图像特征描述子之ORB
原文站点:https://senitco.github.io/2017/07/09/image-feature-orb/
ORB(Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF)算法是对FAST特征点检测和BRIEF特征描述子的一种结合,在原有的基础上做了改进与优化,使得ORB特征具备多种局部不变性,并为实时计算提供了可能。
特征点检测
ORB首先利用FAST算法检测特征点,然后计算每个特征点的Harris角点响应值,从中筛选出 N 个最大的特征点,Harris角点的响应函数如下:
相关内容已在博文 FAST角点检测和 Harris角点检测分别做了详细的介绍。
FAST检测特征点不具备尺度不变性,可以像SIFT特征一样,借助尺度空间理论构建图像高斯金字塔,然后在每一层金字塔图像上检测角点,以实现尺度不变性。对于旋转不变性,原论文中提出了一种利用图像矩(几何矩),在半径为r的邻域内求取灰度质心的方法,从特征点到灰度质心的向量,定义为该特征点的主方向。图像矩定义如下:
I(x,y) 表示像素灰度值,0阶矩 m00 即图像邻域窗口内所有像素的灰度和, m10 和 m01 分别相对 x 和相对 y 的一阶矩,因此图像局部邻域的中心矩或者质心可定义为
特征点与质心形成的向量与 X 轴的夹角定义为特征点的主方向
特征点描述
ORB采用BRIEF作为特征描述方法,BRIEF虽然速度优势明显,但也存在一些缺陷,例如不具备尺度不变性和旋转不变性,对噪声敏感。尺度不变性的问题在利用FAST检测特征点时,通过构建高斯金字塔得以解决。BRIEF中采用 9×9 的高斯卷积核进行滤波降噪,可以在一定程度上缓解噪声敏感问题;ORB中利用积分图像,在 31×31 的Patch中选取随机点对,并以选取的随机点为中心,在 5×5 的窗口内计算灰度平均值(灰度和),比较随机点对的邻域灰度均值,进行二进制编码,而不是仅仅由两个随机点对的像素值决定编码结果,可以有效地解决噪声问题。
至于旋转不变性问题,可利用FAST特征点检测时求取的主方向,旋转特征点邻域,但旋转整个Patch再提取BRIEF特征描述子的计算代价较大,因此,ORB采用了一种更高效的方式,在每个特征点邻域Patch内,先选取256对随机点,将其进行旋转,然后做判决编码为二进制串。n个点对构成矩阵 S
旋转矩阵 Rθ为
旋转后的坐标矩阵为
描述子的区分性
通过上述方法得到的特征描述子具有旋转不变性,称为steered BRIEF(sBRIEF),但匹配效果却不如原始BRIEF算法,因为可区分性减弱了。特征描述子的一个要求就是要尽可能地表达特征点的独特性,便于区分不同的特征点。如下图所示,为几种特征描述子的均值分布,横轴为均值与0.5之间的距离,纵轴为相应均值下特征点的统计数量。可以看出,BRIEF描述子所有比特位的均值接近于0.5,且方差很大;方差越大表明可区分性越好。不同特征点的描述子表现出较大的差异性,不易造成无匹配。但steered BRIEF进行了坐标旋转,损失了这个特性,导致可区分性减弱,相关性变强,不利于匹配。
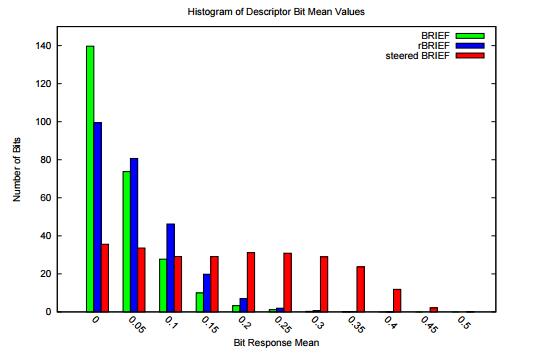
为了解决steered BRIEF可区分性降低的问题,ORB使用了一种基于学习的方法来选择一定数量的随机点对。首先建立一个大约300k特征点的数据集(特征点来源于PASCAL2006中的图像),对每个特征点,考虑其 31×31 的邻域Patch,为了去除噪声的干扰,选择 5×5 的子窗口的灰度均值代替单个像素的灰度,这样每个Patch内就有 N=(31−5+1)×(31−5+1)=27×27=729 个子窗口,从中随机选取2个非重复的子窗口,一共有 M=C2N 中方法。这样,每个特征点便可提取出一个长度为 M 的二进制串,所有特征点可构成一个 300k×M 的二进制矩阵 Q ,矩阵中每个元素取值为0或1。现在需要从 M 个点对中选取256个相关性最小、可区分性最大的点对,作为最终的二进制编码。筛选方法如下:
- 对矩阵 Q 的每一列求取均值,并根据均值与0.5之间的距离从小到大的顺序,依次对所有列向量进行重新排序,得到矩阵 T
- 将 T 中的第一列向量放到结果矩阵 R 中
- 取出 T 中的下一列向量,计算其与矩阵 R 中所有列向量的相关性,如果相关系数小于给定阈值,则将 T 中的该列向量移至矩阵 R 中,否则丢弃
- 循环执行上一步,直到 R 中有256个列向量;如果遍历 T 中所有列, R 中向量列数还不满256,则增大阈值,重复以上步骤。
这样,最后得到的就是相关性最小的256对随机点,该方法称为rBRIEF。
Experiment & Result
OpenCV实现ORB特征检测与描述
#include
#include
#include
#include OpenCV中ORB算法的部分源码实现
//计算Harris角点响应
static void HarrisResponses(const Mat& img, vector();
int step = (int)(img.step/img.elemSize1());
int r = blockSize/2;
float scale = (1 << 2) * blockSize * 255.0f;
scale = 1.0f / scale;
float scale_sq_sq = scale * scale * scale * scale;
AutoBuffer<int> ofsbuf(blockSize*blockSize);
int* ofs = ofsbuf;
for( int i = 0; i < blockSize; i++ )
for( int j = 0; j < blockSize; j++ )
ofs[i*blockSize + j] = (int)(i*step + j);
for( ptidx = 0; ptidx < ptsize; ptidx++ )
{
int x0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.x - r);
int y0 = cvRound(pts[ptidx].pt.y - r);
const uchar* ptr0 = ptr00 + y0*step + x0;
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;
for( int k = 0; k < blockSize*blockSize; k++ )
{
const uchar* ptr = ptr0 + ofs[k];
int Ix = (ptr[1] - ptr[-1])*2 + (ptr[-step+1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[step-1]);
int Iy = (ptr[step] - ptr[-step])*2 + (ptr[step-1] - ptr[-step-1]) + (ptr[step+1] - ptr[-step+1]);
a += Ix*Ix;
b += Iy*Iy;
c += Ix*Iy;
}
pts[ptidx].response = ((float)a * b - (float)c * c - harris_k * ((float)a + b) * ((float)a + b))*scale_sq_sq;
}
}
//计算FAST角点的主方向
static float IC_Angle(const Mat& image, const int half_k, Point2f pt, const vector<int> & u_max)
{
int m_01 = 0, m_10 = 0;
const uchar* center = &image.at (cvRound(pt.y), cvRound(pt.x));
// Treat the center line differently, v=0
for (int u = -half_k; u <= half_k; ++u)
m_10 += u * center[u];
// Go line by line in the circular patch
int step = (int)image.step1();
for (int v = 1; v <= half_k; ++v)
{
// Proceed over the two lines
int v_sum = 0;
int d = u_max[v];
