轻轻松松使用StyleGAN2(五):StyleGAN2 Encoder源代码初探+中文注释,projector.py和project_images.py
StyleGAN2 Encoder使用18x512的dlatents进行迭代优化,实现对目标图片的“无限逼近”并重建高质量图像,保存对应的dlatents用于后续处理。
获取StyleGAN2 Encoder,GitHub上的链接是:
https://github.com/rolux/stylegan2encoder
StyleGAN2 Encoder改写了StyleGAN2的projector.py,增加了project_images.py,其实现的效果要优于StyleGAN2自带的run_projector.py。
StyleGAN2 Encoder的底层依然依赖于StyleGAN2核心的G_main类(生成器)、G_mapping类(映射网络)、G_synthesis_stylegan2类(合成网络)、D_stylegan2类(辨别器)等,这些类的源代码可以查看:./training/networks_stylegan2.py。
在训练过程中,通过对dlatent_avg(dlatent_avg是W空间dlatents向量(18x512)的平均值)进行预测和更新来实现输入的迭代,并且在每次迭代过程中引入噪声,即:迭代的输入 = 迭代的dlatent_avg + 噪声;同时,学习率也在每步迭代过程中进行更改;将迭代的输入通过StyleGAN2网络生成预测图像,再利用VGG16网络计算预测图像和目标图像之间的loss。
在训练的开始,StyleGAN2随机产生10000个向量,并用它们的平均值作为训练的起点,简化了训练过程。
StyleGAN2没有使用tensorflow自带的方法,而是使用dnnlib.tflib来构建优化函数。dnnlib.tflib是英伟达团队在tensorflow上构建的一组库函数,以便于代码维护,也有助于理解代码结构。
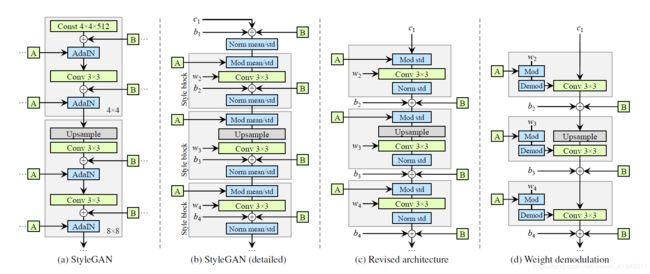
为解决StyleGAN存在的伪影(artifacts)问题,StyleGAN2对StyleGAN的合成网络进行了修改,如下图所示:
其中,(a)是StyleGAN的合成网络,(b)是StyleGAN的实现细节;(c)是StyleGAN2的合成网络,(d)是StyleGAN2的实现细节,其具体说明以及改动的原因,可以查看StyleGAN2的论文:
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1912.04958.pdf
总体上,StyleGAN2 Encoder基于真实人脸图片重建高质量、可操控的人脸图像,较之第一代StyleGAN Encoder效果更好,但同样的GPU条件下(比如:NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080Ti)运行时间更长。
我们花时间研究了一下StyleGAN2 Encoder的projector.py和project_images.py的源代码,其整体代码结构如下图所示,其中浅绿色部分为projector.py,白色部分为project_images.py:
具体的源代码(含中文注释)如下:
projector.py
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import dnnlib
import dnnlib.tflib as tflib
from training import misc
#----------------------------------------------------------------------------
class Projector:
def __init__(self,
# 初始化变量
# vgg16_pkl = 'https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1N2-m9qszOeVC9Tq77WxsLnuWwOedQiD2',
vgg16_pkl= '.\models\\vgg16_zhang_perceptual.pkl',
num_steps = 1000,
initial_learning_rate = 0.1,
initial_noise_factor = 0.05,
verbose = False
):
self.vgg16_pkl = vgg16_pkl
self.num_steps = num_steps
self.dlatent_avg_samples = 10000
self.initial_learning_rate = initial_learning_rate
self.initial_noise_factor = initial_noise_factor
self.lr_rampdown_length = 0.25
self.lr_rampup_length = 0.05
self.noise_ramp_length = 0.75
self.regularize_noise_weight = 1e5
self.verbose = verbose
self.clone_net = True
self._Gs = None
self._minibatch_size = None
self._dlatent_avg = None
self._dlatent_std = None
self._noise_vars = None
self._noise_init_op = None
self._noise_normalize_op = None
self._dlatents_var = None
self._noise_in = None
self._dlatents_expr = None
self._images_expr = None
self._target_images_var = None
self._lpips = None
self._dist = None
self._loss = None
self._reg_sizes = None
self._lrate_in = None
self._opt = None
self._opt_step = None
self._cur_step = None
# 显示信息
def _info(self, *args):
if self.verbose:
print('Projector:', *args)
# 设置StyleGAN网络
def set_network(self, Gs, minibatch_size=1):
assert minibatch_size == 1
self._Gs = Gs
self._minibatch_size = minibatch_size
if self._Gs is None:
return
if self.clone_net:
self._Gs = self._Gs.clone()
