经典的8个内部排序算法
1.直插排序
思想:
每一趟,对于待排序元素a[i],该元素前面的子序列已有序;在有序序列中从后往前查找其插入位置,一边比较一边移动。直至找到插入位置,插入该元素;一共n-1趟。

举例:
待排序序列: 5 8 4 12 9
第一趟: 5 8 4 12 9
第二趟: 4 5 8 12 9
第三趟: 4 5 8 12 9
第四趟: 4 5 8 9 12
代码:
public static void insertSort(int a[]){
int n=a.length;
int toSort;//存储待排序元素
for (int i=1;i<n;i++){//n-1趟
if(a[i]<a[i-1]){//若>=,无需移动插入
toSort=a[i];
int j;
for (j=i-1; j>=0;j--) {//从后往前查找插入位置
if (toSort < a[j])//边比较
a[j + 1] = a[j];//边移动
else break;
}
a[j+1]=toSort;//插入到插入位置
}
}
}
说明:
- 每一趟a[i]不一定到达最终位置;
2.希尔排序
思想:
先将待排序表分割成若干个形如a[i,i+d,i+2d,…,i+kd]的子表 ,分别进行直插排序;当整个表呈现“基本有序”时,再对全体进行一次直插排序。
存在一个增量序列di ,d1=n/2 , di+1=di/2 ,并且最后一个增量1 .
举例:
待排序序列 di={5,3,1}:50 26 38 80 70 90 8 30 40 20
第一趟(增量5): 50 8 30 40 20 90 26 38 80 70
第二趟(增量3): 26 8 30 40 20 80 50 38 90 70
第三趟(增量1): 8 20 26 30 38 40 50 70 80 90
代码:
public static void shellSort(int a[]){
int n=a.length;
int toSort;//存储待排序元素
for (int d=n/2 ;d>=1 ;d=d/2)//增量变化
for (int i=d;i<n ;i++){
if(a[i]<a[i-d]){
toSort=a[i];
int j;
for (j=i-d ;j>=0 ; j-=d){
if(toSort<a[j]) a[j+d]=a[j];
else break;
}
a[j+d]=toSort;
}
}
}
说明:
- 希尔排序的代码只需将1换成d即可;
3.冒泡排序
思想:
每一趟,从后往前,两两比较,逆则交换;每趟结果让最小元素到达最终位置,若该趟没有发生交换,说明表已经有序。最多n-1趟。
举例:
待排序序列:5 8 4 12 9
第一趟: 4 5 8 9 12
第二趟: 4 5 8 9 12
代码:
public static void bubbleSort(int a[]){
boolean flag;//标志某趟是否交换过
int n=a.length;
for (int i=0 ;i<n-1 ;i++){//最多n-1趟
//一趟冒泡
flag=false;
for (int j=n-1 ;j>i ;j--)
if(a[j-1]>a[j]){//若逆则交换
int temp=a[j-1];
a[j-1]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
flag=true;
}
if(!flag)return;//若某趟没有发生交换,说明序列已有序
}
}
说明:
- 如果待排序序列是已有序序列,1趟冒泡即可;
4.快速排序
思想:
一趟快排(划分):
先设置一个枢轴pivot;
(1) 从右往左,找到第一个小于pivot值的元素,交换;
(2) 从左往右,找到第一个大于pivot值的元素,交换;
(1)(2)交替进行,时刻保持low < high;每一趟结果使得pivot到达
最终位置(如同: 小于 pivot 大等于);
然后对pivot最终位置左、右两个子序列分别进行递归排序。
举例:
代码:
/**
* 一趟快排(划分),返回pivot最终位置
*/
public static int partition(int a[],int low,int high){
int pivot=a[low];//枢轴
while(low<high){
//对应(1)
while (low<high && a[high]>=pivot) high--;
a[low]=a[high];
//对应(2)
while (low<high && a[low]<=pivot) low++;
a[high]=a[low];
}
a[low]=pivot;
return low;
}
/**
* 快排,平均性能最优
*/
