ExtJS 学习总结 (一)-- MVVM框架概述
ExtJS是一种富客户端Rich Client框架,是基于JavaScript、CSS和HTML实现的,对多种主流的浏览器都兼容。
ExtJS发展到现在,已经到了ExtJS 6的系列版本了,参见ExtJS官方网址可以下载使用,以下内容基于ExtJS-6.0.0版本。
ExtJS重要的文件和目录:
build/examples目录:示例文件目录
build/ext-all.js文件:ExtJS的库文件(压缩)
build/ext-all-debug.js文件:调试应用程序时使用的ExtJS的库文件(带注释)
build/classic/theme-neptune/resources目录:海王星主题的ExtJS库目录
build/classic/theme-neptune/resources/images海王星主题的图片资源目录
theme-neptune-all.css、theme-neptune-all_1.css、theme-neptune-all_2.css这三个是海王星主题的样式文件
在tomcat安装目录中将ext-6.0.0目录全部拷贝到Tomcat的webapps目录下,即可在启动Tomcat之后直接访问localhost:8080/ext-6.0.0来打开示例。
在页面的head标签中引用ExtJS:
<script type="text/javascript" src="resources/js/extjs/ext-all-debug.js">script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"
href="resources/js/extjs/classic/theme-neptune/resources/theme-neptune-all.css" />编写一个简单的基于ExtJS的JS文件hello.js:
Ext.onReady(function(){
Ext.create('Ext.container.ViewPort',{ //创建ViewPort实例
layout: 'fit', //布局设置为fit
items: [{ //子组件设置
xtype: 'panel', //以xtype方式定义一个panel组件
title: '欢迎', //设置标题
html: "Hello World
" //设置html内容
}]
});
});在页面的head标签中引入编写的JS文件:
<script type="text/javascript" src="resources/js/hello.js">script>Ext.onReady函数会在DOM模型加载完毕后执行,无需等待页面所有资源都加载完毕后才执行。(onload事件需要等待页面所有资源加载完毕才会执行)
至此,我们已经可以在一个页面中引用extjs的库,并用extjs的语法来编写js文件,在页面加载的时候,Ext.onReady函数会执行我们引用的自定义js文件的内容。但是,对于一个大型的项目,将会有非常多的页面以及js文件,如果不对这些文件进行有效的管理,项目的开发和维护都会变得异常困难。所以我们需要借助现在已经发展比较成熟的前端框架来帮助我们维护这些页面和js文件。自ExtJS4系列以来,MVC框架开始被广泛应用,MVC框架概述,到现在已经出现了新的MVVM框架,MVVM框架概述。官方对MVC与MVVM框架的描述(翻译链接)
ExtJS应用的MVVM框架:
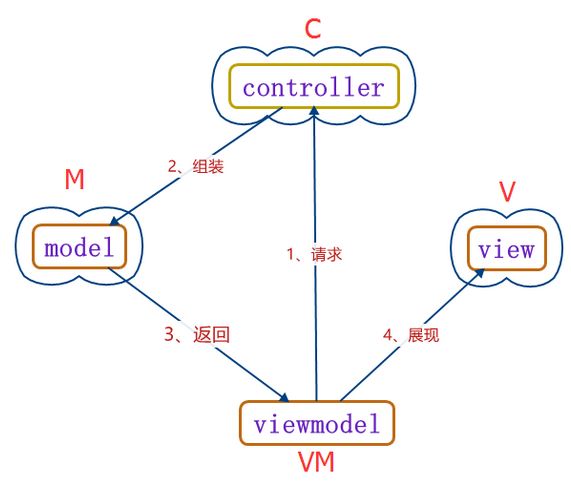
MVC与MVVM的区别就在于MVVM多了一个称为ViewModel的功能抽象视图模型。
M: 模型(Model), 应用的数据模型,由字段名和字段类型的数组定义,用于数据的存储、验证和转换。
V: 视图(View), 由可视化的组件构成视图,用来展现数据,提供与用户交互的用户界面。
C: 控制器(Controller), 用于维护视图和模型的逻辑,例如渲染视图,视图的路由,模型的实例化等等。
VM: 视图模型(View Model), 用来管理绑定到视图的数据及数据模型,自动更新数据。
在View需要展现数据的时候,由ViewModel发起请求到Controller组件,Controller会根据ViewModel中配置的Model组装好正确的数据视图并返回给ViewModel,最后再由ViewModel提供给View的组件来展示。View组件需要绑定ViewModel中的数据模型。
下面用官方的例子来看MVVM模型是如何工作的:
app.js(应用启动类文件)
Ext.application({
name: 'MyApp', //定义该应用的命名空间
extend: 'MyApp.Application', //继承自MyApp.Application
autoCreateViewport: 'MyApp.view.main.Main' //自动创建类名为MyApp.view.main.Main的ViewPort实例
});Application.js(应用程序类文件)
Ext.define('MyApp.Application', {
extend: 'Ext.app.Application', //继承自Ext.app.Application
name: 'MyApp', //应用程序命名空间
stores: [
// 添加全局共享的Store
],
launch: function () {
// 启动应用程序
}