# 向量空间18x512
# Find dlatent stats.
self._info('Finding W midpoint and stddev using %d samples...' % self.dlatent_avg_samples)
# 以123为种子,随机产生dlatent_avg_samples=10000个样本值,赋值给latent_samples
latent_samples = np.random.RandomState(123).randn(self.dlatent_avg_samples, *self._Gs.input_shapes[0][1:])
# 将latent_samples映射到W空间,赋值给dlatent_samples
# dlatent,即:disentangled latent,映射到18x512向量,可以分别控制不同层次的人脸特征,因此说是disentangled(解纠缠)
# components.mapping = tflib.Network('G_mapping'......),见:./training/networks_stylegan2.py
dlatent_samples = self._Gs.components.mapping.run(latent_samples, None) # (10000, 18, 512)
# 计算均值、方差
# _dlatent_avg是_dlatent_var优化迭代的初始值
self._dlatent_avg = np.mean(dlatent_samples, axis=0, keepdims=True) # (1, 18, 512)
self._dlatent_std = (np.sum((dlatent_samples - self._dlatent_avg) ** 2) / self.dlatent_avg_samples) ** 0.5
self._info('std = %g' % self._dlatent_std)
# Find noise inputs.
self._info('Setting up noise inputs...')
self._noise_vars = []
noise_init_ops = []
noise_normalize_ops = []
# 初始化噪声,变量名形如'G_synthesis/noiseXX',完成后break退出
while True:
n = 'G_synthesis/noise%d' % len(self._noise_vars)
if not n in self._Gs.vars:
break
v = self._Gs.vars[n]
self._noise_vars.append(v)
# 将正态分布的随机噪声赋值给v
noise_init_ops.append(tf.assign(v, tf.random_normal(tf.shape(v), dtype=tf.float32)))
# 计算均值、方差
noise_mean = tf.reduce_mean(v)
noise_std = tf.reduce_mean((v - noise_mean)**2)**0.5
# 正则化
noise_normalize_ops.append(tf.assign(v, (v - noise_mean) / noise_std))
self._info(n, v)
# 将噪声组成group
self._noise_init_op = tf.group(*noise_init_ops)
self._noise_normalize_op = tf.group(*noise_normalize_ops)
# Image output graph.
self._info('Building image output graph...')
# 定义变量_dlatents_var,初始化为0,在start函数中赋初始值为_dlatent_avg
self._dlatents_var = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([self._minibatch_size] + list(self._dlatent_avg.shape[1:])), name='dlatents_var') # (1,18,512)
# 定义输入_noise_in
self._noise_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [], name='noise_in')
dlatents_noise = tf.random.normal(shape=self._dlatents_var.shape) * self._noise_in # 与正态分布的随机向量相乘
# 求和,赋值给_dlatents_expr
self._dlatents_expr = self._dlatents_var + dlatents_noise
# components.synthesis将_dlatents_expr生成图像向量
self._images_expr = self._Gs.components.synthesis.get_output_for(self._dlatents_expr, randomize_noise=False)
# Downsample image to 256x256 if it's larger than that. VGG was built for 224x224 images.
# 若生成的图像尺寸超过256x256,把图片调整到256x256
proc_images_expr = (self._images_expr + 1) * (255 / 2)
sh = proc_images_expr.shape.as_list() # 将proc_images_expr.shape元组转换为list
if sh[2] > 256:
factor = sh[2] // 256 # 基于256x256,计算图像的倍数
# 对超过256x256的像素取平均值,并压缩维度,运算后的shape是[-1, sh[1], sh[2]//factor, sh[2]//factor]
proc_images_expr = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reshape(proc_images_expr, [-1, sh[1], sh[2] // factor, factor, sh[2] // factor, factor]), axis=[3,5])
# Loss graph.
self._info('Building loss graph...')
