利用透视变换完成车牌图像校正
1.透视变换原理:
可以看大牛的博客
图像几何变换之透视变换点击打开链接
warpPerspective函数点击打开链接
2.OpenCV实现车牌图像校正
在车牌识别之前,一般都需要对车牌图像进行校正,校正的图像便于后续字符分割。
#include
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
//载入原图像
cv::Mat src = cv::imread("C:\\Users\\dell\\Desktop\\车牌.jpg", 1);
if (src.empty())
{
cout << "原图像载入失败!" << endl;
return -1;
}
//取车牌四边形四个顶点
cv::Point2f srcPts[4];
srcPts[0] = cv::Point2f(318, 273); //左上
srcPts[1] = cv::Point2f(316, 313); //左下
srcPts[2] = cv::Point2f(478, 290); //右上
srcPts[3] = cv::Point2f(474, 333); //右下
//计算原图中四个点的横纵坐标最大值小值,考虑位置特点,无需一一比较
int MinX = std::min(srcPts[0].x, srcPts[1].x);
int MaxX = std::max(srcPts[2].x, srcPts[3].x);
int MinY = std::min(srcPts[0].y, srcPts[2].y);
int MaxY = std::max(srcPts[1].y, srcPts[3].y);
//根据最大最小坐标值设定目标图像中的矩形四个顶点,注意对应关系
cv::Point2f dstPts[4];
dstPts[0] = cv::Point2f(MinX, MinY);
dstPts[1] = cv::Point2f(MinX, MaxY);
dstPts[2] = cv::Point2f(MaxX, MinY);
dstPts[3] = cv::Point2f(MaxX, MaxY);
//计算透视变换矩阵
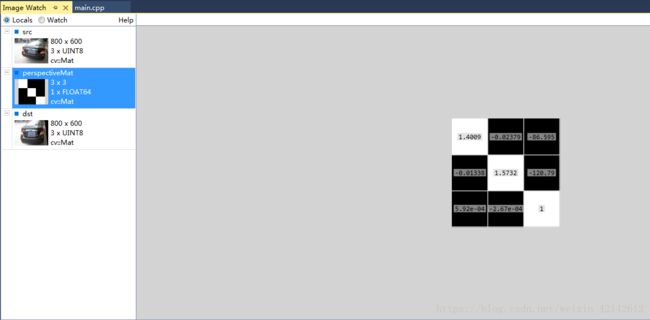
cv::Mat perspectiveMat = getPerspectiveTransform(srcPts, dstPts);
//对原图进行透视变换,完成车牌校正
cv::Mat dst;
cv::warpPerspective(src, dst, perspectiveMat, src.size());
return 0;
} 效果对比:
原图(此图在百度搜索获得,并非自己实物拍摄)
经过透视变换后的图
计算出的透视变换矩阵
3.相关函数解析
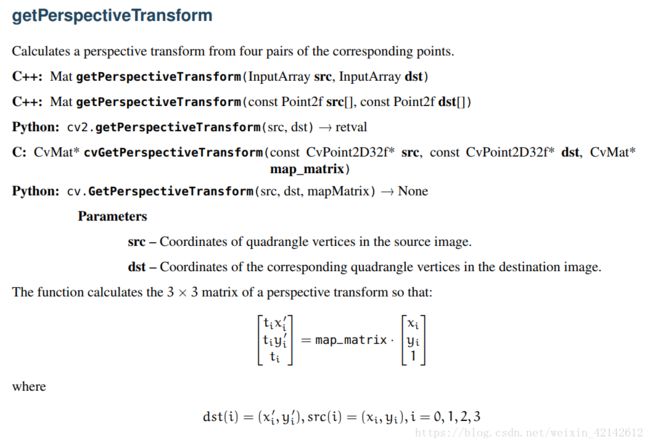
(1)getPerspectiveTransform函数
D:\OpenCV2.4.10\opencv\sources\modules\imgproc\include\opencv2\imgproc\imgproc.hpp函数声明:
//! returns 3x3 perspective transformation for the corresponding 4 point pairs.
