一、内容预览
二、概述
前面进程系列已经更新了四篇,本文(基于Android O源码),梳理应用进程的创建流程。
进程系列第一篇---进程基础
进程系列第二篇---Zygote进程的创建流程
Android进程第三篇---SystemServer进程创建流程
Android进程第四篇---SystemServer进程的启动流程
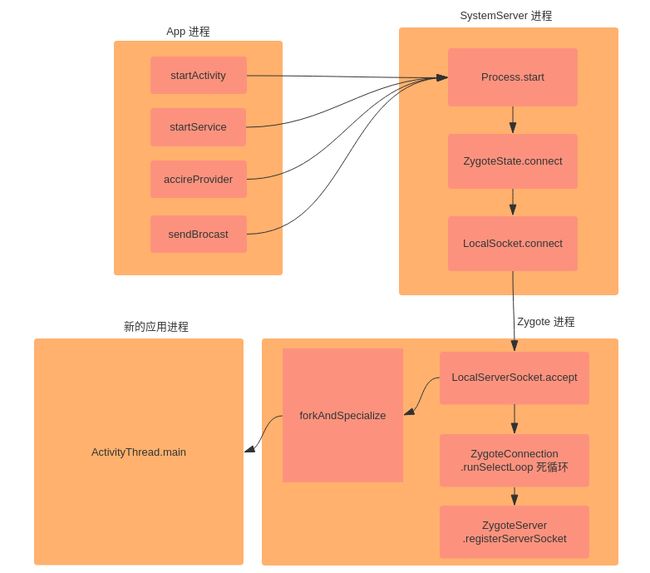
下面是一个进程创建架构图,可以了解一个进程创建的大概流程。
一共涉及了几个角色,发起进程、System进程、Zygote进程、新进程
发起进程
一个App进程可以通过startActivity等系统API请求SystemServer进程创建进程,SystemServer进程把这个活交给了Process.start,这个就是创建进程的入口。System进程
紧接着SystemServer进程通知ZygoteState创建LocalSocket,此时,SystemServer进程一直扮演的都是客户端的角色。Zygote进程
另一方面,在Android开机的过程中,Zygote进程就已经早早的启动了,所以LocalServerSocket就已经很早创建了,runSelectLoop开启了一个死循环一直accept客户端的连接,当SystemServer进程把LocalSocket创建出来之后,就可以使用LocalSocket send/recv数据了,此时就可以通知LocalServerSocket我要创建一个进程。进程fork完成之后,返回结果给System进程的AMS。新进程
Zygote进程把进程fork出来之后,需要做进程的初始化操作,比如设置进程异常的捕获方式,开始Binder线程池等等,最后进入了ActivityThread的main方法,一个有血有肉的进程正式被启动了。
三、进程的创建流程
3.1、发送创建请求,从Process类的start方法开始
所有进程创建的请求都交给Process,从Process类的start方法开始。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
/**
* Start a new process.
*
* If processes are enabled, a new process is created and the
* static main() function of a processClass is executed there.
* The process will continue running after this function returns.
*
*
If processes are not enabled, a new thread in the caller's
* process is created and main() of processClass called there.
*
*
The niceName parameter, if not an empty string, is a custom name to
* give to the process instead of using processClass. This allows you to
* make easily identifyable processes even if you are using the same base
* processClass to start them.
*
* When invokeWith is not null, the process will be started as a fresh app
* and not a zygote fork. Note that this is only allowed for uid 0 or when
* debugFlags contains DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER.
*
* @param processClass The class to use as the process's main entry
* point.
* @param niceName A more readable name to use for the process.
* @param uid The user-id under which the process will run.
* @param gid The group-id under which the process will run.
* @param gids Additional group-ids associated with the process.
* @param debugFlags Additional flags.
* @param targetSdkVersion The target SDK version for the app.
* @param seInfo null-ok SELinux information for the new process.
* @param abi non-null the ABI this app should be started with.
