Attention机制中CBAM以及Dual pooling的pytorch实现
前言:虽然会pytorch框架中的一些基础操作,但是有很多实现直接让自己写还是挺困难的。本次的代码参考senet中的channel-wise加权,CBAM中的channel-attention和spatial-attention, 另外还有kaggle Master@gray 分享的Dual pooling。由于没有特别的逻辑,所以看到哪写到哪吧。
文章目录
- 1. SENET中的channel-wise加权的实现
- 2. CBAM中的通道注意力机制
- 3. CBAM中的空间注意力机制
- 4. CBAM中的融合
- 5. dual pooling的pytorch实现
1. SENET中的channel-wise加权的实现
实现代码参考自:senet.pytorch
selayer:
from torch import nn
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=16):
super(SELayer, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(channel, channel // reduction, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(channel // reduction, channel, bias=False),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avg_pool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.fc(y).view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
以上代码涉及到的API:
- AdaptiveAvgPool2d: 自适应平均池化,参数为(n,m)则将原来的feature(w,h)通过pooling得到(n,m)的feature,如果是(n),则将原来的feature从(w,h)通过pooling得到(n,n)
- Sequential: torch容器,存放网络层等内容。
- Linear: 线性层,参数为(in, out),将原有的in个feature转为out个feature
- ReLU: 激活层, inplace进行原地操作,节省内存
- Sigmoid: 激活层,将输入压缩到0-1
分析forward进行模型的构建:
-
x是输入的feature,一般各个通道意义如下:(batch size,channel, width , height),这里获取了batch(b), channel©
-
x通过AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)以后将得到(batch size, channel, 1, 1), 然后view(b,c)意思是按照b,c进行展开
>>> import torch >>> x = torch.zeros((16,256,256,256)) >>> import torch.nn as nn >>> avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1) >>> avg_pool(x).shape torch.Size([16, 256, 1, 1]) >>>torch.Size([16, 3, 1, 1]) >>> avg_pool(x).view((16,256)).shape torch.Size([16, 256]) >>> avg_pool(x).squeeze().shape # squeeze()函数也可以将所有通道个数为1的进行挤压 torch.Size([16, 256]) -
然后形状为【16, 256】的tensor经过fc:
- (1) Linear: from 256(channel) to 256/16
- (2) ReLu:进行一次激活函数
- (3) Linear: from 256/16 to 256(channel)
- (4) Sigmoid: 激活到0-1,代表每个通道的重要性
- 然后通过view操作转化为【16,256,1,1】形状的tensor
-
现在y得到的是每一个通道对应的分数(0-1),然后需要将其与通道内容相乘,具体操作使用到了tensor的内置函数expand_as(把一个tensor变成和函数括号内一样形状的tensor,用法与expand类似,相当于expand(tensor.size())
- x是【16,256,256,256】形状的特征图,y是【16,256,1,1】大小的channel-wise分数,然后需要将其相乘
- b.expand_as(a)就是将b进行扩充,扩充到a的维度,需要说明的是a的低维度需要比b大,例如b的shape是3*1,如果a的shape是3*2不会出错,但是是2*2就会报错了。
>>> t.shape torch.Size([2, 3]) >>> f.shape torch.Size([5, 6]) >>> f = torch.ones([2,8]) >>> t.expand_as(f) Traceback (most recent call last): File "" , line 1, in <module> RuntimeError: The expanded size of the tensor (8) must match the existing size (3) at non-singleton dimension 1. Target sizes: [2, 8]. Tensor sizes: [2, 3] >>>报错翻译过来就是:RuntimeError:张量(8)的扩展大小必须与非单维度1上的现有大小(3)相匹配。目标大小:[2,8]。 张量大小:[2,3]。
官方API描述:
返回tensor的一个新视图,单个维度扩大为更大的尺寸。 tensor也可以扩大为更高维,新增加的维度将附在前面。 扩大tensor不需要分配新内存,只是仅仅新建一个tensor的视图,其中通过将stride设为0,一维将会扩展位更高维。任何一个一维的在不分配新内存情况下可扩展为任意的数值。
就是必须有一个维度是1,然后用于扩展:
>>> tensor1 = torch.ones((3,4,1,1)) >>> tensor1.expand([3,4,5,5]).shape torch.Size([3, 4, 5, 5]) >>>这样通过expand_as就能得到【16,256,256,256】大小的tensor,其中256*256都是对应通道的1分数,然后与原先的feature相乘,就能得到channel-wise分数计算后的feature。
ps: 虽然看上去想法很简单,但是实际上还是有很多细节需要注意
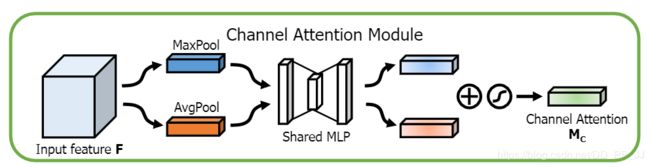
2. CBAM中的通道注意力机制
channel-attention-module跟以上内容想法有一点像,给每个channel进行打分,具体实现如下:
参考来源:CBMA.pytorch