# 定义变量_target_images_var
# 该变量会在下面的start函数中赋初始值
self._target_images_var = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(proc_images_expr.shape), name='target_images_var')
if self._lpips is None:
# 加载vgg16模型
self._lpips = misc.load_pkl(self.vgg16_pkl) # vgg16_zhang_perceptual.pkl
# 使用vgg16模型将proc_images_expr与_target_images_var比较,计算差值
# 变量_target_images_var会在self.start函数中赋值
self._dist = self._lpips.get_output_for(proc_images_expr, self._target_images_var)
# 对差值求和,计算_loss
self._loss = tf.reduce_sum(self._dist)
# Noise regularization graph.
self._info('Building noise regularization graph...')
reg_loss = 0.0
for v in self._noise_vars:
sz = v.shape[2]
while True:
# 沿axis=3滚动一个位置,相乘,平方,沿axis=2滚动一个位置,相乘,取平均数,平方
# 沿axis=2滚动一个位置,相乘,平方,沿axis=2滚动一个位置,相乘,取平均数,平方
# 求和
reg_loss += tf.reduce_mean(v * tf.roll(v, shift=1, axis=3))**2 + tf.reduce_mean(v * tf.roll(v, shift=1, axis=2))**2
if sz <= 8:
break # Small enough already
v = tf.reshape(v, [1, 1, sz//2, 2, sz//2, 2]) # Downscale,维度减半
v = tf.reduce_mean(v, axis=[3, 5]) # 求平均数,压缩维度
sz = sz // 2
self._loss += reg_loss * self.regularize_noise_weight
# Optimizer.
# 用dnnlib.tflib构建优化函数,定义优化迭代计算_opt_step
self._info('Setting up optimizer...')
self._lrate_in = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [], name='lrate_in') # _lrate_in是一个输入项
self._opt = dnnlib.tflib.Optimizer(learning_rate=self._lrate_in) # 定义优化函数
self._opt.register_gradients(self._loss, [self._dlatents_var] + self._noise_vars) # 梯度,_loss是输出,[_dlatents_var] + _noise_vars是输入
self._opt_step = self._opt.apply_updates()
# 运行
def run(self, target_images):
# Run to completion.
# 开始,完成初始化
self.start(target_images)
# 迭代
while self._cur_step < self.num_steps:
self.step()
# Collect results.
# 返回结果
pres = dnnlib.EasyDict()
pres.dlatents = self.get_dlatents()
pres.noises = self.get_noises()
pres.images = self.get_images()
return pres
# 开始
def start(self, target_images):
assert self._Gs is not None
# Prepare target images.
# 准备目标图像(组),即:优化迭代的目标对象
self._info('Preparing target images...')
target_images = np.asarray(target_images, dtype='float32')
target_images = (target_images + 1) * (255 / 2)
sh = target_images.shape
assert sh[0] == self._minibatch_size
# 如果目标图像尺寸太大,就按照_target_images_var的尺寸缩小到256x256
if sh[2] > self._target_images_var.shape[2]:
factor = sh[2] // self._target_images_var.shape[2]
target_images = np.reshape(target_images, [-1, sh[1], sh[2] // factor, factor, sh[3] // factor, factor]).mean((3, 5))
# Initialize optimization state.
self._info('Initializing optimization state...')
# 设置_target_images_var变量、_dlatents_var变量
# 把_dlatent_avg作为_dlatents_var优化迭代的起点,_target_images_var为优化迭代的目标图像(组)
tflib.set_vars({self._target_images_var: target_images, self._dlatents_var: np.tile(self._dlatent_avg, [self._minibatch_size, 1, 1])})
# 初始化噪声
tflib.run(self._noise_init_op)
# 复位优化器状态
self._opt.reset_optimizer_state()
# 迭代计数从0开始
self._cur_step = 0
# 迭代
def step(self):
assert self._cur_step is not None
if self._cur_step >= self.num_steps:
return
if self._cur_step == 0:
self._info('Running...')