});Main.js(Ext.Component的子类组件)
Ext.define('MyApp.view.main.Main', {
extend: 'Ext.container.Container', //继承自Ext.container.Container,一个Ext.Component的组件
xtype: 'app-main', //设置该类的xtype为'app-main'
controller: 'main', //设置该组件绑定的控制器是别名为'main'的控制器类
viewModel: {
type: 'main' //设置该组件的视图模型的类型是别名为'main'的视图模型类
},
layout: {
type: 'border' //设置该组件的布局类型为'border'
},
items: [{ //设置该组件的子组件集合
xtype: 'panel', //该组件使用xtype方式,类型为panel的组件
bind: {
title: '{name}' //标题绑定name字段
},
region: 'west', //border布局中的west region
html: '...
',
width: 250,
split: true,
tbar: [{ //设置top tool bar 顶部按钮集合
text: 'Button',
handler: 'onClickButton' //按钮的处理函数名称(在绑定的Controller中定义的)
}]
},{
region: 'center', //border布局中的center region
xtype: 'tabpanel', //使用xtype方式定义的tabpanel组件
items:[{ //设置tabpanel的字组件集合
title: 'Tab 1',
html: 'Content ...
'
}]
}]
});MainController.js(视图控制器类)
Ext.define('MyApp.view.main.MainController', {
extend: 'Ext.app.ViewController', //继承自Ext.app.ViewController的视图控制器类
requires: [
'Ext.MessageBox' //动态加载Ext.MessageBox类
],
alias: 'controller.main', //设置别名
onClickButton: function () { //定义名为'onClickButton'的事件处理函数,在视图中用此名称绑定处理函数
Ext.Msg.confirm('Confirm', 'Are you sure?', 'onConfirm', this);
},
onConfirm: function (choice) { //定义名为'onConfirm'的事件处理函数,在视图中用此名称绑定处理函数
if (choice === 'yes') {
//
}
}
});MainModel.js(视图模型类)
Ext.define('MyApp.view.main.MainModel', {
extend: 'Ext.app.ViewModel', //继承自Ext.app.ViewModel的视图模型类
alias: 'viewmodel.main', //设置别名
data: { //ViewModel为绑定它的视图提供数据
name: 'MyApp',
loremIpsum: 'Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.'
}
});整个MVVM框架已经搭建完成,现在只需要在页面的head中引用app.js文件,就可以加载该应用程序了。
<script type="text/javascript" src="path/app.js">script>Models和Stores这两个类提供了应用程序的数据信息。在上面的例子中,这两个类可以在ViewModel中进行配置,为ViewModel提供数据。其中,Models定义了数据模型的字段名和类型,Stores定义了数据模型的来源和读取方式,并将数据转化成组件可以识别的Record对象。
定义Model类:
Ext.define('MyApp.model.User', {
extend: 'Ext.data.Model', //继承自Ext.data.Model
fields: [ //设置字段名和字段类型的集合
{name: 'name', type: 'string'}, //字段名和字段类型
{name: 'age', type: 'int'}
]
});定义Store类:
Ext.define('MyApp.store.Users', {
extend: 'Ext.data.Store', //继承自Ext.data.Store
alias: 'store.users', //设置别名
model: 'MyApp.model.User', //设置该store类的model属性
data : [ //设置数据集合(此数据来源是in-line的配置,还可以使用外部的数据来源,只不过要使用proxy来指定数据来源)
{firstName: 'Seth', age: '34'},
{firstName: 'Scott', age: '72'},
{firstName: 'Gary', age: '19'},
{firstName: 'Capybara', age: '208'}
]
});