基于nodeJS从0到1实现一个CMS全栈项目(中)(含源码)
今天给大家介绍的主要是我们全栈CMS系统的后台部分,由于后台部分涉及的点比较多,我会拆解成几部分来讲解,如果对项目背景和技术栈不太了解,可以查看我的上一篇文章
这篇文章除了会涉及node的知识,还会涉及到redis(一个高性能的key-value数据库),前端领域的javascript大部分高级技巧以及ES6语法,所以在学习之前希望大家对其有所了解。
摘要
本文主要介绍CMS服务端部分的实现,具体包括如下内容:
如何使用babel7让node支持更多es6+语法以及nodemon实现项目文件热更新和自动重启
node项目的目录结构设计和思想
如何基于ioredis和json-schema自己实现一个类schema的基础库
基于koa-session封装一个sessionStore库
基于koa/multer封装文件处理的工具类
实现自定义的koa中间键和restful API
模版引擎pug的基本使用及技巧
由于每一个技术点实现的细节很多,建议先学习相关内容,如果不懂的可以和我交流。
正文
一. 如何使用babel7让node支持更多es6+语法以及nodemon实现项目文件热更新和自动重启
最新的node虽然已经支持大部分es6+语法,但是对于import,export这些模块化导入导出的API还没有彻底支持,所以我们可以通过babel去编译支持,如果你习惯使用commonjs的方式,也可以直接使用。这里我直接写出我的配置:
package.json安装babel模块和nodemon热重启
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/cli": "^7.5.5",
"@babel/core": "^7.5.5",
"@babel/node": "^7.5.5",
"@babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties": "^7.5.5",
"@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators": "^7.4.4",
"@babel/preset-env": "^7.5.5",
"nodemon": "^1.19.1"
},配置.babelrc文件,让node支持import,export,class以及装饰器:
// .babelrc
{
"presets": [
[
"@babel/preset-env",
{
"targets": {
"node": "current"
}
}
]
],
"plugins": [
["@babel/plugin-proposal-decorators", { "legacy": true }],
["@babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties", { "loose" : true }]
]
}配置启动脚本。为了使用npm的方式启动项目,我们在package.json里配置如下脚本:
"scripts": {
"start": "export NODE_ENV=development && nodemon -w src --exec \"babel-node src\"",
"build": "babel src --out-dir dist",
"run-build": "node dist",
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
复制代码有关babel7和nodemon以及npm的一些配置问题和使用方式,不过有不懂的可以在文章末尾和我交流。这里提供几个学习链接:
babel7文档教程
nodemon官方文档
用 webpack 4.0 撸单页/多页脚手架 (jquery, react, vue, typescript)
至此,我们node项目的基础设施基本搭建完成了,接下来我们继续深入服务端设计底层。
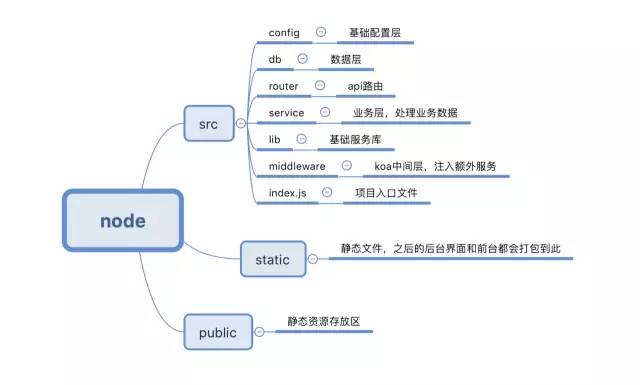
二. node项目的目录结构设计和思想
首先来看看我们完成后的目录设计:
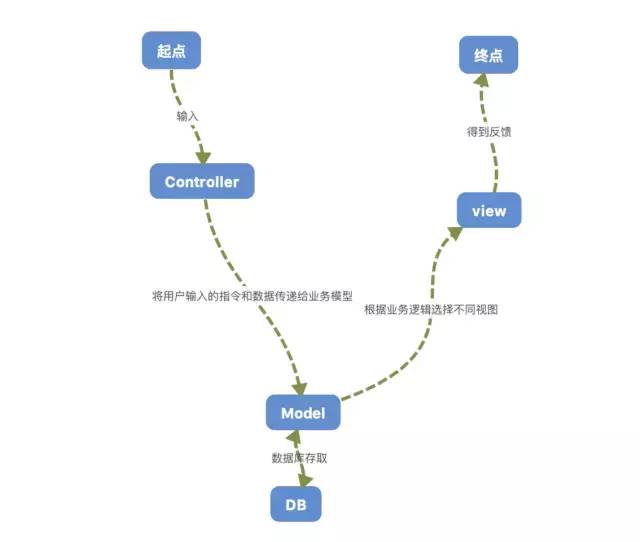
项目参考了很多经典资料和MDN的文档,采用经典的MVC模式,为了方便理解,笔者特意做了一个大致的导图:
这种模式用于应用程序的分层开发,方便后期的管理和扩展,并提供了清晰的设计架构。
Model层我们管理数据对象,它也可以带有逻辑,在数据变化时更新控制器。
View层主要用来展示数据的视图。
Controller控制器作用于模型和视图上。它控制数据流向模型对象,并在数据变化时更新视图,使视图与模型分离开。
三. 基于ioredis和json-schema自己实现一个类schema的基础库
