
Parameters:
inputTree - 已经生成的决策树
featLabels - 存储选择的最优特征标签
testVec - 测试数据列表,顺序对应最优特征标签
Returns:
classLabel - 分类结果
"""
def classify(inputTree, featLabels, testVec):
firstStr = next(iter(inputTree)) #获取决策树结点
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr] #下一个字典
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
for key in secondDict.keys():
if testVec[featIndex] == key:
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict':
classLabel = classify(secondDict[key], featLabels, testVec)
else:
classLabel = secondDict[key]
return classLabel
其代码结构和ID3和C4.5一样,下面就是测试了,同样适用的是电脑购买的数据。
#测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
## Step 1: load data
print("Step 1: load data...")
df=pd.read_csv('data.csv')
data=df.values[:-1,1:].tolist()
dataSet=data[:]
label=df.columns.values[1:-1].tolist()
labels=label[:]
#print(dataSet)
#print(labels)
## Step 2: training...
print("Step 2: training...")
featLabels = []
myTree = createTree(dataSet, labels,featLabels)
#print(myTree)
## Step 3: testing
print("Step 3: testing...")
#测试数据
testVec = ['middle_aged', 'yes', 'excellent', 'low']
print("测试实例:"+ str(testVec))
result = classify(myTree, featLabels, testVec)
## Step 4: show the result
print("Step 4: show the result...")
print("result:"+ str(result))
if result == 'yes':
print("要购买")
else:
print("不购买")
结果如下所示。

【完整代码参考附件5.DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty\DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty_v1\DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty_v1.0.py】
同样对决策树进行可视化操作。可视化的操作和ID3的代码完全一样,结果如下所示。

【完整代码参考附件5.DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty\DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty_v1\DT-CART-buys_computer_Classifty_v1.1.py】
参考文档:
英文文档:http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html
中文文档:http://sklearn.apachecn.org/cn/0.19.0/modules/tree.html
参考文献:
[1]《机器学习》周志华著
[2]《统计学习方法》李航著
[3]L. Breiman, J. Friedman, R. Olshen, and C. Stone. Classification and Regression Trees. Wadsworth, Belmont, CA, 1984.
[4] Quinlan, JR. (1986) Induction of Decision Trees. Machine Learning, 1, 81-106.
[5]J.R. Quinlan. C4. 5: programs for machine learning. Morgan Kaufmann, 1993.
[6]T. Hastie, R. Tibshirani and J. Friedman. Elements of Statistical Learning, Springer, 2009.
本章参考附件
点击进入