背景
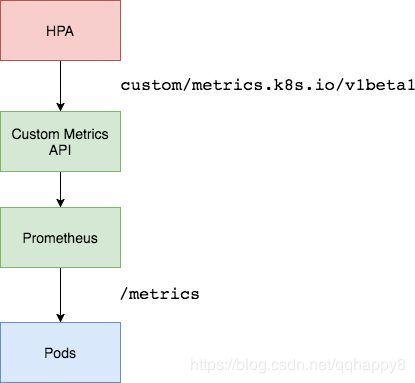
自Kubernetes 1.11版本起,K8s资源采集指标由Resource Metrics API(Metrics Server 实现)和Custom metrics api(Prometheus实现)两种API实现,传统Heapster监控被废弃。前者主要负责采集Node、Pod的核心资源数据,如内存、CPU等;而后者则主要负责自定义指标数据采集,如网卡流量,磁盘IOPS、HTTP请求数、数据库连接数等。
heapster被废弃以后,所有的指标数据都从API接口中获取,kubernetes将资源指标分为了两种:
-
Core metrics(核心指标):由metrics-server提供API,即 metrics.k8s.io,仅提供Node和Pod的CPU和内存使用情况。
-
Custom Metrics(自定义指标):由Prometheus Adapter提供API,即 custom.metrics.k8s.io,由此可支持任意Prometheus采集到的自定义指标。
想让k8s一些核心组件,比如HPA,获取核心指标以外的其它自定义指标,则必须部署一套prometheus监控系统,让prometheus采集其它各种指标,
但是prometheus采集到的metrics并不能直接给k8s用,因为两者数据格式不兼容,还需要另外一个组件(kube-state-metrics),将prometheus的metrics 数据格式转换成k8s API接口能识别的格式,转换以后,因为是自定义API,所以还需要用Kubernetes aggregator在主API服务器中注册,以便直接通过/apis/来访问。
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler实现为一个控制循环,定期查询Resource Metrics API以获取CPU /内存等核心指标和针对特定应用程序指标的Custom Metrics API。
Custom Metrics组件介绍
- node-exporter:prometheus的agent端,收集Node级别的监控数据。
- prometheus:监控服务端,从node-exporter拉取数据并存储为时序数据。
- kube-state-metrics: 将prometheus中可以用PromQL查询到的指标数据转换成k8s对应的数据格式,即转换成Custerom Metrics API接口格式的数据,但是它不能聚合进apiserver中的功能。
- k8s-prometheus-adpater:聚合apiserver,即提供了一个apiserver(custom-metrics-api),自定义APIServer通常都要通过Kubernetes aggregator聚合到apiserver
部署步骤
1.部署好prometheus,node-exporter,kube-state-metrics,开启kube-apiserver的聚合功能,相关教程很多。
2.下载相关yaml文件 ,yaml文件clone于https://github.com/stefanprodan/k8s-prom-hpa,笔者内网环境,使用的为此git仓库的zip包。
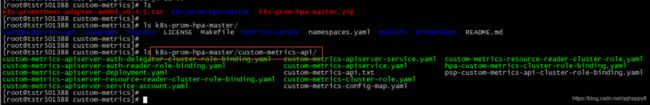
