ceph-iscsi原理及部署
作者:吴业亮
博客:wuyeliang.blog.csdn.net
一.架构及方案
- Ceph Block框架
iSCSI gateway的实现主要有TGT && LIO两种方式。
- TGT
TGT:Linux target framework,为创建、维护SCSI target 驱动(包括iSCSI、FC、SRP等)提供支持。
- 工作在用户空间;
- 在Linux 2.6.38 版本后(含),内核集成了 Linux-IO Target。
在ceph集成原生iscsi之前,通常使用基于用户空间的"scsi-target-utils"套件实现tgt。
基于centos7.x系列,安装"scsi-target-utils"套件后,iscsi并不支持ceph rbd后端存储(通过"tgtadm --lld iscsi --mode system --op show"查看),主要原因是redhat针对套件屏蔽了支持ceph rbd后端存储的代码。
解决方案:
通过"rbd map xxx"将ceph rbd挂载到本地后,再通过iscsi tgt的"direct-store"模式发布ceph块存储。
方案缺点:
"rbd map xxx"挂载ceph rbd是通过"ceph rbd kernel module"的形式,tgt在用户空间实现,导致发布的ceph rbd在内核态与用户态之间频繁切换,影响性能。
- LIO
LIO:Linux-IO Target,用软件实现各种SCIS Target。
- 工作在内核空间;
- 支持较多传输协议,如Fibre Channel(Qlogic,linux3.5)、FCoE(linux3.0)、iSCSI(linux 3.1)、iSER (Mellanox InfiniBand,linux3.10), SRP (Mellanox InfiniBand,linux3.3), USB等;
- 对 iSCSI RFC 规范的支持非常好,包括完整的错误恢复都有支持;
- 从内核 3.17 开始引入用户态后端支持,即 TCMU(Target Core Module in Userspace)
- 在Linux 2.6.38 版本后(含),内核集成了 Linux-IO Target。
本文主要介绍基于LIO的ceph原生iscsi 实现方式,LIO利用用户空间直通(即TCMU)与ceph的librbd库进行交互(tcmu-runner处理LIO TCM后端存储的用户空间端的守护进程,在内核之上多了一个用户态的驱动层,这样只需要根据tcmu的标准来对接接口即可,而不用去直接与内核进行交互),并将rbd image暴露给iSCSI客户端。
二、前提条件
1、版本
- Ceph Luminous 版本的集群或者更新的版本
- RHEL/CentOS 7.5或者Linux kernel v4.16或者更新版本的内核
- 其他控制软件
targetcli-2.1.fb47 or newer package
python-rtslib-2.1.fb68 or newer package
tcmu-runner-1.4.0 or newer package
ceph-iscsi-3.2 or newer package
2、针对ceph-mon或osd节点,并没有特殊的iscsi-gateway参数选项,但降低若干默认的检测osd宕机时间,可以有效降低initiator的连接超时。可在ceph-mon节点修改ceph.conf文件后分发到所有节点,如:
方法一:
# 新增参数
[osd]
osd client watch timeout = 15
osd heartbeat grace = 20
osd heartbeat interval = 5
重启服务
systemctl restart ceph.target
方法二:
命令修改方法
# ceph tell osd.* config set osd_client_watch_timeout 15
# ceph tell osd.* config set osd_heartbeat_grace 20
# ceph tell osd.* config set osd_heartbeat_interval 5
验证方法:
[root@node2 ~]# ceph daemon osd.0 config get osd_client_watch_timeout
{
"osd_client_watch_timeout": "15"
}
[root@node2 ~]# ceph daemon osd.0 config get osd_heartbeat_grace
{
"osd_heartbeat_grace": "20"
}
[root@node2 ~]# ceph daemon osd.0 config get osd_heartbeat_interval
{
"osd_heartbeat_interval": "5"
}
三、自动化部署
环境
1、通过ceph-ansible安装
# yum install ceph-ansible
其他ceph-ansible具体安装参见
https://wuyeliang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/105344968
2、修改/etc/ansible/hosts,新增需要安装iscsi-gateway的节点主机名
[iscsigws]
node1
node2
node3
3、安装
# cd /usr/share/ceph-ansible
# ansible-playbook site.yml --limit iscsigws
4、查看状态
# ceph -s
cluster:
id: 8789218f-5fca-4727-9c74-aff3c2cebeab
health: HEALTH_OK
services:
mon: 3 daemons, quorum node1,node2,node3 (age 14m)
mgr: node2(active, since 14m), standbys: node1, node3
mds: cephfs:1 {0=node2=up:active} 2 up:standby
osd: 48 osds: 48 up (since 14m), 48 in (since 65m)
rgw: 3 daemons active (node1.rgw0, node2.rgw0, node3.rgw0)
tcmu-runner: 2 daemons active (node1:wyl/disk, node2:wyl/disk)
data:
pools: 8 pools, 2200 pgs
objects: 43.01k objects, 107 GiB
usage: 65 GiB used, 9.3 TiB / 9.4 TiB avail
pgs: 2200 active+clean
io:
client: 3.0 KiB/s rd, 2 op/s rd, 0 op/s wr
