A*算法
1.什么是A*算法?
A*算法是静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接的搜索方法,但是它非常耗时,遍历周围所有节点,查找出最优路径,下面为我再Mono中写的四个脚本供大家参考。
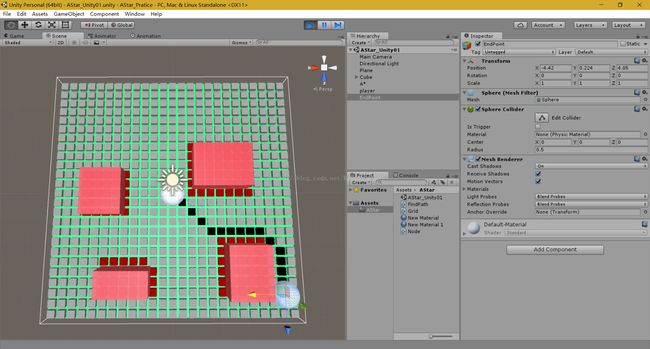
1.首先搭建戏台子。第一步打开unity,创建一个Plane,四个Cube,两个Sphere,一个改名为Player,一个为EndPoint,其中一个Cube作为父物体,,把另外三个Cube设为其子物体,并且给这个父物体Cube
2.开始写脚本
A*算法是居于网格的导航,所以必须用到Unity中自带的Grid和Node组件
第1个脚本
挂载对象:不挂载
作用:供其他脚本调用
注意:不继承Mono
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class Node
{
public bool _canWalk;
//该节点是否可以通过
public Vector3 _worldPos;
//该节点的位置
public int _gridX, _gridY;
//该网格的索引,取得节点
public int gCost;
//起始点与该节点的长度
public int hCost;
//目标点与该节点的长度
public int fCost {//f的值是G和H的和,该节点和该路径的评分
get { return gCost + hCost; }
}
public Node parent;
//指向父对象的指针
public Node (bool CanWalk, Vector3 Position, int x, int y)//构造函数
{
_canWalk = CanWalk;
_worldPos = Position;
_gridX = x;
_gridY = y;
}
}
using System.Collections;
public class Node
{
public bool _canWalk;
//该节点是否可以通过
public Vector3 _worldPos;
//该节点的位置
public int _gridX, _gridY;
//该网格的索引,取得节点
public int gCost;
//起始点与该节点的长度
public int hCost;
//目标点与该节点的长度
public int fCost {//f的值是G和H的和,该节点和该路径的评分
get { return gCost + hCost; }
}
public Node parent;
//指向父对象的指针
public Node (bool CanWalk, Vector3 Position, int x, int y)//构造函数
{
_canWalk = CanWalk;
_worldPos = Position;
_gridX = x;
_gridY = y;
}
}
第2个脚本
挂载对象:空物体A*上
作用:合适的节点加入列表,不合适的点剔除列表
注意:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Grid : MonoBehaviour
{
private Node[,] grid;
//定义grid二维数组
public Vector2 gridSize;
//二维向量保存网格的大小
public float nodeRadius;
//设定每个节点的半径
private float nodeDiameter;
//节点的直径
public LayerMask WhatLayer;
//节点的标签
public int gridCntX, gridCntY;
//保存每个方向上格子的个数
public Transform player;
// 玩家的引用
public List<Node> path = new List<Node> ();
//保存路径
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
nodeDiameter = nodeRadius * 2;//计算节点的直径
gridCntX = Mathf.RoundToInt (gridSize.x / nodeDiameter);//横轴需要多少个格子
gridCntY = Mathf.RoundToInt (gridSize.y / nodeDiameter);//纵轴需要多少个格子
grid = new Node[gridCntX, gridCntY];
CreatGrid ();//创建节点
}
private void CreatGrid ()//创建节点形成网格
{
//起始点
Vector3 startPoint = transform.position - gridSize.x / 2 * Vector3.right - Vector3.forward * gridSize.y / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < gridCntX; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < gridCntY; j++) {
//节点的真实位置
Vector3 worldPoint = startPoint + Vector3.right * (i * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius) +
Vector3.forward * (j * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius);
//节点是否可以行走
bool walkable = !Physics.CheckSphere (worldPoint, nodeRadius, WhatLayer);//圆形的射线
grid [i, j] = new Node (walkable, worldPoint, i, j);
}
}
}
//获取节点的位置
public Node GetFromPosition (Vector3 postion)
{
//在横轴上的相对位置
float percentX = (postion.x + gridSize.x / 2) / gridSize.x;
//在纵轴的相对位置
float percentY = (postion.z + gridSize.y / 2) / gridSize.y;
percentX = Mathf.Clamp01 (percentX);
percentY = Mathf.Clamp01 (percentY);
int x = Mathf.RoundToInt ((gridCntX - 1) * percentX);
int y = Mathf.RoundToInt ((gridCntY - 1) * percentY);
return grid [x, y];
}
void OnDrawGizmos ()//画出网格和节点
{
//画出网格的边缘
Gizmos.DrawWireCube (transform.position, new Vector3 (gridSize.x, 1, gridSize.y));
if (grid == null)
return;
//画出网格里面的节点
foreach (var node in grid) {
Gizmos.color = node._canWalk ? Color.white : Color.red;
//为了有边缘让他大小减小0.1f
Gizmos.DrawCube (node._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
//画出玩家的节点
Node playerNode = GetFromPosition (player.position);
if (playerNode != null && playerNode._canWalk) {
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan;
Gizmos.DrawCube (playerNode._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
//画出路径的颜色
if (path != null) {
foreach (var node in path) {
Gizmos.color = Color.black;
