数据分析学习体验——实际案例_逻辑回归&线性回归
作者: 江俊
日期: 2018年3月27日
主要介绍批量生成profiling图以及五数概括的自建函数。
项目背景
某保养品公司目前有一款产品线销售情况一直不景气,公司预算有限,希望在现有的客户中挖掘出最有可能在30天内购买该产品的用户群
使用语言
R语言
使用模型
逻辑回归+线性回归
建模步骤
一、 了解数据
- 数据结构
- Y变量定义
- X变量类型
- 响应率情况
- 花费金额分布
代码:
rm(list=ls())
setwd("./") #change the location
getwd() #check the location
list.files() #list the files under your location
#########################################################################
######################## Part1 read data ###########################
#########################################################################
filepath<-"./Exercise_Response_data.csv"
raw<-read.csv(filepath,stringsAsFactors = F)
dim(raw)
str(raw)
summary(raw)
var<-data.frame(var=colnames(raw),type=sapply(raw,class))
# 将结果导出到 xlsx表格
require(XLConnect)
#xlsx <- loadWorkbook('Correlation.xlsx',create=TRUE)
xlsx <- loadWorkbook('myhomework.xlsx',create = T)
createSheet(xlsx,name='variable') #name the worksheet as 'correlation'
writeWorksheet(xlsx,var,'variable',startRow=1,startCol=1, header=TRUE) #define the startrow,startcol,header
saveWorkbook(xlsx)
# dv_revenue
summary(raw$dv_revenue)
raw$dv_revenue<-ifelse(is.na(raw$dv_revenue),0,raw$dv_revenue)
# table 自动忽略缺失值
View(table(raw$dv_revenue))
hist(raw$dv_revenue) # dv_revenue hist
quantile(raw$dv_revenue,(1:20)/20,na.rm = T) # dv_revenue quantile
View(t(mean_rev<-quantile(raw$dv_revenue,c(0,0.01,0.1,0.25,0.5,0.75,0.9,0.99,1),na.rm = T)))
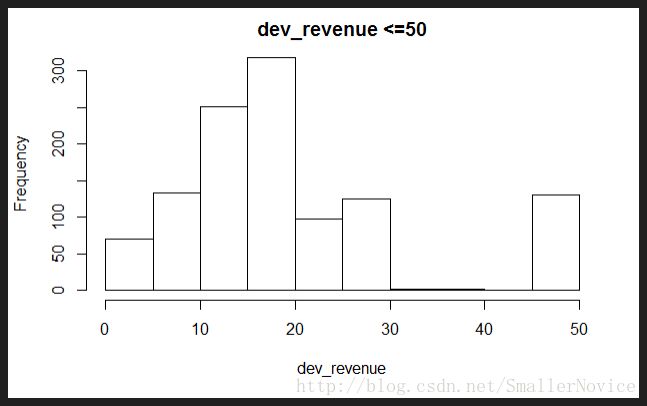
hist(raw[raw$dv_revenue>0 & raw$dv_revenue<=50,"dv_revenue"],main="dev_revenue <=50",xlab = "dev_revenue")
# dv_response
table(raw$dv_response)
prop.table(table(raw$dv_response)) 0 1
22878 1220
0 1
0.94937339 0.05062661 二、拆分数据
- train:训练集
- test:验证集
代码:
#########################################################################
######################## Part2 split into two ######################
#########################################################################
# modeling segments
table(raw$segment)
prop.table(table(raw$segment))
#separate build sample
train<-raw[raw$segment=="build",]
table(train$segment)
#separate inval sample
test<-raw[raw$segment=="inval",]
table(test$segment)执行结果:
build inval
16898 7200
build inval
0.70122 0.29878
build
16898
inval
7200 三、 探索数据
- 分类型、数值型
- X内部表现
- X与Y关系
- 缺失值
批量生成profiling图
代码:
#########################################################################
######################## Part3 profile ############################
#########################################################################
#overall performance
#总体人数,计算总体样本响应情况
overrall<-dim(train)[1]
#相应人数,因为响应的记为1,所以可以直接使用sum()求和
over_responder<-sum(train$dv_response)
#responder<-length(train$dv_response[train$dv_response==1])
#响应率
over_response_rate<-over_responder/overrall
overall_perf<-data.frame(overrall,responder=over_responder,response_rate=over_response_rate)
overall_perf
#variable type
data.frame(table(sapply(train[,4:27],class)))
#character
#查看数据类型为某种的数据名,类似的有:is.character,is.numeric,is.factor
chavar_name<-colnames(train[,4:27])[unlist(lapply(train[,4:27],is.character))]
