DICOM:DICOM三大开源库对比分析之“数据加载”
背景:
上一篇博文DICOM:DICOM万能编辑工具之Sante DICOM Editor介绍了DICOM万能编辑工具,在日常使用过程中发现,“只要Sante DICOM Editor打不开的数据,基本可以判定此DICOM文件格式错误(准确率达99.9999%^_^)”。在感叹Sante DICOM Editor神器牛掰的同时,想了解一下其底层是如何实现的。通过日常使用以及阅读软件帮助手册推断其底层依赖库很可能是dcmtk,就如同本人使用dcmtk、fo-dicom、dcm4che3等诸多DICOM开源库遇到的兼容性问题类似,——dcmtk兼容性最强,fo-dicom次之,dcm4che3最差。
问题:
本篇通过对比dcmtk3.6与dcm4che3.x解析同一特殊dicom文件(包含非标准VR的元素)分析dcmtk、dcm4che以及fo-dicom数据加载的兼容性问题。
特殊的dicom文件内容如下:
28 00 20 01 20 20 02 00 30 F8,具体描述如下:
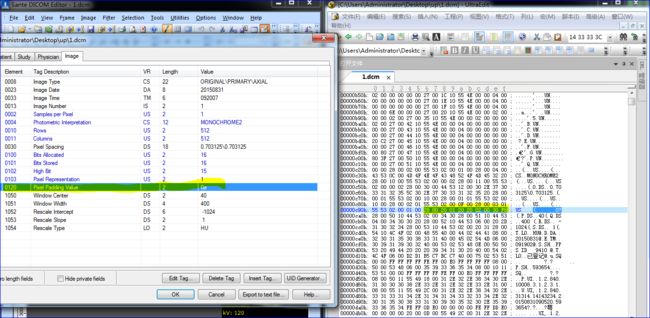
使用dcmtk与fo-dicom加载数据时都未出现错误,例如dcmtk加载数据时的提示如下:
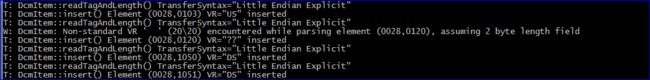
由此可以看出dcmtk已经顺利识别出了非标准VR的元素(0028,0120),并成功加载。
虽然使用fo-dicom加载数据没有出现错误,但是对于上述非标准VR的元素(0028,0120)后的元素未顺利加载,如下图所示:
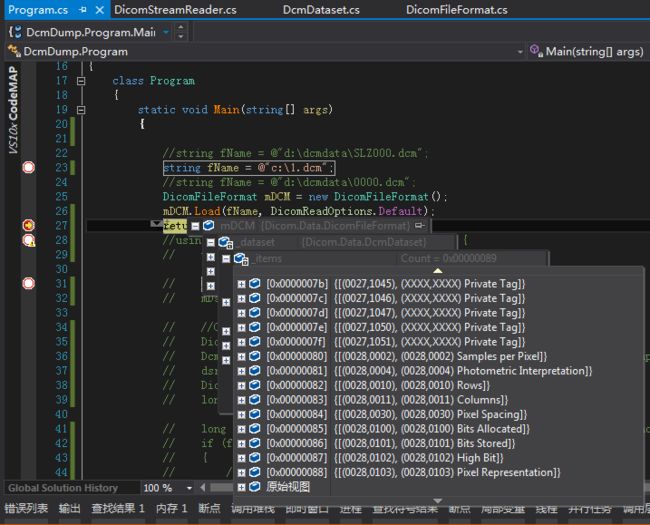
而dcm4che3加载过程中直接弹出了错误,如下所示:
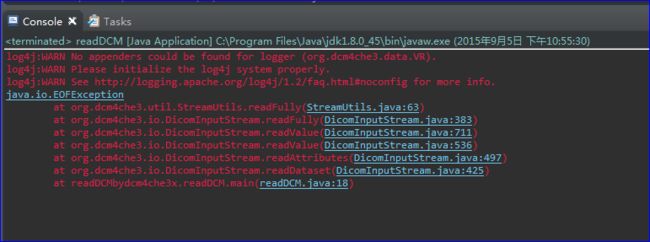
问题分析:
出现该问题的原因是dcm4che3和fo-dicom在解析0028,0120元素时,对于20 20的非标准VR无法识别。下文中将通过分析dcm4che3与dcmtk的源码来定位问题的具体位置并给出解决方案(此处暂时只对比分析了dcm4che3.3.8最新版与dmctk3.6的源码,对于fo-dicom的源码分析待后续整理完成后再补充)。
1. dcmtk3.6源码:
使用dcmtk编写本次数据加载测试工程,简单的示例代码如下:
int main()
{
OFLog::configure(OFLogger::TRACE_LOG_LEVEL);
char* ifname = "c:\\1.dcm";
E_FileReadMode readMode = /*ERM_fileOnly*/ERM_autoDetect;
E_TransferSyntax xfer = EXS_Unknown;
Uint32 maxReadLength = DCM_MaxReadLength;
bool loadIntoMemory = true;
DcmFileFormat dfile;
DcmObject *dset = &dfile;
if (readMode == ERM_dataset) dset = dfile.getDataset();
OFCondition cond = dfile.loadFile(ifname, xfer, EGL_noChange, maxReadLength, readMode);
if (cond.bad())
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}单步调试,可以知道dcmtk加载dicom文件的流程如下:
- 创建DcmMetaInfo、DcmDataset元素
- 分别加载DcmMetaInfo、DcmDataset元素
- 使用DcmItem中的readGroupLength、readTagAndLength、readSubElement逐步加载DcmMetaInfo、DcmDataset的各个子元素。
在DcmItem类中对于非标准VR元素有相应的警告提示信息,
/* if the VR which was read is not a standard VR, print a warning */
if (!vr.isStandard())
{
OFOStringStream oss;
oss << "DcmItem: Non-standard VR '"
<< ((OFstatic_cast(unsigned char, vrstr[0]) < 32) ? ' ' : vrstr[0])
<< ((OFstatic_cast(unsigned char, vrstr[1]) < 32) ? ' ' : vrstr[1]) << "' ("
<< STD_NAMESPACE hex << STD_NAMESPACE setfill('0')
<< STD_NAMESPACE setw(2) << OFstatic_cast(unsigned int, vrstr[0] & 0xff) << "\\"
