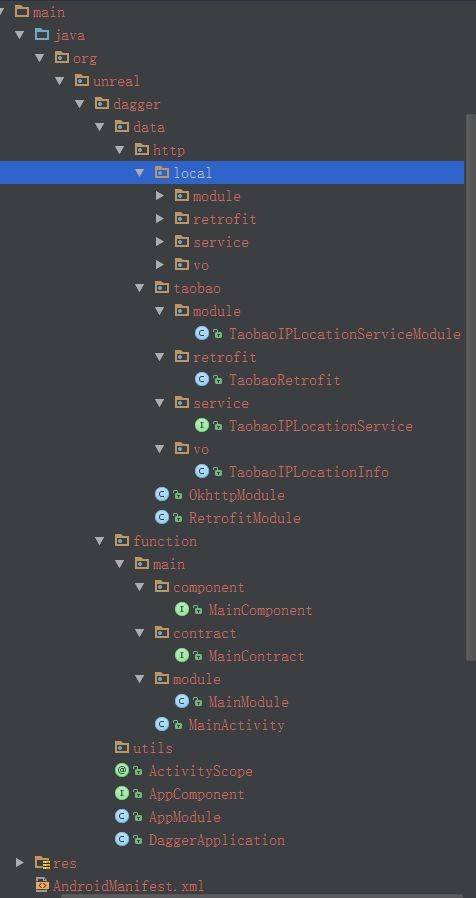
Android Dagger2 MVP架构 一看就明白
Dagger2介绍
好了,介绍一下Dagger2吧!
Dagger2 是Google 的新一代依赖注入框架(依赖注入不讲,你都看到这篇文章了,那你应该懂,如果不懂,请度娘、谷哥之,此文不废话),Dagger2是Dagger1的分支,但两个框架没有严格的继承关系,亦如Struts1 和Struts2 的关系!
那就有人问了,为什么要用Dagger2?
回答:解耦(DI的特性),易于测试(DI的特性),高效(不使用反射,google官方说名比Dagger快13%),易混淆(apt方式生成代码,混淆后依然正常使用)
学习成本
打开官网,映入眼帘的第一句话便是:
Dagger ‡ A fast dependency injector for Android and Java. - Google- 1
如果你是个想要很简单,并且速度很快的就能上手使用Dagger2的客官,你可以点击窗口右上角的X,关闭该文章了!
Dagger2的学习曲线相对比较陡峭,需要理解的概念也较多,需要一点一点的理解,Dagger2概念还是推荐看下面这篇文章。
Android:dagger2让你爱不释手-基础依赖注入框架篇
本文只讲基础概念和使用,具体的概念请参见官方文档或其他博文!
关键的注解
@Inject
这个注解是用来说明该注解下方的属性或方法需要依赖注入。(如果使用在类构造方法上,则该类也会被注册在DI容器中作为注入对象。很重要,理解这个,就能理解Presenter注入到Activity的步骤!)
@Provider
在@Module注解的类中,使用@Provider注解,说明提供依赖注入的具体对象
@Component
简单说就是,可以通过Component访问到Module中提供的依赖注入对象。假设,如果有两个Module,AModule、BModule,如果Component只注册了AModule,而没有注册BModule,那么BModule中提供的对象,无法进行依赖注入!
@SubComponent
该注解从名字上就能知道,它是子Component,会完全继承父Component的所有依赖注入对象!
@Sigleton
被注解的对象,在App中是单例存在的!
@Scope
用来标注依赖注入对象的适用范围。
@Named(@)
因为Dagger2 的以来注入是使用类型推断的,所以同一类型的对象就无法区分,可以使用@Named注解区分同一类型对象,可以理解为对象的别名!
Android Studio 配置Dagger2(eclipse 请点击右上角X)
Step 1
项目根目录下的build.gradle。根目录、根目录、根目录,重要事情说三遍!
在dependencies代码块中加入
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'- 1
加完成后的build.gradle如下
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.1.0'
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
// NOTE: Do not place your application dependencies here; they belong
// in the individual module build.gradle files
//配置DBFlow
}
}
allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url "https://www.jitpack.io" }
jcenter()
mavenCentral()
}
}
task clean(type: Delete) {
delete rootProject.buildDir
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
如果你使用DB-Flow 或 ButterKnif已经添加过了,就不用添加了!
allprojects的内容不需要与我贴出来的完全一致。
Step 2
使用Dagger2的项目下的build.gradle,一般都是app文件夹下的。
在build.gradle文件顶部 apply plugin: ‘com.android.application’ 下方添加
apply plugin: 'android-apt'- 1
dependencies代码块中添加Dagger2的依赖关系
//使用APT生成工具,生成需要的DI代码
apt 'com.google.dagger:dagger-compiler:2.5'
//JSR250的jar包,使用这个和使用glassFish的那个一样,仅为了使用@Inject 和@Named注解
provided 'javax.annotation:jsr250-api:1.0'
//Dagger2 的依赖
compile 'com.google.dagger:dagger:2.5'- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Step3 Make Project,使依赖生效!
