从网页爬取数据
网络是丰富的数据来源,您可以从中提取各种类型的见解和发现。 在本部分,学习如何从Web获取数据,无论是存储在文件中还是HTML中。 您还将学习抓取和解析Web数据的基础知识
从网上导入平面文件
1、从网上导入平面文件
从Web导入了一个文件,将其保存在本地并将其加载到DataFrame中。
导入文件是来自加州大学欧文分校机器学习库的“winequality-red.csv”。 该平面文件包含红葡萄酒理化性质的表格数据,如pH,酒精含量和柠檬酸含量,以及葡萄酒质量等级。
urllib.urlretrieve() 保存,将指定的地址资源保存到本地。
# Import package
from urllib.request import urlretrieve
# Import pandas
import pandas as pd
# Assign url of file: url
url = 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/production/course_1606/datasets/winequality-red.csv'
# Save file locally
urlretrieve(url,'winequality-red.csv')
#urlretrieve()方法直接将远程数据下载到本地。
# Read file into a DataFrame and print its head
df = pd.read_csv('winequality-red.csv', sep=';')
print(df.head())2、从Web打开和读取平面文件
您刚刚从Web导入了一个文件,将其保存在本地并将其加载到DataFrame中。 如果您只想将文件从Web加载到DataFrame而不先在本地保存,则可以使用pandas轻松完成。 特别是,您可以使用函数pd.read_csv(),其中URL作为第一个参数,分隔符sep作为第二个参数。
# Import packages
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
# Assign url of file: url
url = 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/production/course_1606/datasets/winequality-red.csv'
# Read file into a DataFrame: df
df = pd.read_csv(url,sep=';')
# Print the head of the DataFrame
print(df.head())
# Plot first column of df
pd.DataFrame.hist(df.ix[:, 0:1])
plt.xlabel('fixed acidity (g(tartaric acid)/dm$^3$)')
plt.ylabel('count')
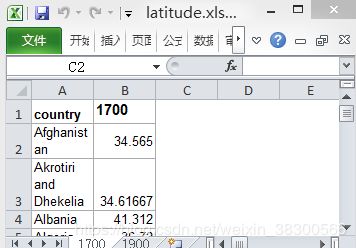
plt.show()3、从Web导入非平面文件
刚刚使用pandas函数pd.read_csv()将Web平面文件从Web加载到DataFrame中,而无需先将其保存在本地。 这个功能非常酷,允许加载所有类型的文件,而不仅仅是平面文件。使用pd.read_excel()导入Excel电子表格。
# Import package
import pandas as pd
# Assign url of file: url
url = 'http://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/course/importing_data_into_r/latitude.xls'
# Read in all sheets of Excel file: xl
x1 = pd.read_excel(url,sheetname = None)
# Print the sheetnames to the shell
print(x1.keys())
# Print the head of the first sheet (using its name, NOT its index)
print(x1['1700'].head())dict_keys(['1700', '1900'])
country 1700
0 Afghanistan 34.565000
1 Akrotiri and Dhekelia 34.616667
2 Albania 41.312000
3 Algeria 36.720000
4 American Samoa -14.307000
请注意,pd.read_excel()的输出是一个Python字典,其中工作表名称作为键,相应的DataFrame作为相应的值。
使用HTTP请求从Web导入文件
url:统一资源定位符。实际上就是用来表示资源在那台web服务器的位置上的一个地址。
http://www.datacamp.com/teach/documentation
url组成:
协议头 http:// https://
域名·或主机 www.datacamp.com
http请求
当我们向网络获取资源
(1)发出web服务器请求
url告诉web服务器我们想要得到的资源的位置 , header 身份头 用来表示请求的身份 cookie,post/get Data 请求的数据
(2)web服务器响应
Response header 资源头部 资源本身
1、使用urllib在Python中执行HTTP请求
# Import packages
from urllib.request import urlopen,Request
# Specify the url
url = "http://www.datacamp.com/teach/documentation"
# This packages the request: request
request = Request(url) #发起请求
# Sends the request and catches the response: response
response = urlopen(request) #将请求返回的内容转换为文件格式
# Print the datatype of response
print(type(response))