在项目开发前,我们需要根据业务结构和内容设计数据模型,数据库部分我这里采用的是redis+json-schema,本来想使用mongodb来实现主数据的存储,但是考虑到自己对新方案的研究和想自己通过二次封装redis实现类mongoose的客户端管理框架,所以这里会采用此方案,关于mongoDB的实现,我之前也有项目案例,感兴趣可以一起交流优化。
我们来先看看CMS设计的视图和内容,我们分管理端和客户端,管理端主要的模块有:
登录模块
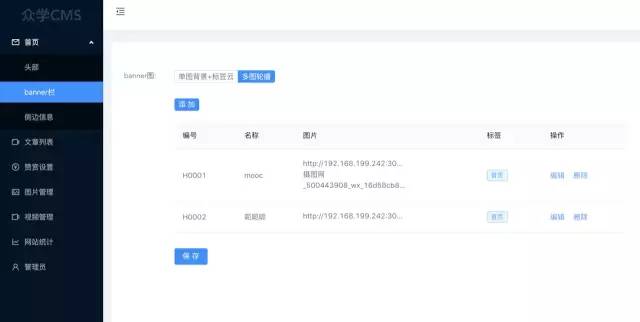
2. 首页配置管理模块
配置页主要包括header头部,banner位,bannerSider侧边栏和文章赞赏设置,我们对对它做一个单独的config数据库。
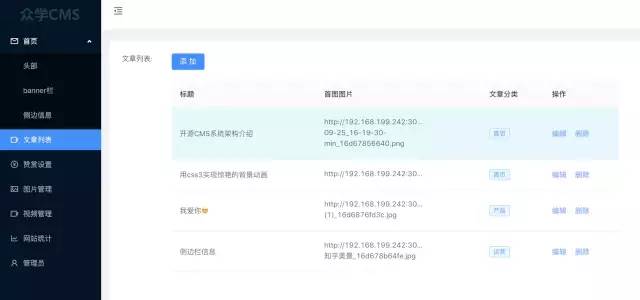
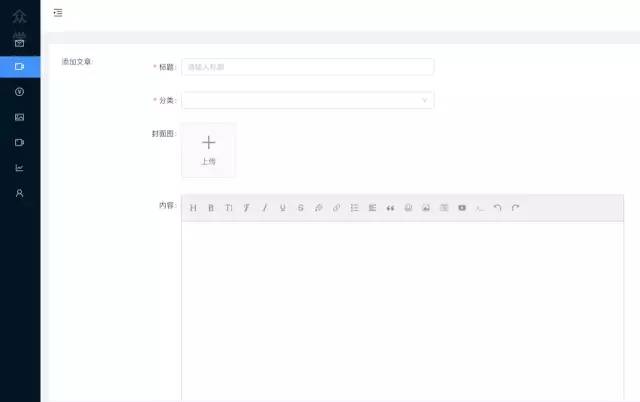
3. 文章管理模块
这里我们需要对文章数据进行存储,包括文章分类,文章首图,文章内容等信息,如下:
4. 图片管理
图片管理主要是方便博主管理图片信息,定位图片的来源,方便后期做埋点跟踪。
网站统计
网站统计只是一个雏形,博主可以根据自己需求做统计分析,提高更大的自定义。
管理员模块
这里用来管理系统的管理员,可以分配管理员权限等。关于权限的设计,可以有更复杂的模式,后面有需要也可以相互交流。
根据以上的展示,我们大致知道了我们需要设计哪些数据库模型,接下来我先带大家封装redis-schema,也是我们用到的数据库的底层工具:
// lib/schema.js
import { validate } from 'jsonschema'
import Redis from 'ioredis'
const redis = new Redis()
class RedisSchema {
constructor(schemaName, schema) {
this.schemaName = schemaName
this.schema = schema
this.redis = redis
}
validate(value, schema, cb) {
const { valid, errors } = validate(value, schema);
if(valid) {
return cb()
}else {
return errors.map(item => item.stack)
}
}
get() {
return this.redis.get(this.schemaName)
}
// 获取整个hash对象
hgetall() {
return this.redis.hgetall(this.schemaName)
}
// 获取指定hash对象的属性值
hget(key) {
return this.redis.hget(this.schemaName, key)
}
// 通过索引获取列表中的元素
lindex(index) {
return this.redis.lindex(this.schemaName, index)
}
// 获取列表中指定范围的元素
lrange(start, end) {
return this.redis.lrange(this.schemaName, start, end)
}
// 获取列表的长度
llen() {
return this.redis.llen(this.schemaName)
}
// 检测某个schemaName是否存在
exists() {
return this.redis.exists(this.schemaName)
}
// 给某个schemaName设置过期时间,单位为秒
expire(time) {
return this.redis.expire(this.schemaName, time)
}
// 移除某个schemaName的过期时间
persist() {
return this.redis.persist(this.schemaName)
}
// 修改schemaName名
rename(new_schemaName) {
return this.redis.rename(this.schemaName, new_schemaName)
}
set(value, time) {
return this.validate(value, this.schema, () => {
if(time) {
return this.redis.set(this.schemaName, value, "EX", time)
}else {
return this.redis.set(this.schemaName, value)
}
})
}
// 将某个schema的值自增指定数量的值
incrby(num) {
return this.redis.incrby(this.schemaName, num)