# gwcli ls
Warning: Could not load preferences file /root/.gwcli/prefs.bin.
o- / .................................................................................................... [...]
o- cluster .................................................................................... [Clusters: 1]
| o- ceph ....................................................................................... [HEALTH_OK]
| o- pools ..................................................................................... [Pools: 8]
| | o- .rgw.root ......................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 1536K]
| | o- cephfs_data ....................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 0.00Y]
| | o- cephfs_metadata ................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 1536K]
| | o- default.rgw.control ............................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 0.00Y]
| | o- default.rgw.log ................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 0.00Y]
| | o- default.rgw.meta ................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 384K]
| | o- rbd ................................................ [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 192K]
| | o- wyl ........................................... [(x3), Commit: 0.00Y/3089638M (0%), Used: 17388864K]
| o- topology .......................................................................... [OSDs: 48,MONs: 3]
o- disks .................................................................................. [0.00Y, Disks: 0]
o- iscsi-targets .......................................................... [DiscoveryAuth: None, Targets: 0
5、后面具体的服务为rbd-target-api,可以通过systemctl来管理
# systemctl rbd-target-api
cd /usr/share/ceph-ansible/
ansible-playbook purge_gateways.yml
四、手动部署环境
1、安装软件
配置源
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# cat ceph-iscsi.repo
[ceph-iscsi]
name=ceph-iscsi noarch packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/ceph-iscsi/3/rpm/el7/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
type=rpm-md
[ceph-iscsi-source]
name=ceph-iscsi source packages
baseurl=http://download.ceph.com/ceph-iscsi/3/rpm/el7/SRPMS
enabled=0
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://download.ceph.com/keys/release.asc
type=rpm-md
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# cat python-rtslib-dev.repo
[python-rtslib]
name=python-rtslib packages for $basearch
baseurl=https://2.chacra.ceph.com/r/python-rtslib/master/67eb1605c697b6307d8083b2962f5170db13d306/centos/7/flavors/default/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
[python-rtslib-noarch]
name=python-rtslib noarch packages
baseurl=https://2.chacra.ceph.com/r/python-rtslib/master/67eb1605c697b6307d8083b2962f5170db13d306/centos/7/flavors/default/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
[python-rtslib-source]
name=python-rtslib source packages
baseurl=https://2.chacra.ceph.com/r/python-rtslib/master/67eb1605c697b6307d8083b2962f5170db13d306/centos/7/flavors/default/SRPMS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# cat tcmu-runner-dev.repo