* @param instructionSet null-ok the instruction set to use.
* @param appDataDir null-ok the data directory of the app.
* @param invokeWith null-ok the command to invoke with.
* @param zygoteArgs Additional arguments to supply to the zygote process.
*
* @return An object that describes the result of the attempt to start the process.
* @throws RuntimeException on fatal start failure
*
* {@hide}
*/
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
return zygoteProcess.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
}
举例:当启动一个Activity的时候,发现Activity所在进程没有被创建,就会调用这个API进程进行创建。Process.start()方法是阻塞操作,等待直到进程创建完成并返回相应的新进程pid,才完成该方法。
ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, entryPointArgs);
}
为了更好的理解各个参数的含义,我debug一下,得到的各个参数值如下图(我调试的过程中发现,头条一启动就有很多进程跟着起来,做ROM工程师真是累啊,虽然只是打开一个应用,背后唤醒的都不止10个进程,每个进程都需要申请系统的资源,相信每一家ROM对进程的存活都有严格的把控!)
3.2、整理进程创建的请求参数
在Process.start之后,有几个链条式的调用,Process.start->ZygoteProcess.start->ZygoteProcess.startViaZygote,返回ZygoteState,ZygoteState封装了Socket的输入和输出流,zygoteInputStream与zygoteWrite,zygoteWrite可以把创建进程的参数从SystemServer进程传递到Zygote进程,zygoteInputStream可以把返回结果从Zygote进程返回到SystemServer进程。以下几个调用就是不断的封装并传递创建进程的请求参数。
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
195 public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
196 final String niceName,
197 int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
198 int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
199 int targetSdkVersion,
200 String seInfo,
201 String abi,
202 String instructionSet,
203 String appDataDir,
204 String invokeWith,
205 String[] zygoteArgs) {
206 try {
207 return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
208 debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
209 abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
210 } catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
211 Log.e(LOG_TAG,
212 "Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
213 throw new RuntimeException(
214 "Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
215 }
216 }
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
329 private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
330 final String niceName,
331 final int uid, final int gid,
332 final int[] gids,
333 int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
334 int targetSdkVersion,
335 String seInfo,
336 String abi,
337 String instructionSet,
338 String appDataDir,
339 String invokeWith,
340 String[] extraArgs)
341 throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
342 ArrayList argsForZygote = new ArrayList();
......
430 synchronized(mLock) {
431 return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
432 }
433 }
该过程主要工作是生成argsForZygote列表,把startViaZygote方法的参数存放到这个列表里面。并且调用zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult请求Zygotefork进程。
3.3、创建Socket,给Zygote进程发送进程创建的请求参数
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
454 @GuardedBy("mLock")
455 private ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
456 Preconditions.checkState(Thread.holdsLock(mLock), "ZygoteProcess lock not held");
457
458 if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
459 try {
460 primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSocket);
461 } catch (IOException ioe) {
462 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);
463 }
464 }
465
466 if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
467 return primaryZygoteState;
468 }
469
470 // The primary zygote didn't match. Try the secondary.