如上图,部署custom-metrics的yaml文件位于./custom-metrics-api目录,其中核心yaml文件为custom-metrics-apiserver-deployment.yaml和custom-metrics-apiservice.yaml,为部署prometheus-adapter的pod,并注册custom-metrics的apiservice。
3.修改custom-metrics-api目录所有的yaml的namespace为alauda-system,因笔者prometheus部署在此namespace。
sed -i 's/namespace: monitoring/namespace: alauda-system/g' *.yaml
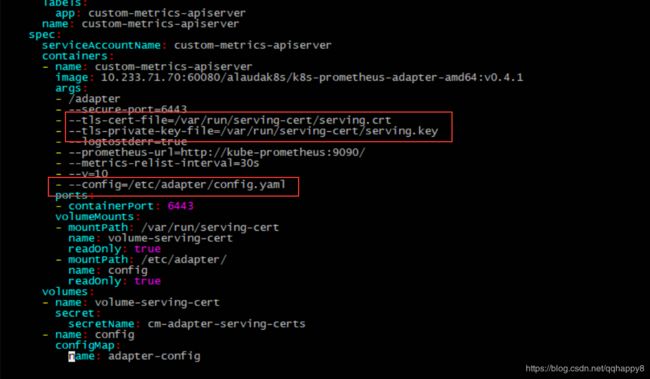
4.参照custom-metrics-apiserver-deployment.yaml里面的prometheus-adapter的启动配置,准备tls证书,笔者复用了master节点的证书。
kubectl create secret generic cm-adapter-serving-certs --from-file=serving.crt=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.crt --from-file=serving.key=/etc/kubernetes/pki/apiserver.key -n alauda-system
![]()
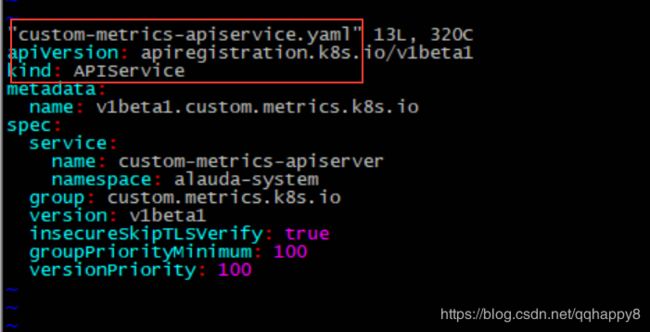
5.按照./custom-metrics-api目录下的资源清单,部署相关资源对象。
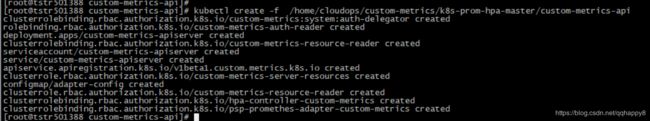
kubectl create -f /home/cloudops/custom-metrics/k8s-prom-hpa-master/custom-metrics-api
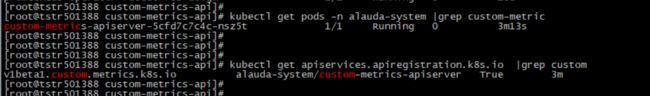
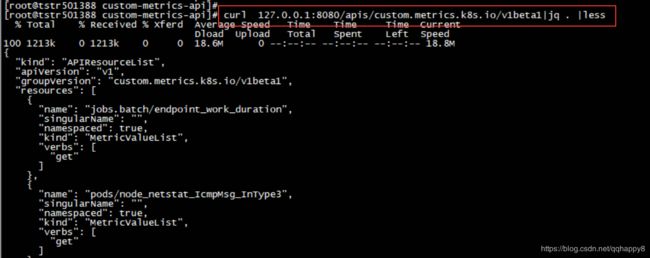
6.检查custom-metrics-apiserver的pod启动成功,custom-metrics-apiservice注册成功,curl此api路径正常返回。
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/ |jq .|less
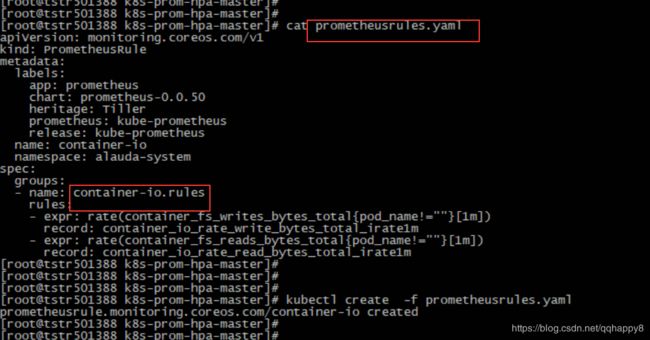
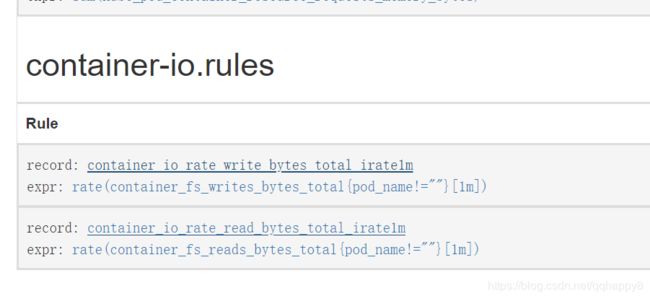
7.创建关于容器IO带宽的prometheusRule,确认rule的指标正常采集。
####cat prometheusrules.yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: PrometheusRule
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
chart: prometheus-0.0.50
heritage: Tiller
prometheus: kube-prometheus
release: kube-prometheus
name: container-io