<< STD_NAMESPACE setw(2) << OFstatic_cast(unsigned int, vrstr[1] & 0xff)
<< ") encountered while parsing element " << newTag << OFStringStream_ends;
OFSTRINGSTREAM_GETSTR(oss, tmpString)
/* encoding of this data element might be wrong, try to correct it */
if (dcmAcceptUnexpectedImplicitEncoding.get())
{
DCMDATA_WARN(tmpString << ", trying again with Implicit VR Little Endian");
/* put back read bytes to input stream ... */
inStream.putback();
bytesRead = 0;
/* ... and retry with Implicit VR Little Endian transfer syntax */
return readTagAndLength(inStream, EXS_LittleEndianImplicit, tag, length, bytesRead);
} else {
DCMDATA_WARN(tmpString << ", assuming " << (vr.usesExtendedLengthEncoding() ? "4" : "2")
<< " byte length field");
}
OFSTRINGSTREAM_FREESTR(tmpString)
}
/* set the VR which was read in the above created tag object. */
newTag.setVR(vr);
/* increase counter by 2 */
bytesRead += 2;在警告后,对于非标准VR元素的处理过程如下:
/* read the value in the length field. In some cases, it is 4 bytes wide, in other */
/* cases only 2 bytes (see DICOM standard part 5, section 7.1.1) */
if (xferSyn.isImplicitVR() || nxtobj == EVR_na) //note that delimitation items don't have a VR
{
inStream.read(&valueLength, 4); //length field is 4 bytes wide
swapIfNecessary(gLocalByteOrder, byteOrder, &valueLength, 4, 4);
bytesRead += 4;
} else { //the transfer syntax is explicit VR
DcmVR vr(newTag.getEVR());
if (vr.usesExtendedLengthEncoding())
{
Uint16 reserved;
inStream.read(&reserved, 2); // 2 reserved bytes
inStream.read(&valueLength, 4); // length field is 4 bytes wide
swapIfNecessary(gLocalByteOrder, byteOrder, &valueLength, 4, 4);
bytesRead += 6;
} else {
Uint16 tmpValueLength;
inStream.read(&tmpValueLength, 2); // length field is 2 bytes wide
swapIfNecessary(gLocalByteOrder, byteOrder, &tmpValueLength, 2, 2);
bytesRead += 2;
valueLength = tmpValueLength;
}
}由上述代码可知,0028,0120的VR=20,20,被dcmtk解析为 EVR_UNKNOWN2B类型,如同代码注释中所描述:
/// used internally for elements with unknown VR with 2-byte length field in explicit VR
EVR_UNKNOWN2B
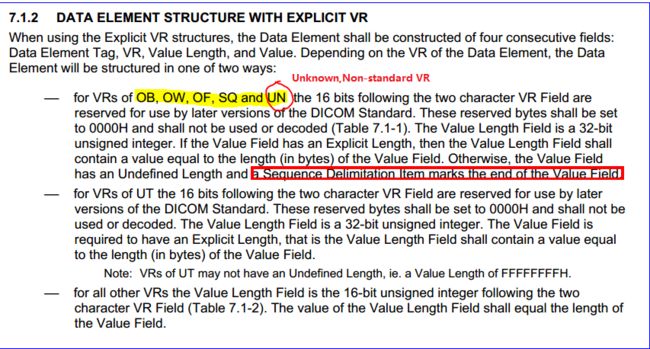
DICOM标准PS5的7.1.2有对于非标准VR的相关描述,如下:
2. dcm4che3.3.8源码:
再对比dcm4che3.3.8的源码,单步调试发现,对于0028,0120的VR=20,20,被dcmtk直接标记为UN类型,