471 if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
472 try {
473 secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSecondarySocket);
474 } catch (IOException ioe) {
475 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);
476 }
477 }
478 //判断当前的abi来选择与zygote还是zygote64来进行通信
479 if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
480 return secondaryZygoteState;
481 }
482
483 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
484 }
通过前面的文章可知道,Zygote进程有两个Socket,这里当主zygote没能匹配成功,则尝试第二个mSecondarySocket来连接。
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/ZygoteProcess.java
92 public static ZygoteState connect(String socketAddress) throws IOException {
93 DataInputStream zygoteInputStream = null;
94 BufferedWriter zygoteWriter = null;
95 final LocalSocket zygoteSocket = new LocalSocket();
96
97 try {
98 zygoteSocket.connect(new LocalSocketAddress(socketAddress,
99 LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED));
100
101 zygoteInputStream = new DataInputStream(zygoteSocket.getInputStream());
102
103 zygoteWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
104 zygoteSocket.getOutputStream()), 256);
105 } catch (IOException ex) {
106 try {
107 zygoteSocket.close();
108 } catch (IOException ignore) {
109 }
110
111 throw ex;
112 }
113
114 String abiListString = getAbiList(zygoteWriter, zygoteInputStream);
115 Log.i("Zygote", "Process: zygote socket " + socketAddress + " opened, supported ABIS: "
116 + abiListString);
117
118 return new ZygoteState(zygoteSocket, zygoteInputStream, zygoteWriter,
119 Arrays.asList(abiListString.split(",")));
120 }
这个方法主要是建立了SystemServer(Client)这一边的Socket---LocalSocket,与Zygote进程的LocalServerSocket成功连接之后,获取这个LocalSocket的输入流zygoteInputStream与输出流zygoteWriter,并且将他们封装到ZygoteState中再返回。关于Socket的工作原理,移步本系列第三篇博客。
253 @GuardedBy("mLock")
254 private static Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
255 ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList args)
256 throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
257 try {
258 // Throw early if any of the arguments are malformed. This means we can
259 // avoid writing a partial response to the zygote.
260 int sz = args.size();
261 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
262 if (args.get(i).indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
263 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("embedded newlines not allowed");
264 }
265 }
266
........
//1、从ZygoteState中取出输入流和输出流
277 final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
278 final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
279 //2、用输入流将创建进程的参数传递给Zygote进程
280 writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
281 writer.newLine();
282
283 for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
284 String arg = args.get(i);
285 writer.write(arg);
286 writer.newLine();
287 }
288
289 writer.flush();
290
291 //创建Process.ProcessStartResult用于存放fork进程的返回结果
292 Process.ProcessStartResult result = new Process.ProcessStartResult();
293
294 // Always read the entire result from the input stream to avoid leaving
295 // bytes in the stream for future process starts to accidentally stumble
296 // upon.
//输入流读取Zygote进程创建进程之后返回的数据,保存在Process.ProcessStartResult中
297 result.pid = inputStream.readInt();
298 result.usingWrapper = inputStream.readBoolean();
299 //通过判断result.pid 是否创建成功
300 if (result.pid < 0) {
301 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
302 }
303 return result;
304 } catch (IOException ex) {
305 zygoteState.close();
306 throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
307 }
308 }
这段做的工作主要是从ZygoteState中取出输入流和输出流,然后和Server端的Zygote进程的LocketServerSocket进行通信。将AMS中创建进程的参数传递给Zygote进程。Zygote进程fork完成之后, inputStream.readInt()就能读取出返回结果,如果小于0,代表创建失败,不小于0代表创建成功。
这段代码存在一个问题,如果Zygote进程fork进程超时,System这段迟迟不能get到返回结果,会引起什么后果?