namespace: alauda-system
spec:
groups:
- name: container-io.rules
rules:
- expr: rate(container_fs_writes_bytes_total{pod_name!=""}[1m])
record: container_io_rate_write_bytes_total_irate1m
- expr: rate(container_fs_reads_bytes_total{pod_name!=""}[1m])
record: container_io_rate_read_bytes_total_irate1m
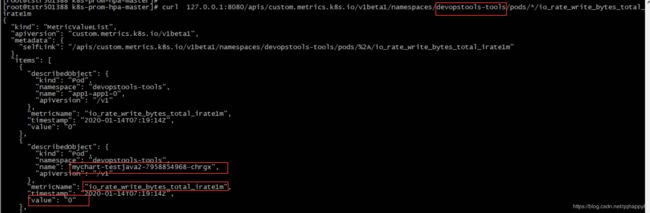
8.检查基于IO的custom-metrics通过kube-api能正常访问,注意替换namespace为本地环境。
curl 127.0.0.1:8080/apis/custom.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/devopstools-tools/pods/*/io_rate_write_bytes_total_irate1m
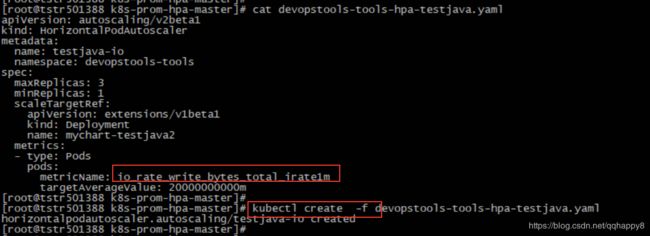
9.创建一个基于IO带宽的HPA对象(基于pod的io写带宽,阈值为20M),笔者使用的为一个tomcat的pod。
####cat devopstools-tools-hpa-testjava.yaml
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: testjava-io
namespace: devopstools-tools
spec:
maxReplicas: 3
minReplicas: 1
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
name: mychart-testjava2
metrics:
- type: Pods
pods:
metricName: io_rate_write_bytes_total_irate1m
targetAverageValue: 20000000000m
至此,基于IO写带宽的HPA创建完成
验证
1.在HPA的作用对象的容器pod里面,通过dd命令,加大此pod的IO带宽。
2.通过kubectl describe hpa检查HPA是否正常工作。
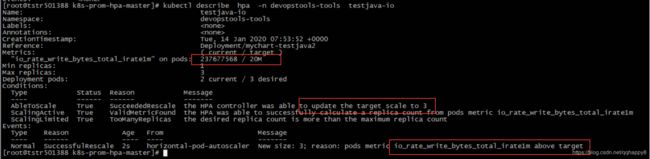
如上图,因为IO写带宽超过阈值(20M),deployment控制的pod副本数增加到3。
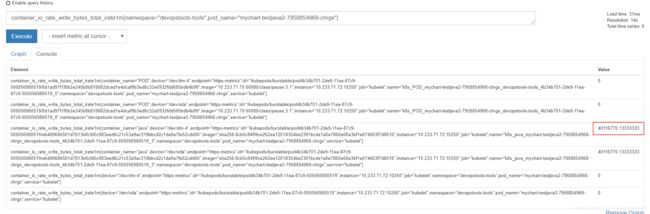
3.在prometheus端查询pod的IO带宽(下图显示io带宽40M以上),也表明HPA工作正常。
后记
1.基于IO带宽的HPA,和基于cpu和内存的HPA相比,生产实用性不一定很大,本文只是证明custom-metrics的可行性。
2.基于容器的IOPS的HPA暂未成功,原因为prometheus查询的容器iops(container_fs_io_current)始终为0,google到的原因为cadvisor的bug,待进一步调研。
参考 https://github.com/stefanprodan/k8s-prom-hpa