public static VR valueOf(int code) {
try {
VR vr = VALUE_OF[indexOf(code)];
if (vr != null)
return vr;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {}
LOG.warn("Unrecogniced VR code: {0}H - treat as UN",
Integer.toHexString(code));
return UN;
}并且在dcm4che3中对于UN类型定义为
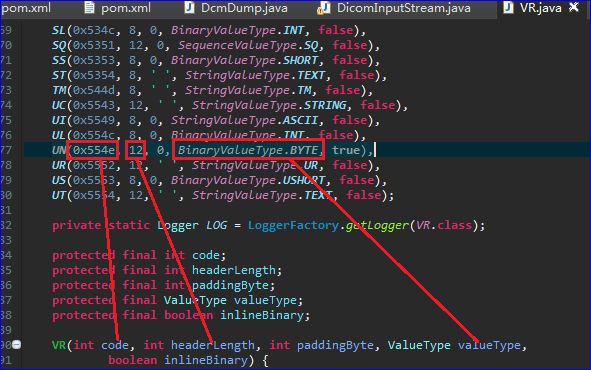
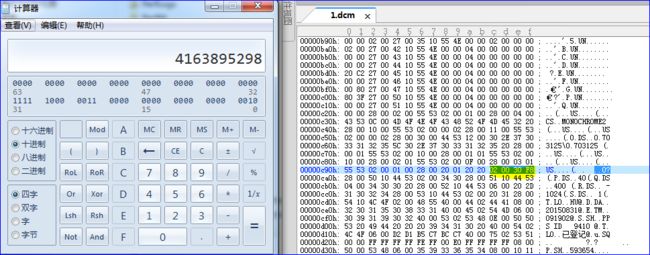
此处UN类型是参照上述截图中DICOM3.0标准对于VR=UN(unknown)类型的标签约束来定义的,即,其VR字段应该是四个字节。然而此处0028,0120的VR=20,20后的Value Length只有两个字节02 00。因此导致dcm4che3在加载0028,0120元素时,将其长度错误地解析为4163895298,即十六进制的F8 30 00 02,如下图所示:
解决方案:
至此我们找到了dcm4che3错误解析0028,0120的VR=20,20非标准VR元素的原因。对于这种非标准VR不能统一当做VR.UN类型进行处理,而应该根据其后续的Value Length的具体长度为2或者4来进行分类处理(关于该问题后续博文会继续深入剖析,请注意),需要修改的地方有两处:
1. 正确解析Non-standard VR:
//VR.java,Line 110
public static VR valueOf(int code) {
try {
VR vr = VALUE_OF[indexOf(code)];
if (vr != null)
return vr;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {}
LOG.warn("Unrecogniced VR code: {0}H - treat as UN",
Integer.toHexString(code));
//return UN;
LOG.warn("zssure:to solve non-standard VR,Unrecogniced VR code: {0}H - treat as UN",
Integer.toHexString(code));
return null;//zssure:to solve non-standard VR
}
2. 正确读取Non-standard VR的VL:
//DicomInputStream.java Line 386
public int readHeader() throws IOException {
byte[] buf = buffer;
tagPos = pos;
readFully(buf, 0, 8);
switch(tag = ByteUtils.bytesToTag(buf, 0, bigEndian)) {
case Tag.Item:
case Tag.ItemDelimitationItem:
case Tag.SequenceDelimitationItem:
vr = null;
break;
default:
if (explicitVR) {
vr = VR.valueOf(ByteUtils.bytesToVR(buf, 4));
//zssure:to solve non-standard VR
//referred:dcmtk/dcitem.cc/readTagAndLength,Line 970
if(vr == null)
{
length = ByteUtils.bytesToUShort(buf, 6, bigEndian);
return tag;
}
//zssure:end
if (vr.headerLength() == 8) {
length = ByteUtils.bytesToUShort(buf, 6, bigEndian);
return tag;
}
readFully(buf, 4, 4);
} else {
vr = VR.UN;
}
}
length = ByteUtils.bytesToInt(buf, 4, bigEndian);
return tag;
}测试文件下载:
本文中使用的测试数据已经上传到了我Github的CSDN仓库中,可自行下载,为了保护患者隐私已经进行了匿名化处理。
Download Non-standard VR test dcm file
后续博文介绍:
1. 由dcm4che3.x库看Java流操作之”流的拷贝”
2. Eclipse自动编译dcm4che3.x源码
3. DICOM三大开源库对比分析之“数据加载”(续)
作者:[email protected]
时间:2015-09-05