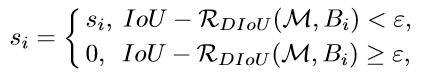YOLOV4学习系列(三) 结合代码讲解DIOU-NMS
前言
NMS(非最大抑制)是目标检测算法后处理中常用的技术,用来将redundant检测框给过滤掉。YOLOV4没有用经典的NMS,取而代之的是DIOU-NMS。本博客接下来会讲解其原理和代码实现。
原理
在经典的NMS中,得分最高的检测框和其它检测框逐一算出一个对应的IOU值,并将该值超过NMS threshold的框全部过滤掉。可以看出,在经典NMS算法中,IOU是唯一考量的因素。
但是在实际应用场景中,当两个不同物体挨得很近时,由于IOU值比较大,往往经过NMS处理后,只剩下一个检测框,这样导致漏检的错误情况发生。
基于此,DIOU-NMS就不仅仅考虑IOU,还考虑两个框中心点之间的距离。如果两个框之间IOU比较大,但是两个框的距离比较大时,可能会认为这是两个物体的框而不会被过滤掉。 其公式如下:
这里其实没有列出DIOU是具体如何计算的(后面会结合代码讲解)。公式大体上讲了得分最高的预测框M和其它框Bi的(IOU-DIOU)值比较小时,Bi的得分值Si仍然保持,否则,当(IOU-DIOU)大于NMS threshold值时,Si值就设成0了,即被过滤掉。
代码
我们来结合代码来看下YOLOV4的DIOU-NMS的具体实现。
// https://github.com/Zzh-tju/DIoU-darknet
// https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08287
void diounms_sort(detection *dets, int total, int classes, float thresh, NMS_KIND nms_kind, float beta1)
{
int i, j, k;
k = total - 1;
for (i = 0; i <= k; ++i) {
if (dets[i].objectness == 0) {
detection swap = dets[i];
dets[i] = dets[k];
dets[k] = swap;
--k;
--i;
}
}
total = k + 1;
for (k = 0; k < classes; ++k) {
for (i = 0; i < total; ++i) {
dets[i].sort_class = k;
}
qsort(dets, total, sizeof(detection), nms_comparator_v3);
for (i = 0; i < total; ++i)
{
if (dets[i].prob[k] == 0) continue;
box a = dets[i].bbox;
for (j = i + 1; j < total; ++j) {
box b = dets[j].bbox;
if (box_iou(a, b) > thresh && nms_kind == CORNERS_NMS)
{
float sum_prob = pow(dets[i].prob[k], 2) + pow(dets[j].prob[k], 2);
float alpha_prob = pow(dets[i].prob[k], 2) / sum_prob;
float beta_prob = pow(dets[j].prob[k], 2) / sum_prob;
dets[j].prob[k] = 0;
}
else if (box_iou(a, b) > thresh && nms_kind == GREEDY_NMS) {
dets[j].prob[k] = 0;
}
else {
if (box_diounms(a, b, beta1) > thresh && nms_kind == DIOU_NMS) {
dets[j].prob[k] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}上面代码重点在下面这段:
if (box_diounms(a, b, beta1) > thresh && nms_kind == DIOU_NMS) {
dets[j].prob[k] = 0;
box_diounms()就是用来计算diou的值,如下所示。
float box_diounms(box a, box b, float beta1)
{
boxabs ba = box_c(a, b);
float w = ba.right - ba.left;
float h = ba.bot - ba.top;
float c = w * w + h * h;
float iou = box_iou(a, b);
if (c == 0) {
return iou;
}
float d = (a.x - b.x) * (a.x - b.x) + (a.y - b.y) * (a.y - b.y);
float u = pow(d / c, beta1);
float diou_term = u;
return iou - diou_term;
}box_c是a和b框的最小外接框 ,
c是该最小外接框的对角线长的平方;
iou是经典的iou求法,即a、b框的交并比;
d为两框中心点距离的平方;
u值则是d/c的beta1次方。注意算diou值时需要引入一个新的参数beta1。 这个需要在cfg里面yolo层参数中指定,缺省为0.6。
最终得diou值为 iou-u, 跟上面原理中得公式完全一致。