# Be polite and close the response!
response.close()
2、使用urllib在Python中打印HTTP请求结果
urllib.request模块提供了最基本的构造HTTP请求的方法,利用它可以模拟浏览器的一个请求发起过程。
Request() 向服务器发起请求 urlopen()可以将请求返回的内容转换为文件格式
利用最基本的urlopen()方法,可以完成最基本的简单网页的GET请求抓取。
利用urlopen()方法可以实现最基本请求的发起,但这几个简单的参数并不足以构建一个完整的请求。如果请求中需要加入Headers等信息,就可以利用更强大的Request类来构建。
得到的response,它是一个HTTPResposne类型的对象。它主要包含read()、readinto()、getheader(name)、getheaders()、fileno()等方法,以及msg、version、status、reason、debuglevel、closed等属性。调用read()方法可以得到返回的网页内容,调用status属性可以得到返回结果的状态码,如200代表请求成功,404代表网页未找到等。
# Import packages
from urllib.request import urlopen, Request
# Specify the url
url = "http://www.datacamp.com/teach/documentation"
# This packages the request
request = Request(url) #向服务器发起请求
# Sends the request and catches the response: response
response = urlopen(request) #将请求返回的内容转换为文件格式
# Extract the response: html
html = response.read() #查看返回内容
# Print the html
print(html)
# Be polite and close the response!
response.close()3、使用requests在Python中执行HTTP请求
rllib库中的urlopen()方法实际上是以GET方式请求网页,而requests中相应的方法就是get()方法,
这里我们调用get()方法实现与urlopen()相同的操作,得到一个Response对象,
将请求打包到URL,发送请求并使用单个函数request.get捕获响应
requests提高更高接口的
# Import package
import requests
# Specify the url: url
url = "http://www.datacamp.com/teach/documentation"
# Packages the request, send the request and catch the response: r
r = requests.get(url)
# Extract the response: text
text = r.text
# Print the html
print(text)Scraping the web in Python
1、使用BeautifulSoup解析HTML
BeautifulSoup就是Python的一个HTML或XML的解析库,可以用它来方便地从网页中提取数据。利用它可以省去很多烦琐的提取工作,提高了解析效率。
首先执行http请求,我们将它当作第一个参数传给BeautifulSoup对象,此时就完成了BeaufulSoup对象的初始化。然后,将这个对象赋值给soup变量。接下来,就可以调用soup的各个方法和属性解析这串HTML代码了。
首先,调用prettify()方法。这个方法可以把要解析的字符串以标准的缩进格式输出。这里需要注意的是,输出结果里面包含body和html节点,也就是说对于不标准的HTML字符串BeautifulSoup,可以自动更正格式。这一步不是由prettify()方法做的,而是在初始化BeautifulSoup时就完成了。
使用BeautifulSoup包来解析、优化、从HTML中提取信息。 从Guido van Rossum的网页上抓取数据,将对HTML进行筛选,然后提取文本和超链接。.
# Import packages
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Specify url: url
url = 'https://www.python.org/~guido/'
# Package the request, send the request and catch the response: r
r = requests.get(url)
# Extracts the response as html: html_doc
html_doc =r.text
print(html_doc)
# Create a BeautifulSoup object from the HTML: soup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc)
print(soup)
# Prettify the BeautifulSoup object: pretty_soup
pretty_soup = soup.prettify()
# Print the response
print(pretty_soup)html_doc
soup
pretty_soup
2、使用BeautifulSoup将网页转换为数据:获取文本
从HTML汤中提取信息的基础知识。 在本练习中,您将了解如何从BDFL的网页中提取文本,以及打印网页的标题。
soup.title可以选出HTML中的title节点,再使用get_text()方法就可以得到里面的文本了。
# Import packages
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Specify url: url
url = 'https://www.python.org/~guido/'
# Package the request, send the request and catch the response: r
r = requests.get(url)
# Extract the response as html: html_doc
html_doc = r.text
# Create a BeautifulSoup object from the HTML: soup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc)
# Get the title of Guido's webpage: guido_title
guido_title = soup.title
# Print the title of Guido's webpage to the shell
print(guido_title)
# Get Guido's text: guido_text
guido_text = soup.get_text()
# Print Guido's text to the shell
print(guido_text)
2、使用BeautifulSoup将网页转换为数据:获取超链接
find_all,顾名思义,就是查询所有符合条件的元素。给它传入一些属性或文本,就可以得到符合条件的元素,它的功能十分强大。
find_all(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs)
这里我们调用了find_all()方法,传入name参数,其参数值为a。也就是说,我们想要查询所有a节点,返回结果是列表类型,每个元素依然都是bs4.element.Tag类型。
# Import packages
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
# Specify url
url = 'https://www.python.org/~guido/'
# Package the request, send the request and catch the response: r
r = requests.get(url)
# Extracts the response as html: html_doc
html_doc = r.text
# create a BeautifulSoup object from the HTML: soup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc)
# Print the title of Guido's webpage
print(soup.title)
# Find all 'a' tags (which define hyperlinks): a_tags
a_tags = soup.find_all(name = 'a')
# Print the URLs to the shell
for link in a_tags:
print(link.get('href'))