配置单例对象,上代码!(还是配置,配置、配置)
分析一下,我们一般都需要哪些东西是单例的,Http 请求类,SharedPreference等等。
Step 1 创建ActivityScope
@Scope
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ActivityScope {
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
该类用于区分与@Sigleton或其他@Scope的作用域。
Strp2 创建module
我们首先来分析一下,需要哪些类是单例的,单例创建的,都和Application关联起来。
1、提供 shredPreference,创建AppModule
@Module
public class AppModule {
private Context context;
public AppModule(DaggerApplication application) {
this.context = application;
}
@Singleton
@Provides
public Context ProviderApplicationContext(){
return context;
}
@Singleton
@Provides
@Named("default")
public SharedPreferences providerDefaultSharedPreferences(){
return PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
@Named("encode")
public SharedPreferences providerEncodeSharedPreferences(){
return context.getSharedPreferences("encode",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
2、因为是使用的Retrofit 所以要提供 OkhttpClient ,RetrofitClient
创建OkhttpModule
@Module
public class OkhttpModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
@Named("cache")
public OkHttpClient providerAutoCacheOkHttpClient(){
HttpLoggingInterceptor interceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
interceptor.setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY);
Interceptor cacheInterceptor = new Interceptor() {
@Override
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Request request = chain.request();
Response response = chain.proceed(request);
String cacheControl = request.cacheControl().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(cacheControl)) {
cacheControl = "public, max-age=" + 3600 * 6 + " ,max-stale=2419200";
}
return response.newBuilder()
.header("Cache-Control", cacheControl)
.removeHeader("Pragma")
.build();
}
};
return new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(interceptor)
.addNetworkInterceptor(cacheInterceptor)
.retryOnConnectionFailure(true)
.connectTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
}
@Singleton
@Provides
@Named("default")
public OkHttpClient providerOkHttpClient(){
HttpLoggingInterceptor interceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
interceptor.setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY);
return new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addNetworkInterceptor(interceptor)
.retryOnConnectionFailure(true)
.connectTimeout(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
创建RetrofitModule
@Module
public class RetrofitModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
public LocalRetrofit providerLocalRetrofit(@Named("default") OkHttpClient okHttpClient){
return new LocalRetrofit(okHttpClient);
}
@Singleton
@Provides
public TaobaoRetrofit providerTaobaoRetrofit(@Named("cache") OkHttpClient okHttpClient){
return new TaobaoRetrofit(okHttpClient);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
这里因为有时候的http请求是针对多个地址的,所以我又封装了两个提供retrofit的类
TaobaoRetrofit
private static final String BASE_URL = "http://ip.taobao.com/";
private static Retrofit retrofit;
public TaobaoRetrofit(OkHttpClient okHttpClient) {
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.client(okHttpClient)
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create())
.addConverterFactory(FastJsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
}
public Retrofit getRetrofit() {
return retrofit;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
LocalRetrofit
public class LocalRetrofit {
private static final String BASE_URL = "http://xxxxxx.xxx.xxxx/";
private static Retrofit retrofit;
public LocalRetrofit(OkHttpClient okHttpClient) {
retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(BASE_URL)
.client(okHttpClient)
.addCallAdapterFactory(RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.create())
.addConverterFactory(FastJsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
}
public Retrofit getRetrofit() {
return retrofit;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
我希望网络请求中的Service对调用者是黑盒,调用者只需要知道调用哪个Service即可,创建过程不需要了解,所以又提供了ServiceModule
LocalServiceModule
@Module
public class LocalServiceModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
public UserService providerUserService(LocalRetrofit retrofit){
return retrofit.getRetrofit().create(UserService.class);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
TaobaoIPLocationServiceModule
@Module
public class TaobaoIPLocationServiceModule {
@Singleton
@Provides
public TaobaoIPLocationService proidverIPLocationServiceModule(TaobaoRetrofit taoBaoRetrofitClient) {
return taoBaoRetrofitClient.getRetrofit().create(TaobaoIPLocationService.class);
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
单例的module 创建完毕!
Step 3 创建AppCompontent(个人感觉类于Spring的Context类)
@Singleton
//关键代码在这!component会把Module里的提供的对象,注册到容器里
@Component(modules = {AppModule.class,
OkhttpModule.class,
RetrofitModule.class,
LocalServiceModule.class,
TaobaoIPLocationServiceModule.class})
public interface AppComponent {
//SubComponent 继承当前Component
MainComponent addSub(MainModule mainModule);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
Step 4 make Project

点击绿色下箭头按钮,make project。
Dagger2会自动生成Dagger前缀的Dagger注入工具。
Step5 改造Application
public class DaggerApplication extends Application {
private static AppComponent appComponent;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
}
public static DaggerApplication get(Context context) {
return (DaggerApplication) context.getApplicationContext();
}
private void setupApplicationComponent() {
//Dagger开头的注入类DaggerAppComponent
appComponent = DaggerAppComponent.builder()
//此时appModule方法是过时方法,因为我们没有使用到任何一个module中提供的对象
.appModule(new AppModule(this))
.build();
}
//获取AppComponent 以便于SubComponent继承
public AppComponent getAppComponent() {
if(appComponent == null){
this.setupApplicationComponent();
}
return appComponent;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
正片 MVP
提供了那么多对象,到底怎么用???