Gizmos.DrawCube (node._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
}
}
//获取节点格子周围节点的方法
public List<Node> GetNeibourhood (Node node)
{
List<Node> neibourhood = new List<Node> ();
for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
continue;
}
int tempX = node._gridX + i;
int tempY = node._gridY + j;
//是否越界
if (tempX < gridCntX && tempX > 0 && tempY > 0 && tempY < gridCntY) {
neibourhood.Add (grid [tempX, tempY]);
}
}
}
return neibourhood;
}
}
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Grid : MonoBehaviour
{
private Node[,] grid;
//定义grid二维数组
public Vector2 gridSize;
//二维向量保存网格的大小
public float nodeRadius;
//设定每个节点的半径
private float nodeDiameter;
//节点的直径
public LayerMask WhatLayer;
//节点的标签
public int gridCntX, gridCntY;
//保存每个方向上格子的个数
public Transform player;
// 玩家的引用
public List<Node> path = new List<Node> ();
//保存路径
// Use this for initialization
void Start ()
{
nodeDiameter = nodeRadius * 2;//计算节点的直径
gridCntX = Mathf.RoundToInt (gridSize.x / nodeDiameter);//横轴需要多少个格子
gridCntY = Mathf.RoundToInt (gridSize.y / nodeDiameter);//纵轴需要多少个格子
grid = new Node[gridCntX, gridCntY];
CreatGrid ();//创建节点
}
private void CreatGrid ()//创建节点形成网格
{
//起始点
Vector3 startPoint = transform.position - gridSize.x / 2 * Vector3.right - Vector3.forward * gridSize.y / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < gridCntX; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < gridCntY; j++) {
//节点的真实位置
Vector3 worldPoint = startPoint + Vector3.right * (i * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius) +
Vector3.forward * (j * nodeDiameter + nodeRadius);
//节点是否可以行走
bool walkable = !Physics.CheckSphere (worldPoint, nodeRadius, WhatLayer);//圆形的射线
grid [i, j] = new Node (walkable, worldPoint, i, j);
}
}
}
//获取节点的位置
public Node GetFromPosition (Vector3 postion)
{
//在横轴上的相对位置
float percentX = (postion.x + gridSize.x / 2) / gridSize.x;
//在纵轴的相对位置
float percentY = (postion.z + gridSize.y / 2) / gridSize.y;
percentX = Mathf.Clamp01 (percentX);
percentY = Mathf.Clamp01 (percentY);
int x = Mathf.RoundToInt ((gridCntX - 1) * percentX);
int y = Mathf.RoundToInt ((gridCntY - 1) * percentY);
return grid [x, y];
}
void OnDrawGizmos ()//画出网格和节点
{
//画出网格的边缘
Gizmos.DrawWireCube (transform.position, new Vector3 (gridSize.x, 1, gridSize.y));
if (grid == null)
return;
//画出网格里面的节点
foreach (var node in grid) {
Gizmos.color = node._canWalk ? Color.white : Color.red;
//为了有边缘让他大小减小0.1f
Gizmos.DrawCube (node._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
//画出玩家的节点
Node playerNode = GetFromPosition (player.position);
if (playerNode != null && playerNode._canWalk) {
Gizmos.color = Color.cyan;
Gizmos.DrawCube (playerNode._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
//画出路径的颜色
if (path != null) {
foreach (var node in path) {
Gizmos.color = Color.black;
Gizmos.DrawCube (node._worldPos, Vector3.one * (nodeDiameter - .1f));
}
}
}
//获取节点格子周围节点的方法
public List<Node> GetNeibourhood (Node node)
{
List<Node> neibourhood = new List<Node> ();
for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
continue;
}
int tempX = node._gridX + i;
int tempY = node._gridY + j;
//是否越界
if (tempX < gridCntX && tempX > 0 && tempY > 0 && tempY < gridCntY) {
neibourhood.Add (grid [tempX, tempY]);
}
}
}
return neibourhood;
}
}
第3个脚本
// 挂载对象:空物体
// 功能:实现A*寻路实现路径
// 注意:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class FindPath : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform player, Endpoint;
private Grid _grid;
//整个网格的引用
void Start ()
{
_grid = GetComponent<Grid> ();
}
void Update ()
{
FindingPath (player.position, Endpoint.position);
}
void FindingPath (Vector3 StartPos, Vector3 EndPos)
{
//获取开始和结束的节点
Node startNode = _grid.GetFromPosition (StartPos);
Node EndNode = _grid.GetFromPosition (EndPos);