#字符型数据索引
charater_index<-which(colnames(train) %in% chavar_name)
lapply(train[,chavar_name],table)
#整数型,注意可能是分类型数值
intvar_name<-colnames(train[,4:27])[unlist(lapply(train[4:27],is.integer))]
summary(train[,intvar_name])
#根据结果记录分类型数值的变量名
var_fenlei<-c(chavar_name,"Occupation","Education","Frequency_of_last_mth")
lapply(train[,var_fenlei],table)
#根据分类型和连续型将原数据集分成两类,方便后续profile的批量处理
#分类型数值的索引
fenlei_index<-which(colnames(train) %in% var_fenlei)
#除开id列,响应变量列,字符型,分类型数值以外的连续数值型变量
#which(colnames(train[,4:27]) %in% c("rid","dv_response","dv_revenue"))
numvar_name<-colnames(train[,-c(1:3,fenlei_index,28:ncol(train))])
#数值型数值的索引
lianxu_index<-which(colnames(train) %in% numvar_name)
############################################### 1. Profiling for category variables####################################################
#install.packages('plyr')
library(plyr)
###################################### 1.profile 分类型数值 #########################################
#封装函数,分类型数值
#数据集,索引,索引长度
profile_fenlei<-function(x,y,n){
results<-data.frame(var=NA,category=NA,count=NA,responder=NA,
percent=NA,response_rate=NA,index=NA)
for(i in 1:n){
prof<-ddply(x,.(x[,y[i]]),summarise,count=length(id),responder=sum(dv_response)) #group by hh_gender_m_flg
#prof
#添加百分比结果
propf<-within(prof,{
index<-responder/count/over_response_rate*100
response_rate<-responder/count*100
percent<-count/overrall*100
}) #add response_rate,index, percentage
propf<-data.frame(var=colnames(train)[y[i]],propf)
colnames(propf)[2]<-"category"
#行连接
results<-rbind(results,propf)
}
#去除首行的空值
results<-results[-1,]
row.names(results)<-1:nrow(results)
return(results)
}
#分类数值的profile
results_fenlei<-profile_fenlei(train[,1:28],fenlei_index,length(fenlei_index))
results_fenlei$category[is.na(results_fenlei$category)]<-"unknown"
results_fenlei$category[results_fenlei$category==""]<-"unknown"
View(results_fenlei)
# #xlsx <- loadWorkbook('Correlation.xlsx',create=TRUE)
# xlsx <- loadWorkbook('myhomework.xlsx')
# createSheet(xlsx,name='profile') #name the worksheet as 'correlation'
# writeWorksheet(xlsx,results_fenlei,'profile',startRow=1,startCol=1, header=TRUE) #define the startrow,startcol,header
# saveWorkbook(xlsx)
#
#
###################################### 1.profile 分类型数值 #########################################
##################################### 2.profile 连续型数值 #########################################
######封装函数
#数据集,索引,索引长度,分段个数
profile_lianxu<-function(x,y,n,m){
var_data=x
results<-data.frame(var=NA,category=NA,count=NA,responder=NA,
percent=NA,response_rate=NA,index=NA)
for(i in 1:n){
#分离成两部分:缺失值和无缺失值
nomissing<-data.frame(var_data[!is.na(var_data[,y[i]]),]) #select the no missing value records
missing<-data.frame(var_data[is.na(var_data[,y[i]]),]) #select the missing value records
##################3.2.1 numeric Profiling:missing part
missing2<-ddply(missing,.(missing[,y[i]]),summarise,count=length(id),responder=sum(dv_response)) #group by pos_revenue_base_sp_6mo
colnames(missing2)[1]<-"category"
#View(missing2)
missing_perf<-within(missing2,{