下面是真正的正片、正片、正片。
[码字。。。。好累 (?_?)]
Step1 创建Activity的module
因为Activity的类的构造器,我们无法加入@Inject注解,所以必须提供Module才能提供View接口的实例化对象。
@Module
public class MainModule {
private MainContract.View view;
//构造方法传递View 接口的实例化对象
public MainModule(MainContract.View view){
this.view = view;
}
//在DI容器中提供View接口的实例化对象
@ActivityScope
@Provides
public MainContract.View providerView(){
return view;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
Step2 创建Activity的Conponent
//生命周期管理
@ActivityScope
//很重要!这个Component应该是AppComponent的子Component,所以要使用这个注解
//不使用@Component注解的Dependents属性是因为希望能统一管理子Component
@Subcomponent(modules = MainModule.class)
public interface MainComponent {
//方法参数中,只能传递被注入对象!要在哪个类中注入,写哪个类,注入到父类没用!
void inject(MainActivity mainActivity);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Step3 改造AppComponent(重要)
在AppComponent类中添加一行
MainComponent addSub(MainModule mainModule);- 1
代码如下
@Singleton
@Component(modules = {AppModule.class,
OkhttpModule.class,
RetrofitModule.class,
LocalServiceModule.class,
TaobaoIPLocationServiceModule.class})
public interface AppComponent {
MainComponent addSub(MainModule mainModule);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Step3 MVP模式类中使用Dagger2
1、创建MainContract(不需要改造)
public interface MainContract {
interface View{
void showLocationInfo(TaobaoIPLocationInfo taobaoIPLocationInfo);
void showError(String message);
}
interface presenter{
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
2、创建Presenter(注意@Inject)
public class MainPresenter implements MainContract.presenter {
private final MainContract.View view;
private final SharedPreferences sharedPreferences;
private final TaobaoIPLocationService locationService;
private final UserService userService;
//此处关键,用来提供Presenter 的实例化对象
@Inject
public MainPresenter(MainContract.View view,
//注入Default SharedPreferences
@Named("default") SharedPreferences sharedPreferences,
TaobaoIPLocationService locationService,
UserService userService) {
this.view = view;
this.sharedPreferences = sharedPreferences;
this.locationService = locationService;
this.userService = userService;
}
//IP定位测试
public void main(){
locationService.getIPInfo("myip")
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.io())
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe(new Subscriber() {
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable e) {
view.showError(e.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onNext(TaobaoIPLocationInfo taobaoIPLocationInfo) {
view.showLocationInfo(taobaoIPLocationInfo);
}
});
}
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
3、Activity(需要关注addSub方法、Inject方法)
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements MainContract.View{
//注入presenter 对象
@Inject
MainPresenter mainPresenter;
private TextView city;
private TextView cityCode;
private TextView ip;
private TextView isp;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
setupActivityComponent();
bindView();
mainPresenter.main();
}
private void bindView() {
city = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.city);
cityCode = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.cityCode);
ip = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.ip);
isp = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.isp);
}
/**
* 初始化属于自己Activity的Component对象
* 本例将MainComponent添加成为AppComponent的子Component
*/
private void setupActivityComponent() {
DaggerApplication.get(this)
.getAppComponent()
//将AppComponent继承然后转换成MainComponent
//MainModule的构造器中传递的是View接口的实例化对象
.addSub(new MainModule(this))
//注入到当前类中
.inject(this);
}
/**
* MVP Presenter 中的回调
* @param taobaoIPLocationInfo IP定位后的返回信息
*/
@Override
public void showLocationInfo(TaobaoIPLocationInfo taobaoIPLocationInfo) {
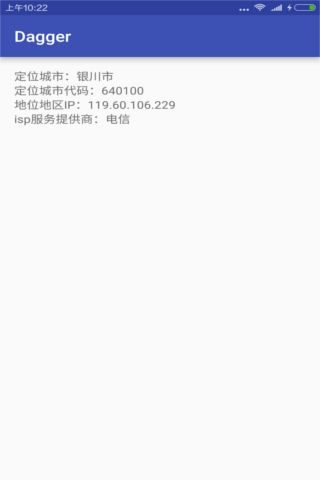
city.setText(String.format("定位城市:%s", taobaoIPLocationInfo.getData().getCity()));
cityCode.setText(String.format("定位城市代码:%s", taobaoIPLocationInfo.getData().getCity_id()));
ip.setText(String.format("地位地区IP:%s", taobaoIPLocationInfo.getData().getIp()));
isp.setText(String.format("isp服务提供商:%s", taobaoIPLocationInfo.getData().getIsp()));
}
/**
* MVP Presenter 中的回调
*/
@Override
public void showError(String message) {
Toast.makeText(this,message,Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
运行程序,然后看到下面的界面!Success
代码已经上传至Github,请下载后参照博客文档,自行体会,有很多东西只可意会、不可言传。
https://github.com/ChineseLincoln/Dagger2Mvp