public static void quickSort(int a[], int low, int high){
if (low<high){
int pivotPos=partition(a,low,high); //第一趟快排并获取第一个pivot最终位置
//分别对两个子表进行递归排序
quickSort(a,low,pivotPos-1);
quickSort(a,pivotPos+1,high);
}
}
说明:
- 快排是各种内部排序算法平均性能最优的算法;
5.简单选择排序
思想:
每一趟选择最小元素,交换到其最终位置,一共n-1趟。
举例:
待排序序列:5 8 4 12 9
第一趟: 4 8 5 12 9
第二趟: 4 5 8 12 9
第三趟: 4 5 8 12 9
第四趟: 4 5 8 9 12
代码:
public static void selectSort(int a[]){
int n=a.length;
int min;
for (int i=0; i<n-1 ;i++){//n-1趟
min= i;//记录最小元素下标
for (int j=i+1 ;j< n; j++)//从a[i...n-1]中选择最小元素
if (a[j] <a[min]) min= j;
if (min!=i) {//与第i个位置交换
int temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[min];
a[min]=temp;
}
}
}
说明:
- 与冒泡的关系:相同点:每一趟最小元素到达最终位置;不同点:趟数。
6.堆排序
思想:
以大顶堆(双亲结点总是大于等于子结点关键字的完全二叉树)为例,
- (1)建大顶堆:从第n/2-1个结点开始,反复调整,直至所有结点满足大顶堆的性质;
- (2)n-1 趟交换、调整:
举例:
待排序序列: 53 17 78 09 45 65 87 32
(2)n-1 趟交换、调整:
代码:
/**
* 建立大顶堆
*/
public static void buildMaxHeap(int a[]){
int n=a.length;
for (int i=n/2-1; i>=0; i--){//从n/2-1开始,反复调整
adjustDown(a,i,n-1);//...
}
}
/**
* 向下调整第k个元素到l元素形成的子堆
* 限制0=
public static void adjustDown(int a[],int k,int l){
int temp=a[k];//暂存子堆根节点
for (int i=2*k ;i<=l;i*=2){//沿较大结点向下筛选
if (i<l && a[i]<a[i+1]) i++;//取较大结点下标
if (temp >= a[i]) break;//如果双亲结点本来就大,子堆已经是大顶堆,无需再调整
else {
a[k]=a[i];//上调
k=i;//孩子当下一次双亲
}
}
a[k]=temp;//把子堆根节点放到最终位置
}
/**
* 堆排序
*/
public static void heapSort(int a[]){
int n=a.length;
buildMaxHeap(a);//初始建堆
for (int i=n-1; i>0; i--){//n-1 趟交换、调整
int temp=a[0];
a[0]=a[i];
a[i]=temp;
adjustDown(a,0,i-1);//...调整剩余的i个元素
}
}
说明:
- 不同待排序序列构造的大顶堆不一定相同;
7.归并排序
思想:
2-路归并为例:将排序表***划分***成左右俩个子表,对这两子表分别进行递归排序,然后将这两个有序子表***归并***成一个有序表;
举例:
代码:
/**
* 将两个升序表合并成一个升序表
* a[low...mid]和a[mid+1...high]
*/
public static void merge(int a[],int low,int mid,int high){
int b[]=new int[a.length];//辅助数组
for (int k=low ;k<=high;k++){
b[k]=a[k];//将a中所有元素复制到b中
}
int i=low,j=mid+1,k=low;//三个有序表的下标
while (i<=mid && j<=high){
if (b[i] <= b[j]) a[k++]=b[i++];//比较两个有序表中的元素,将较小值存入a中
else a[k++]=b[j++];
}
while (i<=mid) a[k++]=b[i++];//第一个有序未检测完,复制
while (j<=high) a[k++]=b[j++];//第二个有序表未检测完,复制
}
/**
* 归并排序:基于划分和归并