for (int u = -d; u <= d; ++u)
{
int val_plus = center[u + v*step], val_minus = center[u - v*step];
v_sum += (val_plus - val_minus);
m_10 += u * (val_plus + val_minus);
}
m_01 += v * v_sum;
}
return fastAtan2((float)m_01, (float)m_10);
}
//计算ORB特征描述子
static void computeOrbDescriptor(const KeyPoint& kpt, const Mat& img, const Point* pattern, uchar* desc, int dsize, int WTA_K)
{
float angle = kpt.angle;
//angle = cvFloor(angle/12)*12.f;
angle *= (float)(CV_PI/180.f);
float a = (float)cos(angle), b = (float)sin(angle);
const uchar* center = &img.at(cvRound(kpt.pt.y), cvRound(kpt.pt.x));
int step = (int)img.step;
#if 1
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点的值
center[cvRound(pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a)*step + \
cvRound(pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b)]
#else
float x, y;
int ix, iy;
#define GET_VALUE(idx) \ //取旋转后一个像素点,插值法
(x = pattern[idx].x*a - pattern[idx].y*b, \
y = pattern[idx].x*b + pattern[idx].y*a, \
ix = cvFloor(x), iy = cvFloor(y), \
x -= ix, y -= iy, \
cvRound(center[iy*step + ix]*(1-x)*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix]*(1-x)*y + \
center[iy*step + ix+1]*x*(1-y) + center[(iy+1)*step + ix+1]*x*y))
#endif
if( WTA_K == 2 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)//每个特征描述子长度为32个字节
{
int t0, t1, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
val = t0 < t1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(2); t1 = GET_VALUE(3);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 1;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 3;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(10); t1 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 5;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 6;
t0 = GET_VALUE(14); t1 = GET_VALUE(15);
val |= (t0 < t1) << 7;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 3 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 12)
{
int t0, t1, t2, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1); t2 = GET_VALUE(2);
val = t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0);
t0 = GET_VALUE(3); t1 = GET_VALUE(4); t2 = GET_VALUE(5);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(6); t1 = GET_VALUE(7); t2 = GET_VALUE(8);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(9); t1 = GET_VALUE(10); t2 = GET_VALUE(11);
val |= (t2 > t1 ? (t2 > t0 ? 2 : 0) : (t1 > t0)) << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else if( WTA_K == 4 )
{
for (int i = 0; i < dsize; ++i, pattern += 16)
{
int t0, t1, t2, t3, u, v, k, val;
t0 = GET_VALUE(0); t1 = GET_VALUE(1);
t2 = GET_VALUE(2); t3 = GET_VALUE(3);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val = k;
t0 = GET_VALUE(4); t1 = GET_VALUE(5);
t2 = GET_VALUE(6); t3 = GET_VALUE(7);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 2;
t0 = GET_VALUE(8); t1 = GET_VALUE(9);
t2 = GET_VALUE(10); t3 = GET_VALUE(11);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 4;
t0 = GET_VALUE(12); t1 = GET_VALUE(13);
t2 = GET_VALUE(14); t3 = GET_VALUE(15);
u = 0, v = 2;
if( t1 > t0 ) t0 = t1, u = 1;
if( t3 > t2 ) t2 = t3, v = 3;
k = t0 > t2 ? u : v;
val |= k << 6;
desc[i] = (uchar)val;
}
}
else
CV_Error( CV_StsBadSize, "Wrong WTA_K. It can be only 2, 3 or 4." );
#undef GET_VALUE
}
reference
- Paper: ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF
- http://blog.csdn.net/hujingshuang/article/details/46984411
- http://blog.csdn.net/zouzoupaopao229/article/details/52625678
- https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000004200111
- http://www.cnblogs.com/ronny/p/4083537.html
- http://blog.csdn.net/luoshixian099/article/details/48523267
- http://blog.csdn.net/tiandijun/article/details/40679581