CV_EXPORTS Mat getPerspectiveTransform( const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[] );函数说明:
输入参数:
src-原图四边形的四个顶点
dst-目标图像中对应的四个顶点
返回值:
Mat类型, 3*3的透视变换矩阵
注意输入类型必须为Point2f。
D:\OpenCV2.4.10\opencv\sources\modules\imgproc\src\imgwarp.cpp函数实现:
/* Calculates coefficients of perspective transformation
* which maps (xi,yi) to (ui,vi), (i=1,2,3,4):
*
* c00*xi + c01*yi + c02
* ui = ---------------------
* c20*xi + c21*yi + c22
*
* c10*xi + c11*yi + c12
* vi = ---------------------
* c20*xi + c21*yi + c22
*
* Coefficients are calculated by solving linear system:
* / x0 y0 1 0 0 0 -x0*u0 -y0*u0 \ /c00\ /u0\
* | x1 y1 1 0 0 0 -x1*u1 -y1*u1 | |c01| |u1|
* | x2 y2 1 0 0 0 -x2*u2 -y2*u2 | |c02| |u2|
* | x3 y3 1 0 0 0 -x3*u3 -y3*u3 |.|c10|=|u3|,
* | 0 0 0 x0 y0 1 -x0*v0 -y0*v0 | |c11| |v0|
* | 0 0 0 x1 y1 1 -x1*v1 -y1*v1 | |c12| |v1|
* | 0 0 0 x2 y2 1 -x2*v2 -y2*v2 | |c20| |v2|
* \ 0 0 0 x3 y3 1 -x3*v3 -y3*v3 / \c21/ \v3/
*
* where:
* cij - matrix coefficients, c22 = 1
*/
cv::Mat cv::getPerspectiveTransform( const Point2f src[], const Point2f dst[] )
{
Mat M(3, 3, CV_64F), X(8, 1, CV_64F, M.data);
double a[8][8], b[8];
Mat A(8, 8, CV_64F, a), B(8, 1, CV_64F, b);
for( int i = 0; i < 4; ++i )
{
a[i][0] = a[i+4][3] = src[i].x;
a[i][1] = a[i+4][4] = src[i].y;
a[i][2] = a[i+4][5] = 1;
a[i][3] = a[i][4] = a[i][5] =
a[i+4][0] = a[i+4][1] = a[i+4][2] = 0;
a[i][6] = -src[i].x*dst[i].x;
a[i][7] = -src[i].y*dst[i].x;
a[i+4][6] = -src[i].x*dst[i].y;
a[i+4][7] = -src[i].y*dst[i].y;
b[i] = dst[i].x;
b[i+4] = dst[i].y;
}
solve( A, B, X, DECOMP_SVD );
((double*)M.data)[8] = 1.;
return M;
}(2)warpPerspective函数
函数声明:
//! warps the image using perspective transformation
CV_EXPORTS_W void warpPerspective( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,
InputArray M, Size dsize,
int flags=INTER_LINEAR,
int borderMode=BORDER_CONSTANT,
const Scalar& borderValue=Scalar());函数说明:
参数说明:
InputArray src 原图像。
OutputArray dst 目标图像,其类型和src一致,其size由后续参数dsize设定。
InputArray M 透视变换矩阵,3*3。
Size dsize 目标图像的size。
int flags 插值方法标识符,默认为INTER_LINEAR,也就是默认双线性插值。
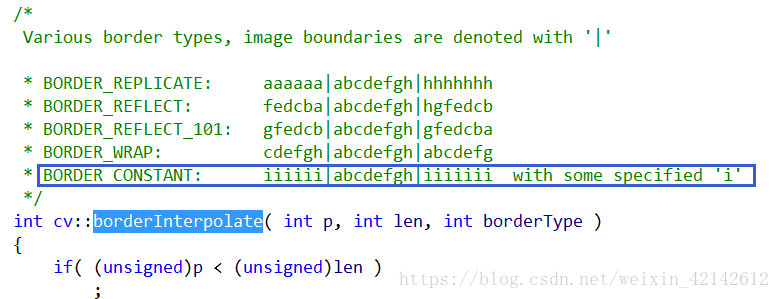
int borderMode 边界扩展方式,默认为BORDER_CONSTANT,也就是默认用指定值填充边界,该值由后续参数borderValue设定。
const Scalar& borderValue 边界填充值,默认为0。
函数实现:
void cv::warpPerspective( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, InputArray _M0,
Size dsize, int flags, int borderType, const Scalar& borderValue )
{
Mat src = _src.getMat(), M0 = _M0.getMat();
_dst.create( dsize.area() == 0 ? src.size() : dsize, src.type() );
Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
CV_Assert( src.cols > 0 && src.rows > 0 );
if( dst.data == src.data )
src = src.clone();
double M[9];
Mat matM(3, 3, CV_64F, M);
int interpolation = flags & INTER_MAX;
if( interpolation == INTER_AREA )
interpolation = INTER_LINEAR;
CV_Assert( (M0.type() == CV_32F || M0.type() == CV_64F) && M0.rows == 3 && M0.cols == 3 );
M0.convertTo(matM, matM.type());
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if( tegra::warpPerspective(src, dst, M, flags, borderType, borderValue) )
return;
#endif
if( !(flags & WARP_INVERSE_MAP) )
invert(matM, matM);
/*
#if defined (HAVE_IPP) && (IPP_VERSION_MAJOR >= 7)
int depth = src.depth();
int channels = src.channels();
if( ( depth == CV_8U || depth == CV_16U || depth == CV_32F ) &&
( channels == 1 || channels == 3 || channels == 4 ) &&
( borderType == cv::BORDER_TRANSPARENT || borderType == cv::BORDER_CONSTANT ) )
{
int type = src.type();
ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc ippFunc =
type == CV_8UC1 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_8u_C1R :
type == CV_8UC3 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_8u_C3R :
type == CV_8UC4 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_8u_C4R :
type == CV_16UC1 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_16u_C1R :
type == CV_16UC3 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_16u_C3R :
type == CV_16UC4 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_16u_C4R :
type == CV_32FC1 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_32f_C1R :
type == CV_32FC3 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_32f_C3R :
type == CV_32FC4 ? (ippiWarpPerspectiveBackFunc)ippiWarpPerspectiveBack_32f_C4R :
0;
int mode =
flags == INTER_LINEAR ? IPPI_INTER_LINEAR :
flags == INTER_NEAREST ? IPPI_INTER_NN :
flags == INTER_CUBIC ? IPPI_INTER_CUBIC :
0;
if( mode && ippFunc )
{
double coeffs[3][3];
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
for( int j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
{
coeffs[i][j] = matM.at(i, j);
}
}
bool ok;
Range range(0, dst.rows);
IPPwarpPerspectiveInvoker invoker(src, dst, coeffs, mode, borderType, borderValue, ippFunc, &ok);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
if( ok )
return;
}
}
#endif
*/
Range range(0, dst.rows);
warpPerspectiveInvoker invoker(src, dst, M, interpolation, borderType, borderValue);
parallel_for_(range, invoker, dst.total()/(double)(1<<16));
}