[tcmu-runner]
name=tcmu-runner packages for $basearch
baseurl=https://1.chacra.ceph.com/r/tcmu-runner/master/9c84f7a4348ac326ac269fbdda507953dba6ec2c/centos/7/flavors/default/$basearch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
[tcmu-runner-noarch]
name=tcmu-runner noarch packages
baseurl=https://1.chacra.ceph.com/r/tcmu-runner/master/9c84f7a4348ac326ac269fbdda507953dba6ec2c/centos/7/flavors/default/noarch
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
[tcmu-runner-source]
name=tcmu-runner source packages
baseurl=https://1.chacra.ceph.com/r/tcmu-runner/master/9c84f7a4348ac326ac269fbdda507953dba6ec2c/centos/7/flavors/default/SRPMS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
type=rpm-md
ceph相关的ISCSI软件包可以从redhat通过的源代码进行编译或者下载centos已经编译好的。
# yum install ceph-iscsi tcmu-runner targetcli python-rtslib -y
# ceph osd pool create rbd 150 150
# ceph osd pool application enable rbd rbd --yes-i-really-mean-it
2 创建配置文件
创建/etc/ceph/iscsi-gateway.cfg ,此文件主要设置iscsi服务的网关。
[config]
# Name of the Ceph storage cluster. A suitable Ceph configuration file allowing
# access to the Ceph storage cluster from the gateway node is required, if not
# colocated on an OSD node.
cluster_name = ceph
# Place a copy of the ceph cluster's admin keyring in the gateway's /etc/ceph
# drectory and reference the filename here
gateway_keyring = ceph.client.admin.keyring
# API settings.
# The API supports a number of options that allow you to tailor it to your
# local environment. If you want to run the API under https, you will need to
# create cert/key files that are compatible for each iSCSI gateway node, that is
# not locked to a specific node. SSL cert and key files *must* be called
# 'iscsi-gateway.crt' and 'iscsi-gateway.key' and placed in the '/etc/ceph/' directory
# on *each* gateway node. With the SSL files in place, you can use 'api_secure = true'
# to switch to https mode.
# To support the API, the bear minimum settings are:
api_secure = false
# Additional API configuration options are as follows, defaults shown.
# api_user = admin
# api_password = admin
# api_port = 5001
trusted_ip_list = 192.168.70.81,192.168.70.82,192.168.70.83
3、 同步文件到其他节点
# scp /etc/ceph/iscsi-gateway.cfg node2:/etc/ceph
# scp /etc/ceph/iscsi-gateway.cfg node3:/etc/ceph
4、 启动API服务
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable rbd-target-api
# systemctl start rbd-target-api
# systemctl status rbd-target-api
● rbd-target-api.service - Ceph iscsi target configuration API
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rbd-target-api.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-05-31 11:35:04 CST; 4s ago
Main PID: 25372 (rbd-target-api)
CGroup: /system.slice/rbd-target-api.service
└─25372 /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/rbd-target-api
May 31 11:35:04 node1 systemd[1]: Started Ceph iscsi target configuration API.
May 31 11:35:04 node1 systemd[1]: Starting Ceph iscsi target configuration API...