# Hyperparameters.
t = self._cur_step / self.num_steps # 完成比例
# 噪声强度 = 当前dlatent标准差 * 初始噪声因子 * 噪声斜面长度剩余比例的平方
noise_strength = self._dlatent_std * self.initial_noise_factor * max(0.0, 1.0 - t / self.noise_ramp_length) ** 2
# 计算学习率
lr_ramp = min(1.0, (1.0 - t) / self.lr_rampdown_length)
lr_ramp = 0.5 - 0.5 * np.cos(lr_ramp * np.pi)
lr_ramp = lr_ramp * min(1.0, t / self.lr_rampup_length)
learning_rate = self.initial_learning_rate * lr_ramp
# Train.
# 训练,tflib.run
feed_dict = {self._noise_in: noise_strength, self._lrate_in: learning_rate}
_, dist_value, loss_value = tflib.run([self._opt_step, self._dist, self._loss], feed_dict)
tflib.run(self._noise_normalize_op) # 每次迭代,随机生成噪声
# Print status.
# 打印/显示迭代状态
self._cur_step += 1
if self._cur_step == self.num_steps or self._cur_step % 10 == 0:
self._info('%-8d%-12g%-12g' % (self._cur_step, dist_value, loss_value))
if self._cur_step == self.num_steps:
self._info('Done.')
def get_cur_step(self):
return self._cur_step
def get_dlatents(self):
return tflib.run(self._dlatents_expr, {self._noise_in: 0})
def get_noises(self):
return tflib.run(self._noise_vars)
def get_images(self):
return tflib.run(self._images_expr, {self._noise_in: 0})
project_images.py
import argparse
import os
import shutil
import numpy as np
import dnnlib
import dnnlib.tflib as tflib
import pretrained_networks
import projector
import dataset_tool
from training import dataset
from training import misc
def project_image(proj, src_file, dst_dir, tmp_dir, video=False):
data_dir = '%s/dataset' % tmp_dir # ./stylegan2-tmp/dataset
if os.path.exists(data_dir):
shutil.rmtree(data_dir)
image_dir = '%s/images' % data_dir # ./stylegan2-tmp/dataset/images
tfrecord_dir = '%s/tfrecords' % data_dir # ./stylegan2-tmp/dataset/tfrecords
os.makedirs(image_dir, exist_ok=True)
# 将源图片文件copy到./stylegan2-tmp/dataset/images下
shutil.copy(src_file, image_dir + '/')
# 在./stylegan2-tmp/dataset/tfrecords下生成tfrecord临时文件
# tfrecord临时文件序列化存储了不同lod下的图像的shape和数据
# 举例,如果图像是1024x1024,则tfr_file命名从10--2,如:tfrecords-r10.tfrecords...tfrecords-r05.tfrecords...
dataset_tool.create_from_images(tfrecord_dir, image_dir, shuffle=0)
# TFRecordDataset类在“dataset.py”中定义,从一组.tfrecords文件中加载数据集到dataset_obj
# load_dataset是个helper函数,用于构建dataset对象(在TFRecordDataset类创建对象实例时完成)
dataset_obj = dataset.load_dataset(
data_dir=data_dir, tfrecord_dir='tfrecords',
max_label_size=0, repeat=False, shuffle_mb=0
)
# 生成用于优化迭代的目标图像(组)
print('Projecting image "%s"...' % os.path.basename(src_file))
# 取下一个minibatch=1作为Numpy数组
images, _labels = dataset_obj.get_minibatch_np(1)
# 把images的取值从[0. 255]区间调整到[-1, 1]区间
images = misc.adjust_dynamic_range(images, [0, 255], [-1, 1])
# Projector初始化:start
proj.start(images)
if video:
video_dir = '%s/video' % tmp_dir
os.makedirs(video_dir, exist_ok=True)
while proj.get_cur_step() < proj.num_steps:
print('\r%d / %d ... ' % (proj.get_cur_step(), proj.num_steps), end='', flush=True)
# Projector优化迭代:step
proj.step()
# 如果配置了video选项,将优化过程图像存入./ stylegan2 - tmp / video
if video:
filename = '%s/%08d.png' % (video_dir, proj.get_cur_step())
misc.save_image_grid(proj.get_images(), filename, drange=[-1,1])
print('\r%-30s\r' % '', end='', flush=True)
# 在目的地目录中保存图像,保存dlatents文件
os.makedirs(dst_dir, exist_ok=True)
filename = os.path.join(dst_dir, os.path.basename(src_file)[:-4] + '.png')
misc.save_image_grid(proj.get_images(), filename, drange=[-1,1])
filename = os.path.join(dst_dir, os.path.basename(src_file)[:-4] + '.npy')
np.save(filename, proj.get_dlatents()[0])