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.fc1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // 16, 1, bias=False)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // 16, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.fc2(self.relu1(self.fc1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = avg_out + max_out
return self.sigmoid(out)
API跟上边类似,只添加了卷积,也很简单。需要说明的是貌似Linear和Conv2d中的参数很相似,但是实际上,两者还是很不一样的,Linear接受的是线性的2维数组(batch, 一维特征),Con2d接受的是4维数组(batch, 通道,w, h)。
直接看forward函数:
- 第一行,进行了adaptiveAvgPooling, conv2d, relu, conv2d
- 第二行,进行了AdaptiveMaxPooling, conv2d, relu, conv2d
- 第三行,将两个向量进行相加
- 第四行,将对应结果进行激活,得到通道注意力分数。
3. CBAM中的空间注意力机制
实现参考来源:CBAM-pytorch
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
return self.sigmoid(x)
![]()
Spatial attention module中支持kernel_size=3或者7,默认设置为7。
以上涉及到的API:
- torch.mean: 求平均值,dim指的是沿着某一个通道进行计算平均值。这里dim=1,说明沿着通道channel进行平均,对所有channel的feature上相应的像素进行求平均值。
- torch.max: 同上,进行求最大值。
分析forward函数:
-
第一行:沿着通道维度进行进行平均,得到一个(batch, 1, w, h)的feature
-
第二行:沿着通道维度进行求最大值,得到一个(batch, 1, w, h)的feature
-
第三行:将两个feature通过cat的方式拼接起来,得到一个(batch, 2, w, h)的feature
-
第四行:对这个feature进行卷积
o u t _ f e a t u r e = i n _ f e a u t r e + 2 × p a d d i n g − k e r n e l _ s i z e s t r i d e + 1 out\_feature = \frac{in\_feautre + 2 \times padding - kernel\_size}{stride}+1 out_feature=stridein_feautre+2×padding−kernel_size+1
之所以设置如果kernel_size=7的时候padding=3是因为需要将out_feature和in_feature相等,可以带入公式进行计算。 -
第五行:进行激活,将得分约束至【0-1】
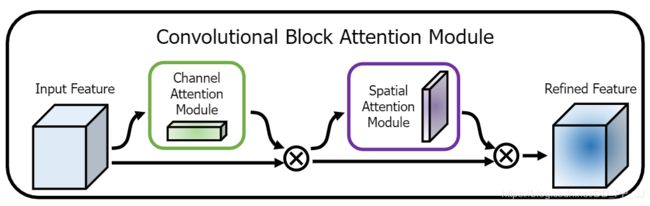
4. CBAM中的融合
参考代码:cbam.pytorch
resnet中主要是用在basicBlock中,代码如下:
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.ca = ChannelAttention(planes)
self.sa = SpatialAttention()
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.ca(out) * out # 广播机制
out = self.sa(out) * out # 广播机制
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
5. dual pooling的pytorch实现
参考来源:gray大佬
class res18(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(res18, self).__init__()
self.base = resnet18(pretrained=True)
self.feature = nn.Sequential(
self.base.conv1,
self.base.bn1,
self.base.relu,
self.base.maxpool,
self.base.layer1,
self.base.layer2,
self.base.layer3,
self.base.layer4
)
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.reduce_layer = nn.Conv2d(1024, 512, 1)
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(512, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, x):
bs = x.shape[0]
x = self.feature(x)
x1 = self.avg_pool(x)
x2 = self.max_pool(x)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)
x = self.reduce_layer(x).view(bs, -1)
logits = self.fc(x)
return logits
这种是在模型层进行改造的一种小trick了,常见的做法:global max/average pooling + fc layer,这里试concat(global max-pooling, global average pooling) + fc layer,其实就是为了丰富特征层,max pooling更加关注重要的局部特征,而average pooling试更加关注全局的特征。不一定有效,我试过不少次,有效的次数比较少,但不少人喜欢这样用.
— gray
以上就是dual pooling的实现,具体分析如下:
-
第一行:得到batch-size
-
第二行:得到feature, gray大佬这里用的是一个sequential将所有的模块装载进来,其实也可以用这种方法:
self.base_model = nn.Sequential(*list(model_ft.children())[:-3]) # 取除了后三个全部的层
children方法里就是返回当前模型子模块的迭代器,可以查看源代码,然后选择将其中一部分去掉,比如fc层等,也可以使用gray大佬的这种方法。
查找的过程中找到一个中间层可视化的简单代码:https://www.jianshu.com/p/0a23db1df55a
- 第四,五行,通过avg_pool,max_pool得到对应的feature
- 第六行,进行concate操作,进行拼接
- 第七行,使用了一个卷积层进行降维通道,并进行view展开成一维向量。
- 第八层,进行全连接层的分类。
后记:自己跟熟练使用pytorch还有很大差距,继续看大佬的代码,然后慢慢学着复现。如果有问题请联系我,或者评论。