试想一下,当 AMS 需要创建进程时, 会通过 Socket 与 zygote 进程通信, 当 zygote 接收到请求后会 fork 出一个子进程, 并将其 pid 返回给 AMS。需要注意的是, 在收到 pid 之前, AMS 会一直持锁等待,而且这里持有的是AMS大锁, 所以就会 block 其他重要线程, 导致系统卡死,用户反馈内容也会主要围绕 "系统卡死" "按键没有反应" 等等。
那如何解决这个问题?google其实有注意到,准备加一个超时机制,但是一直没有加上,但是这种情况也是治标不治本,解决这种问题还是要具体分析,是内存碎片严重导致fork进程申请page失败,还是其他原因,需要根据Log具体对待。
3.4、Zygote进程接收请求参数
到这里,Client段的工作就全部看完了,现在去看看Socket的服务端。再次回顾一下那段“模板”代码。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
//1、创建ZygoteServer
ZygoteServer zygoteServer = new ZygoteServer();
try {
//2、创建一个Server端的Socket
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
//3、加载进程的资源和类
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
if (startSystemServer) {
//4、开启SystemServer进程,这是受精卵进程的第一次分裂
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
//5、启动一个死循环监听来自Client端的消息
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
//6、关闭SystemServer的Socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
//7、这里捕获这个异常调用MethodAndArgsCaller的run方法。
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
注释写的很详细了,不多做解释,直接看runSelectLoop方法。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteServer.java
136 void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
137 ArrayList fds = new ArrayList();
138 ArrayList peers = new ArrayList();
139 //将服务端LocalServerSocket的fd加进fds中
140 fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
141 peers.add(null);
142
143 while (true) {
144 StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
145 for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
146 pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
147 pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
148 pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
149 }
150 try {
//处理轮询状态,当pollFds有事件到来则往下执行,否则阻塞在这里
151 Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
152 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
153 throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
154 }
//当接收到客户端发出连接请求 或者数据处理请求到来,则往下执行;否则进入continue,跳出本次循环。
155 for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
156 if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
157 continue;
158 }
//当i为0的时候,创建ZygoteConnection,实质就创建LocalServerSocket
159 if (i == 0) {
160 ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
161 peers.add(newPeer);
//将LocalServerSocket的fd添加到fds
162 fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
163 } else {
将LocalServerSocket的fd取出来,执行runOnce
164 boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
165 if (done) {
//完成之后将fd与ZygoteConnection移除
166 peers.remove(i);
167 fds.remove(i);
168 }
169 }
170 }
171 }
172 }
173}
runSelectLoop中有一个while死循环,接收进程创建请求,当来了一个请求,就会走runOnce方法
78 /**
79 * Waits for and accepts a single command connection. Throws
80 * RuntimeException on failure.
81 */
82 private ZygoteConnection acceptCommandPeer(String abiList) {
83 try {
84 return createNewConnection(mServerSocket.accept(), abiList);
85 } catch (IOException ex) {
86 throw new RuntimeException(
87 "IOException during accept()", ex);
88 }
89 }
acceptCommandPeer中调用createNewConnection,返回值是一个ZygoteConnection,封装了mServerSocket的输入流mSocketReader与输出流mSocketOutStream,这个与Clinet端的ZygoteState有着异曲同工之妙啊。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
91 ZygoteConnection(LocalSocket socket, String abiList) throws IOException {
92 mSocket = socket;
93 this.abiList = abiList;
94
95 mSocketOutStream
96 = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
97
98 mSocketReader = new BufferedReader(
99 new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()), 256);
100
101 mSocket.setSoTimeout(CONNECTION_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
102
103 try {
104 peer = mSocket.getPeerCredentials();
105 } catch (IOException ex) {
106 Log.e(TAG, "Cannot read peer credentials", ex);
107 throw ex;
108 }
109 }
3.5、Zygote进程处理创建进程请求,fork进程
在ZygoteConnection创建好了之后,就执行runOnce真正处理进程的创建请求了。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
134 boolean runOnce(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
135
136 String args[];
137 Arguments parsedArgs = null;
138 FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
139
140 try {
//把进程创建的参数读取出来
141 args = readArgumentList();
142 descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
143 } catch (IOException ex) {
144 Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
145 closeSocket();
146 return true;
147 }
148
149 if (args == null) {
150 // EOF reached.
//参数为null,需要关闭之前创建的Socket,进程创建请求参数为null还没有仔细的调查过
151 closeSocket();
152 return true;
153 }
........
162
163 int pid = -1;
164 FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
165 FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
166
167 try {
//将进程创建请求参数整理成Arguments对象
168 parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);
........