*/
public static void mergeSort(int a[], int low, int high){
if(low< high){
int mid= low+(high-low)/2;//划分
mergeSort(a,low,mid);//对左子表递归排序
mergeSort(a,mid+1,high);//对右子表递归排序
merge(a,low,mid,high);//合并两个有序表
}
}
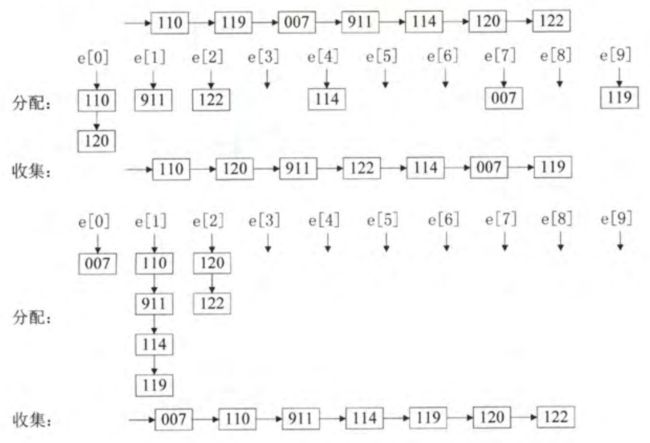
8.基数排序
思想:
d表示数位数和趟数;r表示进制数和队列数;
步骤见举例
举例:
代码:
/**
* 基数排序:不是基于比较,而是基于分配和收集;以十进制数r=10为例
* d是排序表数最大位数,同时也是排序趟数
*/
public static void radixSort(int a[], int d)
{
int n=a.length;
int k = 0;//数组遍历指针
int w = 1;//1,10,100分别代表个位,十位,百位
int[][] queue = new int[10][n];//r个长度为n的队列
int[]order = new int[10]; //队列指针
for (int m=0 ;m<d ;m++) {//d趟分配与收集
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//分配
int queueNo = ((a[i] / w) % 10);//队列号
queue[queueNo][order[queueNo]++] = a[i];//入队
}
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {//收集
if(order[i] != 0)//长度为0的队列不收集
for(int j = 0; j < order[i]; j++)
a[k++] = queue[i][j];
order[i] = 0;//队列指针复位
}
w *= 10;//跳位
k = 0;//遍历指针复位
}
}
说明:
- 基数排序不是基于比较,而是基于分配和收集;
- 一共d趟分配与收集,所以时间复杂度为O(d(n+r));借助r个队列,所以空间复杂度为O®;
9.测试代码
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestSorting {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int []a=new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++){//生成[0,100)范围的10个随机数作为排序表
a[i]=(int)(Math.random()*100);
}
System.out.println("排序前的数组为:"+ Arrays.toString(a));
//内部排序算法测试
// SortInner.insertSort(a);
// SortInner.shellSort(a);
// SortInner.bubbleSort(a);
// SortInner.quickSort(a,0,a.length-1);
// SortInner.selectSort(a);
// SortInner.heapSort(a);
// SortInner.mergeSort(a,0,a.length-1);
SortInner.radixSort(a,2);
System.out.println("排序后的数组为:"+Arrays.toString(a));
}
}
输出:
排序前的数组为:[57, 73, 76, 15, 88, 23, 10, 11, 64, 55]
排序后的数组为:[10, 11, 15, 23, 55, 57, 64, 73, 76, 88]
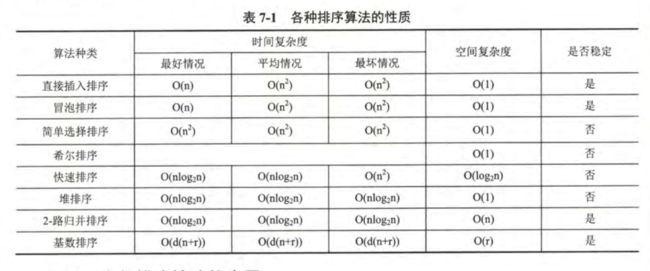
10.各种排序算法的比较
- 一般说的排序的时间复杂度是O(n*log n);
- 上表的空间复杂度是平均情况;快排最坏空间复杂度为O(n),当且仅当排序表初始有序时;
- 冒泡,简单选择,堆排序每一趟最大或最小元素到达最终位置;
- 快速排序每一趟有一个元素到达最终位置;快排时间平均性能最优;
- 当排序表初始状态基本有序时,适合采用直插或者冒泡;
- 本文介绍的从单个元素起两两归并的排序算法并不提倡,建议将归并和直插结合使用;先用直插求得较长的有序子序列后,然后再两两归并;
- 前面3个简单排序适用于n较小,后面四个排序适用于n较大;
- 当n很大且位数较小又可以分解时,适合用基数排序。