}
// 将某个schema的值自增指定数量的值
decrby(num) {
return this.redis.decrby(this.schemaName, num)
}
hmset(key, value) {
if(key) {
if(this.schema.properties){
return this.validate(value, this.schema.properties[key], () => {
return this.redis.hmset(this.schemaName, key, JSON.stringify(value))
})
}else {
return this.validate(value, this.schema.patternProperties["^[a-z0-9]+$"], () => {
return this.redis.hmset(this.schemaName, key, JSON.stringify(value))
})
}
}else {
return this.validate(value, this.schema, () => {
// 将第一层键值json化,以便redis能正确存储键值为引用类型的值
for(key in value) {
let v = value[key];
value[key] = JSON.stringify(v);
}
return this.redis.hmset(this.schemaName, value)
})
}
}
hincrby(key, num) {
return this.redis.hincrby(this.schemaName, key, num)
}
lpush(value) {
return this.validate(value, this.schema, () => {
return this.redis.lpush(this.schemaName, JSON.stringify(value))
})
}
lset(index, value) {
return this.redis.lset(this.schemaName, index, JSON.stringify(value))
}
lrem(count, value) {
return this.redis.lrem(this.schemaName, count, value)
}
del() {
return this.redis.del(this.schemaName)
}
hdel(key) {
return this.redis.hdel(this.schemaName, key)
}
}
export default RedisSchema这个笔者自己封装的库还有很多可扩展的地方,比如增加类事物处理,保存前拦截器等等,我会在第二版改进,这里只供参考。关于json-schema更多的知识,如有不懂,可以在我们的交流区沟通学习。我们定义一个管理员的schema:
/db/schema/admin.js
import RedisSchema from '../../lib/schema'
// 存放管理员数据
const adminSchema = new RedisSchema('admin', {
id: "/admin",
type: "object",
properties: {
username: {type: "string"},
pwd: {type: "string"},
role: {type: "number"} // 0 超级管理员 1 普通管理员
}
})
export default adminSchema由上可以知道,管理员实体包含username用户名,密码pwd,角色role,对于其他的数据库设计,也可以参考此方式。
四. 基于koa-session封装一个sessionStore库
由于session的知识网上很多资料,这里就不耽误时间了,这里列出我的方案:
function getSession(sid) {
return `session:${sid}`
}
class sessionStore {
constructor (client) {
this.client = client
}
async get (sid) {
let id = getSession(sid)
let result = await this.client.get(id)
if (!result) {
return null
} else {
try{
return JSON.parse(result)
}catch (err) {
console.error(err)
}
}
}
async set (sid, value, ttl) {
let id = getSession(sid)
try {
let sessStr = JSON.stringify(value)