238 //创建子进程,底层调用fork函数,返回值有两个,基于写时复制
239 pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
240 parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
241 parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.instructionSet,
242 parsedArgs.appDataDir);
243 } catch (ErrnoException ex) {
244 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
245 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
246 logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
247 } catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
248 logAndPrintError(newStderr,
249 "Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
250 }
251
252 try {
//pid==0代表是新创建的子进程
253 if (pid == 0) {
254 //关闭从Zygote进程继承而来的Socket
255 zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
256 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
257 serverPipeFd = null;
//处理子进程接下来的工作
258 handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
259
260 // should never get here, the child is expected to either
261 // throw Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
262 return true;
263 } else {
264 //大于0,是父进程,也就是Zygote进程
265 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
266 childPipeFd = null;
//处理父进程接下来的工作
267 return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
268 }
269 } finally {
270 IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
271 IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
272 }
273 }
在调用Zygote.forkAndSpecialize之前,需要调用readArgumentList把创建进程的请求参数从Socket中读取出来,放在一个名为result的String数组中。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
631 /**
632 * Reads an argument list from the command socket/
633 * @return Argument list or null if EOF is reached
634 * @throws IOException passed straight through
635 */
636 private String[] readArgumentList()
637 throws IOException {
......
649 int argc;
650
651 try {
652 String s = mSocketReader.readLine();
653
654 if (s == null) {
655 // EOF reached.
656 return null;
657 }
658 argc = Integer.parseInt(s);
659 } catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
660 Log.e(TAG, "invalid Zygote wire format: non-int at argc");
661 throw new IOException("invalid wire format");
662 }
663
664 // See bug 1092107: large argc can be used for a DOS attack
665 if (argc > MAX_ZYGOTE_ARGC) {
666 throw new IOException("max arg count exceeded");
667 }
668
669 String[] result = new String[argc];
670 for (int i = 0; i < argc; i++) {
671 result[i] = mSocketReader.readLine();
672 if (result[i] == null) {
673 // We got an unexpected EOF.
674 throw new IOException("truncated request");
675 }
676 }
677
678 return result;
679 }
参数有了就调用Zygote.forkAndSpecialize方法fork进程了,关于进程的fork,第三篇写的更详细,这里不赘述。
99 public static int forkAndSpecialize(int uid, int gid, int[] gids, int debugFlags,
100 int[][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int[] fdsToClose,
101 int[] fdsToIgnore, String instructionSet, String appDataDir) {
102 VM_HOOKS.preFork();
103 // Resets nice priority for zygote process.
104 resetNicePriority();
//jni技术调用fork函数
105 int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize(
106 uid, gid, gids, debugFlags, rlimits, mountExternal, seInfo, niceName, fdsToClose,
107 fdsToIgnore, instructionSet, appDataDir);
108 // Enable tracing as soon as possible for the child process.
109 if (pid == 0) {
110 Trace.setTracingEnabled(true);
111
112 // Note that this event ends at the end of handleChildProc,
113 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "PostFork");
114 }
115 VM_HOOKS.postForkCommon();
116 return pid;
117 }
3.6、进程创建成功,新进程做初始化
当forkAndSpecialize完成之后,进程就被创建出来了,但是这个进程是光秃秃的,还需一些工作要处理,即走进handleChildProc方法。
786 private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
787 FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
788 throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
.......
//设置进程名字
811 if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
812 Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
813 }
814
815 // End of the postFork event.
816 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
817 if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
818 WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
819 parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
820 VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(),
821 pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
822 } else {
//做进程的一些初始化操作,与System进程创建一致的
823 ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
824 parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
825 }
826 }
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
829 public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
830 ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
831 if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
832 Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
833 }
834
835 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
//见本系列第三篇文章3.5.1
836 RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
837 //见本系列第三篇文章3.5.2
838 RuntimeInit.commonInit();
//见本系列第三篇文章3.5.3
839 ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
//见本系列第三篇文章3.5.4
840 RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
841 }
842
zygoteInit与System进程创建是一致的,每个进程在创建出来之后,都需要做四件事情。
- 重定向log输出
- 通用的一些初始化,比如设置进程的异常捕获方式、时区等
- 调用nativeZygoteInit进行Zygote的初始化,开启Binder线程池
- 调用applicationInit进行应用的初始化
在此不赘述,可移步见本系列第三篇文章。这里看一下applicationInit进行应用的初始化。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
289 protected static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
290 throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
.....