def render_video(src_file, dst_dir, tmp_dir, num_frames, mode, size, fps, codec, bitrate):
import PIL.Image
import moviepy.editor
def render_frame(t):
frame = np.clip(np.ceil(t * fps), 1, num_frames)
image = PIL.Image.open('%s/video/%08d.png' % (tmp_dir, frame))
if mode == 1:
canvas = image
else:
canvas = PIL.Image.new('RGB', (2 * src_size, src_size))
canvas.paste(src_image, (0, 0))
canvas.paste(image, (src_size, 0))
if size != src_size:
canvas = canvas.resize((mode * size, size), PIL.Image.LANCZOS)
return np.array(canvas)
src_image = PIL.Image.open(src_file)
src_size = src_image.size[1]
duration = num_frames / fps
filename = os.path.join(dst_dir, os.path.basename(src_file)[:-4] + '.mp4')
video_clip = moviepy.editor.VideoClip(render_frame, duration=duration)
video_clip.write_videofile(filename, fps=fps, codec=codec, bitrate=bitrate)
def main():
# 解析命令行参数
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Project real-world images into StyleGAN2 latent space')
parser.add_argument('src_dir', help='Directory with aligned images for projection')
parser.add_argument('dst_dir', help='Output directory')
parser.add_argument('--tmp-dir', default='./stylegan2-tmp', help='Temporary directory for tfrecords and video frames')
parser.add_argument('--network-pkl', default='gdrive:networks/stylegan2-ffhq-config-f.pkl', help='StyleGAN2 network pickle filename')
parser.add_argument('--vgg16-pkl', default='https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1N2-m9qszOeVC9Tq77WxsLnuWwOedQiD2', help='VGG16 network pickle filename')
parser.add_argument('--num-steps', type=int, default=1000, help='Number of optimization steps')
parser.add_argument('--initial-learning-rate', type=float, default=0.1, help='Initial learning rate')
parser.add_argument('--initial-noise-factor', type=float, default=0.05, help='Initial noise factor')
parser.add_argument('--verbose', type=bool, default=False, help='Verbose output')
parser.add_argument('--video', type=bool, default=False, help='Render video of the optimization process')
parser.add_argument('--video-mode', type=int, default=1, help='Video mode: 1 for optimization only, 2 for source + optimization')
parser.add_argument('--video-size', type=int, default=1024, help='Video size (height in px)')
parser.add_argument('--video-fps', type=int, default=25, help='Video framerate')
parser.add_argument('--video-codec', default='libx264', help='Video codec')
parser.add_argument('--video-bitrate', default='5M', help='Video bitrate')
args = parser.parse_args()
print('Loading networks from "%s"...' % args.network_pkl)
_G, _D, Gs = pretrained_networks.load_networks(args.network_pkl)
# 调用Projector
proj = projector.Projector(
vgg16_pkl = args.vgg16_pkl,
num_steps = args.num_steps,
initial_learning_rate = args.initial_learning_rate,
initial_noise_factor = args.initial_noise_factor,
verbose = args.verbose
)
# 为Projector设定StyleGAN2网络模型
proj.set_network(Gs)
src_files = sorted([os.path.join(args.src_dir, f) for f in os.listdir(args.src_dir) if f[0] not in '._'])
# 遍历源文件目录下的所有图片
for src_file in src_files:
# 调用project_image
project_image(proj, src_file, args.dst_dir, args.tmp_dir, video=args.video)
# 如果配置了video选项,调用render_video,将优化过程图像写入视频流
if args.video:
render_video(
src_file, args.dst_dir, args.tmp_dir, args.num_steps, args.video_mode,
args.video_size, args.video_fps, args.video_codec, args.video_bitrate
)
shutil.rmtree(args.tmp_dir)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
(完)