整合Mybatis分为两种模式,一种是xml配置,一种是注解。(类似JPA)
我在这里重点放在xml配置上,因为如果想用注解的话,建议直接用jpa代替,因为Jpa有更成熟的CRUD接口更方便开发。我在后文中也会把注解方式说清楚。
大概介绍下流程:
- 借助idea实现mybatis逆向工程
- 用xml配置实现整合
- 用cmd命令行实现mybatis逆向工程
- 用mapping.xml配置实现数据交互
- 用注解的方式实现数据交互
首先我的开发环境:
jdk1.8+maven3+IDEA
1. mybatis逆向攻城
逆向工程方式很多,我目前接触到的就两种,一种是借助于ide开发工具,一种是在cmd中执行命令。(其实二者原理都一样,都是执行maven的generator命令,具体请看下文)。
1. 完善pom文件
4.0.0
springboot-mybatis
springboot-mybatis
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
jar
springboot-mybatis
Demo project for Spring Boot
springboot-integration
springboot-integration
1.0-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
1.3.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.35
com.alibaba
druid
1.0.11
com.alibaba
druid-spring-boot-starter
1.1.0
junit
junit
test
com.github.pagehelper
pagehelper
5.0.4
springboot-mybatis
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-surefire-plugin
true
org.mybatis.generator
mybatis-generator-maven-plugin
1.3.2
true
true
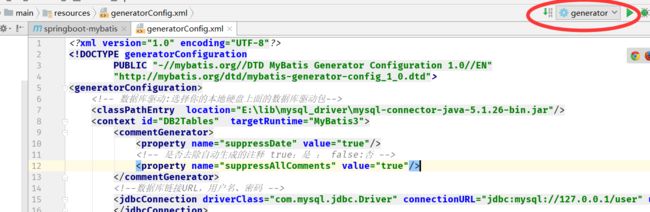
2. 逆向所需配置文件generatorConfig.xml
3. 利用IDE创建逆向工程启动类
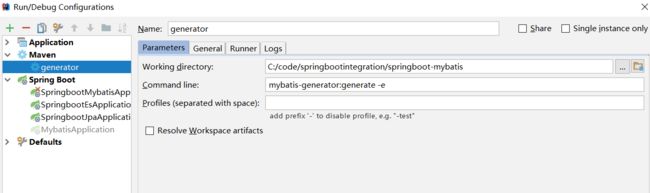
4. add一个Maven configuration
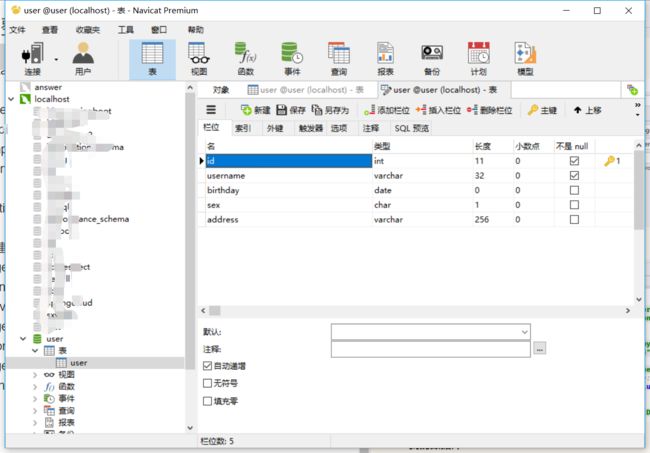
5. 我的数据库和表结构
6. application配置文件
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
name: test
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/user
username: root
password: root
# druid 连接池
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
filters: stat
maxActive: 20
initialSize: 1
maxWait: 60000
minIdle: 1
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: select 'x'
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
maxOpenPreparedStatements: 20
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.fant.model
#pagehelper分页插件
pagehelper:
helperDialect: mysql
reasonable: true
supportMethodsArguments: true
params: count=countSql
运行generator工程 自动生成代码
生成的文件
User.java
package com.fantj.model;
import java.util.Date;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Date birthday;
private String sex;
private String address;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username == null ? null : username.trim();
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex == null ? null : sex.trim();
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address == null ? null : address.trim();
}
}
UserMapper .java
package com.fantj.mapper;
import com.fantj.model.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int insert(User record);
int insertSelective(User record);
User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(User record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(User record);
List selectAll();
}
UserMapper.xml
id, username, birthday, sex, address
delete from user
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
insert into user (id, username, birthday,
sex, address)
values (#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}, #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{birthday,jdbcType=DATE},
#{sex,jdbcType=CHAR}, #{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR})
insert into user
id,
username,
birthday,
sex,
address,
#{id,jdbcType=INTEGER},
#{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{birthday,jdbcType=DATE},
#{sex,jdbcType=CHAR},
#{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
update user
username = #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
birthday = #{birthday,jdbcType=DATE},
sex = #{sex,jdbcType=CHAR},
address = #{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
update user
set username = #{username,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
birthday = #{birthday,jdbcType=DATE},
sex = #{sex,jdbcType=CHAR},
address = #{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
where id = #{id,jdbcType=INTEGER}
修改启动类
逆向生成代码后,我们还需要在启动类上添加一个@MapperScan("com.fantj.mapper")注解,告诉我们的Mapper需要扫描的包,这样就不用每个Mapper上都添加@Mapper注解了。
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.fantj.mapper")
public class MybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
完善controller和service