303 final Arguments args;
304 try {
305 args = new Arguments(argv);
306 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
307 Slog.e(TAG, ex.getMessage());
308 // let the process exit
309 return;
310 }
.....
315 // 唤醒进程的main方法
316 invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
317 }
此处的args.startClass为android.app.ActivityThread.java,当fork System进程的时候,args.startClass为com.android.server.SystemServer.java。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
231 private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
232 throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
233 Class cl;
234
235 try {
236 cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
237 } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
238 throw new RuntimeException(
239 "Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
240 ex);
241 }
242
243 Method m;
244 try {
//"main是写死的,Android所有应用进程的入口就是android.app.ActivityThread.java中的main方法
245 m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
246 } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
247 throw new RuntimeException(
248 "Missing static main on " + className, ex);
249 } catch (SecurityException ex) {
250 throw new RuntimeException(
251 "Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
252 }
.......
266 throw new Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
267 }
invokeStaticMain主要反射了android.app.ActivityThread.java中的main方法,得到Method对象m,为了清除栈帧,为新创建的进行一个干净的环境,最后抛出一个异常Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller。这个异常会在ZygoteInit的main中被捕获。
frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
.....
//1、启动一个死循环监听来自Client端的消息
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
//2、关闭SystemServer的Socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
//3、这里捕获这个异常调用MethodAndArgsCaller的run方法。
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
捕获之后,调用MethodAndArgsCaller的run方法,终于进入了ActivityThread的main方法了,一个有血有肉的进程就启动成功了。
225 public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
226 implements Runnable {
227 /** method to call */
228 private final Method mMethod;
229
230 /** argument array */
231 private final String[] mArgs;
232
233 public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
234 mMethod = method;
235 mArgs = args;
236 }
237
238 public void run() {
239 try {
240 mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
241 } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
242 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
243 } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
244 Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
245 if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
246 throw (RuntimeException) cause;
247 } else if (cause instanceof Error) {
248 throw (Error) cause;
249 }
250 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
251 }
252 }
253 }
254}
进程被创建出来了,系统中资源和类我们就可以直接使用了,这是怎么回事?由于Android系统基本所有进程的创建都是交给Zygote进程创建的,而进程的fork基于写时复制技术,所以Zygote进程启动时候加载的资源也会被应用进程所使用,如下图,原来进程中所需要的资源,库等都是由它老子办好了,继承过来就行。资源的加载过程参考本系列第二篇博客。
四、总结
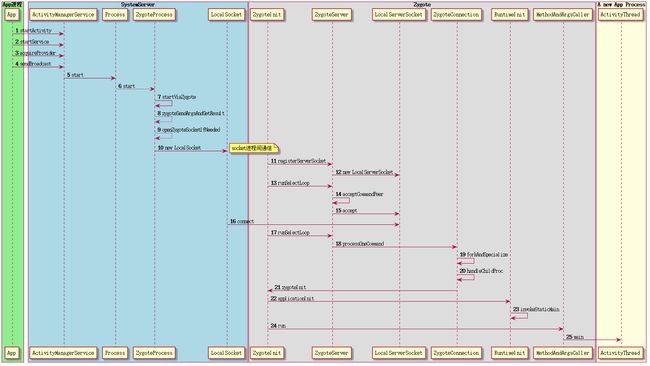
应用进程的创建和System进程的创建基本上一致,尤其是在fork进程之后的逻辑,是一模一样的,不同的是,System进程是Zygote进程的大儿子,由自己亲手创建,而其他应用进程是通过Process.start发送创建请求,Zygote帮忙创建的。这个过程其实不算复杂,创建流程的详细序列图如下。
进程的创建花了四篇的篇幅,从Zygote进程的创建,System进程的创建和启动,在到应用进程的创建,到此就结束了,下面将会梳理AMS中进程的数据结构---ProcessRecord。