index<-responder/count/over_response_rate*100
response_rate<-responder/count*100
percent<-count/overrall*100
})
#View(missing_perf)
nomissing_value<-nomissing[,y[i]] #put the nomissing values into a variable
nomissing$category<-cut(nomissing_value,unique(quantile(nomissing_value,(0:m)/m)),include.lowest = T) #separte into 10 groups
#View(table(nomissing$var_category)) #take a look at the 10 category
prof2<-ddply(nomissing,.(category),summarise,count=length(id),responder=sum(dv_response))#group by the 10 groups
#View(prof2)
nonmissing_perf<-within(prof2,{
index<-responder/count/over_response_rate*100
response_rate<-responder/count*100
percent<-count/overrall*100
})#add avg_revenue,index,percent
#View(nonmissing_perf)
#set missing_perf and non-missing_Perf together
#View(missing_perf)
#View(nonmissing_perf)
#colnames(nonmissing_perf)[3]<-"responder"
lastprofile<-rbind(nonmissing_perf,missing_perf) #set 2 data together
lastprofile<-data.frame(var=colnames(train)[y[i]],lastprofile)
#行连接
results<-rbind(results,lastprofile)
}
#去除首行的空值
results<-results[-1,]
row.names(results)<-1:nrow(results)
return(results)
}
#连续数值的profile
results_lianxu<-profile_lianxu(train[,1:34],lianxu_index,length(lianxu_index),10)
results_lianxu$category[is.na(results_lianxu$category)]<-"unknown"
View(results_lianxu)
######封装函数
##################################### 2.profile 连续型数值 #########################################
#将两个 profile 合成一个整体,输出到xlsx表格
#xlsx <- loadWorkbook('Correlation.xlsx',create=TRUE)
final_profile<-rbind(results_fenlei,results_lianxu)
View(final_profile)
xlsx <- loadWorkbook('myhomework.xlsx')
createSheet(xlsx,name='profile') #name the worksheet as 'correlation'
writeWorksheet(xlsx,final_profile,'profile',startRow=1,startCol=1, header=T) #define the startrow,startcol,header
saveWorkbook(xlsx)生成连续型数值的五数概括
代码:
#########################################################################
######################## Part4 means ##############################
#########################################################################
# 连续性数据的五数概括
dat_n<-train[,lianxu_index]
mean_var<-data.frame(var=1:ncol(dat_n),mean=NA,median=NA,"0%"=NA,
"1%"=NA,"10%"=NA,"25%"=NA,"50%"=NA,
"75%"=NA,"90%"=NA,"99%"=NA,"100%"=NA,
max=NA,missing=NA)
colnames(mean_var)[4:12]<-c("Minimum","1st Pthl","10th Pctl","25th Pctl","50th Pctl","75th Pctl","90th Pctl",
"99th Pctl","Maximum")
for(i in 1:ncol(dat_n)){
mean_var$var[i]=colnames(dat_n)[i]
mean_var$mean[i]=mean(dat_n[,i],na.rm=TRUE) #na.rm=TRUE去除NA的影响
mean_var$median[i]=median(dat_n[,i],na.rm=TRUE)
mean_var[i,4:12]=quantile(dat_n[,i],c(0,0.01,0.1,0.25,0.5,0.75,0.9,0.99,1),na.rm=TRUE)
mean_var$max[i]=max(dat_n[,i],na.rm=TRUE)
mean_var$missing[i]=sum(is.na(dat_n[,i]))
}
# #销毁临时变量
# dat_n<-NULL
#在列表中查看数值变量的统计信息
View(mean_var)
# 导出到 xlsx 表格
xlsx <- loadWorkbook('myhomework.xlsx')
createSheet(xlsx,name='means') #name the worksheet as 'correlation'
writeWorksheet(xlsx,mean_var,'means',startRow=1,startCol=1, header=T) #define the startrow,startcol,header
saveWorkbook(xlsx)未完待续。。。
转载请注明出处