UserController.java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET,value = "/delete/{id}")
public void delete(@PathVariable("id")int id){
userService.delete(id);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST,value = "/insert")
public void insert(User user){
userService.insert(user);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST,value = "/update/{id}")
public void update(@RequestParam User user){
userService.update(user);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET,value = "/{id}/select")
public User select(@PathVariable("id")int id){
return userService.selectById(id);
}
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET,value = "/selectAll/{pageNum}/{pageSize}")
public List selectAll(@PathVariable("pageNum") int pageNum, @PathVariable("pageSize") int pageSize){
return userService.selectAll(pageNum,pageSize);
}
}
UserService.java
package com.fantj.service;
import com.fantj.model.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
/** 删除 */
public void delete(int id);
/** 增加*/
public void insert(User user);
/** 更新*/
public int update(User user);
/** 查询单个*/
public User selectById(int id);
/** 查询全部列表*/
public List selectAll(int pageNum, int pageSize);
}
UserServiceImpl .java
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* 删除
*
* @param id
*/
@Override
public void delete(int id) {
userMapper.deleteByPrimaryKey(id);
}
/**
* 增加
*
* @param user
*/
@Override
public void insert(User user) {
userMapper.insert(user);
}
/**
* 更新
*
* @param user
*/
@Override
public int update(User user) {
return userMapper.updateByPrimaryKey(user);
}
/**
* 查询单个
*
* @param id
*/
@Override
public User selectById(int id) {
return userMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
}
/**
* 查询全部列表,并做分页
*
* @param pageNum 开始页数
* @param pageSize 每页显示的数据条数
*/
@Override
public List selectAll(int pageNum, int pageSize) {
//将参数传给这个方法就可以实现物理分页了,非常简单。
PageHelper.startPage(pageNum,pageSize);
return userMapper.selectAll();
}
}
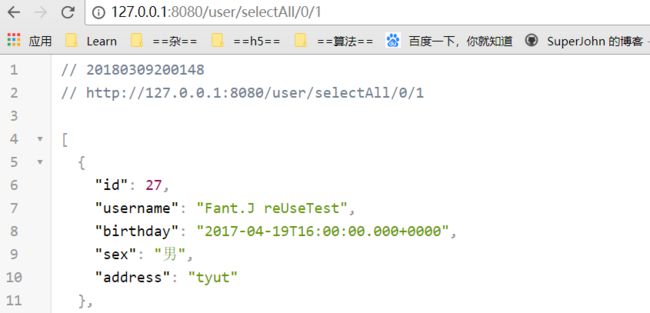
浏览器访问127.0.0.1/user/selectAll/0/1
说明我们成功了。
一个小甜点
有人问,get方法可以直接从浏览器地址中的url来测试,那post请求怎么测试呢?
个人建议用postman工具,也可以写测试类用代码来完成测试。也可以使用idea的一个测试工具Test RESTful Web Service
注解方式
好了,配置方式我们介绍完了,我在这里稍微聊一聊注解开发方式,个人建议如果想用注解开发,直接用jpa,可以更方便自己的开发。
mybatis java api :http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/java-api.html
UserMapper.java
package com.fantj.mapper;
import com.fantj.model.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
/*int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int insert(User record);
int insertSelective(User record);
User selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int updateByPrimaryKeySelective(User record);
int updateByPrimaryKey(User record);
List selectAll();*/
//如果实例对象中的属性名和数据表中字段名不一致,用@Result注解进行说明映射关系,我在这里只是告诉你怎么写
@Select("SELECT * FROM user")
@Results({
@Result(property = "username", column = "username"),
@Result(property = "sex", column = "sex"),
@Result(property = "address",column = "address")
})
List selectAll();
@Select("SELECT * FROM user WHERE id = #{id}")
@Results({
@Result(property = "sex", column = "sex"),
@Result(property = "username", column = "username")
})
User selectByPrimaryKey(int id);
@Insert({"INSERT INTO user(username,birthday,sex,address}) VALUES(#{userName}, #{birthday}, #{sex},#{address})"})
void insert(User user);
@Update("UPDATE user SET userName=#{userName} WHERE id =#{id}")
int updateByPrimaryKey(User user);
@Delete("DELETE FROM user WHERE id =#{id}")
int deleteByPrimaryKey(int id);
}
注解的一些解释
- @Select 是查询类的注解,所有的查询均使用这个
- @Result 修饰返回的结果集,关联实体类属性和数据库字段一一对应,如果实体类* 属性和数据库属性名保持一致,就不需要这个属性来修饰。
- @Insert 插入数据库使用,直接传入实体类会自动解析属性到对应的值
- @Update 负责修改,也可以直接传入对象
- @delete 负责删除
注意将application配置文件中的mybatis.mapper-locations:属性注视掉再启动项目。否则它会报错:Mapped Statements collection already contains value for com.fantj.mapper.UserMapper.insert 。意思是mapper中方法重复。
最后一个甜点
还有一个东西忘说了 -.-,就是用cmd来逆向生成代码。
声称语句
java -jar mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2.jar -configfile generator.xml -overwrite
src目录请忽略,这是生成的目录。
好了 干货都分享了,谢谢大家。0.0