//开始集合
List<Node> openSet = new List<Node> ();
//结束集合
HashSet<Node> closeSet = new HashSet<Node> ();
//起点放到开始节点当中
openSet.Add (startNode);
//循环查询
while (openSet.Count > 0) {
Node currentNode = openSet [0];
//遍历开启列表的所有元素
for (int i = 0; i < openSet.Count; i++) {
if (openSet [i].fCost < currentNode.fCost ||
openSet [i].fCost == currentNode.fCost
&& openSet [i].hCost < currentNode.hCost) {
currentNode = openSet [i];
}
}
openSet.Remove (currentNode);
closeSet.Add (currentNode);
//当前节点是否是结束节点,如果是结束查询
if (currentNode == EndNode) {
//生成路径
GeneratePath (startNode, EndNode);
return;
}
//选择最优的节点
foreach (var node in _grid.GetNeibourhood(currentNode)) {
//不需要操作直接跳过
if (!node._canWalk || closeSet.Contains (node))
continue;
//新的消费,当前格子与开始格子的距离
int newCost = currentNode.gCost + GetDistanceNodes (currentNode, node);
//新的消费比当前的消费小的时候,不在开始列表
if (newCost < node.gCost || !openSet.Contains (node)) {
node.gCost = newCost;
node.hCost = GetDistanceNodes (node, EndNode);
node.parent = currentNode;
//没有包含节点,放到开始节点之中
if (!openSet.Contains (node)) {
openSet.Add (node);
}
}
}
}
}
//生成路径
private void GeneratePath (Node startNode, Node endNode)
{
List<Node> path = new List<Node> ();
Node temp = endNode;
while (temp != startNode) {
path.Add (temp);
temp = temp.parent;
}
path.Reverse ();
_grid.path = path;
}
//获取两个节点距离的方法
int GetDistanceNodes (Node a, Node b)
{
int cntX = Mathf.Abs (a._gridX - b._gridX);
int cntY = Mathf.Abs (a._gridY - b._gridY);
if (cntX > cntY) {
//X轴更大
return 14 * cntY + 10 * (cntX - cntY);
} else {
//Y轴更大
return 14 * cntX + 10 * (cntY - cntX);
}
}
}
// 功能:实现A*寻路实现路径
// 注意:
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class FindPath : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform player, Endpoint;
private Grid _grid;
//整个网格的引用
void Start ()
{
_grid = GetComponent<Grid> ();
}
void Update ()
{
FindingPath (player.position, Endpoint.position);
}
void FindingPath (Vector3 StartPos, Vector3 EndPos)
{
//获取开始和结束的节点
Node startNode = _grid.GetFromPosition (StartPos);
Node EndNode = _grid.GetFromPosition (EndPos);
//开始集合
List<Node> openSet = new List<Node> ();
//结束集合
HashSet<Node> closeSet = new HashSet<Node> ();
//起点放到开始节点当中
openSet.Add (startNode);
//循环查询
while (openSet.Count > 0) {
Node currentNode = openSet [0];
//遍历开启列表的所有元素
for (int i = 0; i < openSet.Count; i++) {
if (openSet [i].fCost < currentNode.fCost ||
openSet [i].fCost == currentNode.fCost
&& openSet [i].hCost < currentNode.hCost) {
currentNode = openSet [i];
}
}
openSet.Remove (currentNode);
closeSet.Add (currentNode);
//当前节点是否是结束节点,如果是结束查询
if (currentNode == EndNode) {
//生成路径
GeneratePath (startNode, EndNode);
return;
}
//选择最优的节点
foreach (var node in _grid.GetNeibourhood(currentNode)) {
//不需要操作直接跳过
if (!node._canWalk || closeSet.Contains (node))
continue;
//新的消费,当前格子与开始格子的距离
int newCost = currentNode.gCost + GetDistanceNodes (currentNode, node);
//新的消费比当前的消费小的时候,不在开始列表
if (newCost < node.gCost || !openSet.Contains (node)) {
node.gCost = newCost;
node.hCost = GetDistanceNodes (node, EndNode);
node.parent = currentNode;
//没有包含节点,放到开始节点之中
if (!openSet.Contains (node)) {
openSet.Add (node);
}
}
}
}
}
//生成路径
private void GeneratePath (Node startNode, Node endNode)
{
List<Node> path = new List<Node> ();
Node temp = endNode;
while (temp != startNode) {
path.Add (temp);
temp = temp.parent;
}
path.Reverse ();
_grid.path = path;
}
//获取两个节点距离的方法
int GetDistanceNodes (Node a, Node b)
{
int cntX = Mathf.Abs (a._gridX - b._gridX);
int cntY = Mathf.Abs (a._gridY - b._gridY);
if (cntX > cntY) {
//X轴更大
return 14 * cntY + 10 * (cntX - cntY);
} else {
//Y轴更大
return 14 * cntX + 10 * (cntY - cntX);
}
}
}
以上即为实现A*算法的所有脚本,挂载后把所需引用对象引用进去即可实现,最后实现的效果图如下:
最后A*算法虽然是路径最优算法,但是对资源的占用比较大,优化方法为二叉堆,这里暂时不做介绍,本文为本人纯手打,代码均为本人亲力手敲,如有雷同,纯属巧合。