May 31 11:35:05 node1 rbd-target-api[25372]: Started the configuration object watcher
May 31 11:35:05 node1 rbd-target-api[25372]: Checking for config object changes every 1s
May 31 11:35:05 node1 rbd-target-api[25372]: * Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/
5、配置ISCSI服务
5.1 创建target
# gwcli
/> cd iscsi-targets
/iscsi-target> create iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw
/iscsi-targets> cd iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw/
/iscsi-target...-gw:iscsi-igw> cd gateways
5.2 创建ISCSI网关
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node1 192.168.70.81
OS version/package checks have been bypassed
Adding gateway, sync'ing 0 disk(s) and 0 client(s)
ok
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node2 192.168.70.82
OS version/package checks have been bypassed
Adding gateway, sync'ing 0 disk(s) and 0 client(s)
ok
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node3 192.168.70.83
OS version/package checks have been bypassed
Adding gateway, sync'ing 0 disk(s) and 0 client(s)
ok
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> ls
o- gateways .................................................................................................. [Up: 3/3, Portals: 3]
o- node1 .................................................................................................. [192.168.70.81 (UP)]
o- node2 .................................................................................................. [192.168.70.82 (UP)]
o- node3 .................................................................................................. [192.168.70.83 (UP)]
如果操作系统非Centos或redhat,则需要加skipchecks=true参数。
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node1 192.168.70.81 skipchecks=true
遇到问题“The first gateway defined must be the local machine”,必须先创建本地节点
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node1 10.130.70.91
The first gateway defined must be the local machine
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node2 10.130.70.91
Adding gateway, sync'ing 0 disk(s) and 0 client(s)
ok
遇到问题Failed : Gateway creation failed, gateway(s) unavailable:node2(UNKNOWN state),需要三个节点都升级内核,升级内核参见:https://wuyeliang.blog.csdn.net/article/details/67644077
/iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> create node1 10.130.70.90 skipchecks=true
OS version/package checks have been bypassed
Adding gateway, sync'ing 0 disk(s) and 0 client(s)
Failed : Gateway creation failed, gateway(s) unavailable:node2(UNKNOWN state)
遇到问题Is the API server running and in the right mode (http/https)?
注意关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld
5.3 创建RBD image
> /iscsi-target...-igw/gateways> cd /disks
> /disks> create pool=rbd image=disk_1 size=90G
5.4 创建客户端名称