if(ttl && typeof ttl === 'number') {
await this.client.set(id, sessStr, "EX", ttl)
} else {
await this.client.set(id, sessStr)
}
} catch (err) {
console.log('session-store', err)
}
}
async destroy (sid) {
let id = getSession(sid)
await this.client.del(id)
}
}
module.exports = sessionStore这里主要实现了session的get,set,del操作,我们主要用来处理用户的登录信息。
五. 基于koa/multer封装文件处理的工具类
文件上传的方案我是在github上看的koa/multer,基于它封装文件上传的库,但凡涉及到文件上传的操作都会使用它。
import multer from '@koa/multer'
import { resolve } from 'path'
import fs from 'fs'
const rootImages = resolve(__dirname, '../../public/uploads')
//上传文件存放路径、及文件命名
const storage = multer.diskStorage({
destination: function (req, file, cb) {
cb(null, rootImages)
},
filename: function (req, file, cb) {
let [name, type] = file.originalname.split('.');
cb(null, `${name}_${Date.now().toString(16)}.${type}`)
}
})
//文件上传限制
const limits = {
fields: 10,//非文件字段的数量
fileSize: 1024 * 1024 * 2,//文件大小 单位 b
files: 1//文件数量
}
export const upload = multer({storage,limits})
// 删除文件
export const delFile = (path) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.unlink(path, (err) => {
if(err) {
reject(err)
}else {
resolve(null)
}
})
})
}
// 删除文件夹
export function deleteFolder(path) {
var files = [];
if(fs.existsSync(path)) {
files = fs.readdirSync(path);
files.forEach(function(file,index){
var curPath = path + "/" + file;
if(fs.statSync(curPath).isDirectory()) { // recurse
deleteFolder(curPath);
} else { // delete file
fs.unlinkSync(curPath);
}
});
fs.rmdirSync(path);
}
}
export function writeFile(path, data, encode) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.writeFile(path, data, encode, (err) => {
if(err) {
reject(err)
}else {
resolve(null)
}
})
})
}这套方案包含了上传文件,删除文件,删除目录的工具方法,可以拿来当轮子使用到其他项目,也可以基于我的轮子做二次扩展。
关于实现自定义的koa中间键和restful API和模版引擎pug的基本使用及技巧部分,由于时间原因,我会在明天继续更新,以上部分如有不懂的,可以和笔者交流学习。
最后
接下来的两天将推出服务端剩下的部分,CMS全栈的管理后台和客户端部分的实现。包括:
实现自定义的koa中间键和restful API
koa路由和service层实现
模版引擎pug的基本使用及技巧
vue管理后台页面的实现及源码分享
react客户端前台的具体实现及源码分享
pm2部署以及nginx服务器配置
项目完整源码地址我会在十一之前告诉大家,欢迎在公众号《趣谈前端》戳我,邀请大家加入我们一起讨论。
回复 学习路径,将获取笔者多年从业经验的前端学习路径的思维导图
回复 lodash,将获得Lodash API中文翻译高清源文件
趣谈前端
Vue、React、小程序、Node
前端 算法|性能|架构|安全