Linux平台可以查看/etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi文件获取InitiatorName。如果修改了默认的名称,必须重启iscsid服务,否则在登录iscsi服务端的时候会报错。
> /disks> cd /iscsi-target/iqn.2003-01.com.redhat.iscsi-gw:iscsi-igw/hosts
> /iscsi-target...eph-igw/hosts> create iqn.1994-05.com.redhat:rh7-client
5.5 设置客户端认证
> /iscsi-target...at:rh7-client> auth username=myiscsiusername password=myiscsipassword
5.6 客户端映射磁盘
/iscsi-target...at:rh7-client> disk add rbd/disk_1
五、windows的多路径连接
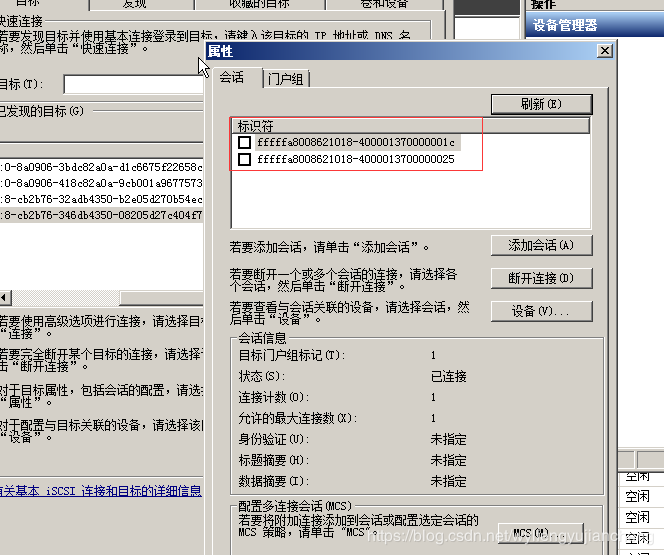
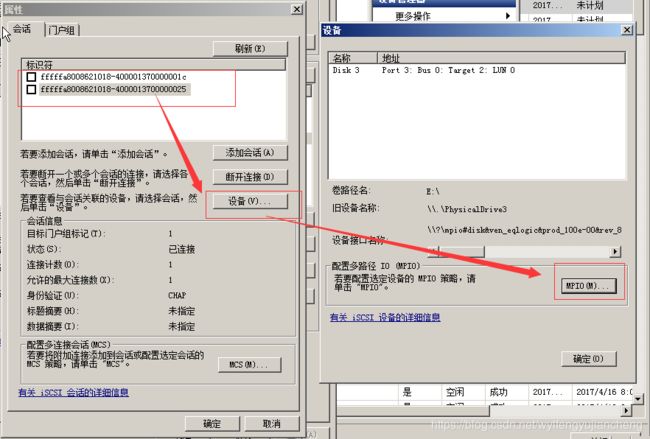
下面分享下Windows下多路径功能配置
如果没有添加MultipathI/O功能,在iSCSI发起程序属性——》设备——》中看到“MPIO”显示会是灰色。

配置MPIO支持ISCSI
此时再查看属性
六.iSCSI initiator
- 安装initiator与multipath工具
- iscsi-initiator-utils是通用initiator套件;
- device-mapper-multipath是多路径工具
# yum install iscsi-initiator-utils device-mapper-multipath -y
- 设置multipath服务,启用multipath服务,生成”/etc/multipath.conf”文件
# mpathconf --enable --with_multipathd y
在”/etc/multipath.conf”文件新增配置,针对LIO后端存储设置多路径ha
devices {
device {
vendor "LIO-ORG"
hardware_handler "1 alua"
path_grouping_policy "failover"
path_selector "queue-length 0"
failback 60
path_checker tur
prio alua
prio_args exclusive_pref_bit
fast_io_fail_tmo 25
no_path_retry queue
}
}
重新加载multinpath服务
# systemctl reload multipathd
- iscsi discovery
1)设置chap认证
# 开启initiator的chap认证,并设置username/password,与iscsi-target设置保持一致;
# CHAP Settings部分,涉及57/61/62行
# vim /etc/iscsi/iscsid.conf
node.session.auth.authmethod = CHAP
node.session.auth.username = iscsiname
node.session.auth.password = iscsipassword
2)设置initiatoe-name
# 设置initiator-name,保持与iscsi-target设置的initiator-name一致
# vim /etc/iscsi/initiatorname.iscsi
InitiatorName=iqn.2020-04.192.168.70.50:iscsi-initiator
3)发现iscsi-target
# 发现iscsi存储:iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p ISCSI_IP,ISCSI_IP默认采用3260端口;
# 查看iscsi发现记录:iscsiadm -m node
# 删除iscsi发现记录:iscsiadm -m node -o delete -T LUN_NAME -p ISCSI_IP
# iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p 192.168.70.57
4)登陆iscsi-target
# 登录iscsi存储:iscsiadm -m node -T LUN_NAME -p ISCSI_IP -l
# 登出iscsi存储:iscsiadm -m node -T LUN_NAME -p ISCSI_IP -u
# 显示会话情况:iscsiadm -m session
# iscsiadm -m node -T iqn.2018-09.192.168.70.5x:iscsi-gw -l
# 1个后端存储,通过3条路径连接
# multipath -ll
# 通过多路径连接后端存储,生成多个盘符;
# 通过multipath服务汇聚,生成盘符/dev/mapper/mpathx,mount时间直接使用;
# 或:lsscsi
# fdisk -l
- mount验证
# mkfs.xfs /dev/mapper/mpatha
# 挂载分区
# mount /dev/mapper/mpatha /mnt
# 查看挂载情况
# df -Th
- 修改/etc/fstab设置开机启动挂载
/dev/mapper/mpatha1 /mnt xfs noatime,_netdev 0 0
参数说明:
# filesystem parameters列设置挂载时间;
# noatime:禁止更新文件与目录的inode访问时间,以获得更快的访问速度;
# _netdev:标识文件系统位于网络上,防止网络启动前挂载
# rbd
参考:
https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rbd/iscsi-target-cli/
https://www.lagou.com/lgeduarticle/43742.html
https://blog.51cto.com/candon123/2125049
https://blog.51cto.com/ityunwei2017/1916244
https://www.cnblogs.com/netonline/p/10432653.html