#2020寒假集训#树形基础入门(Tree)代码笔记
树的基础定义
【无根树】一棵没有固定根结点的树(树→图:无向图)
(补充一)无根树可以任意指定一个节点作为根节点,将根节点“提起”,其它节点自然“垂下”
【无根树】在无根树的基础上,指定一个结点称为根 (树→图:有向图)
(补充二)有根树在很多时候仍以无向图表示,只是规定了结点之间的上下级关系
Part One 适用于无根树&有根树
- 森林(Forest):每个连通分量(连通块)都是树的图。按照定义,一棵树也是森林
- 生成树(Spanning Tree):一个连通无向图的生成子图,同时要求是树。即在图的边集中选择N-1条,将所有顶点连通
- 结点的深度(Depth):到根结点的路径上的边数
- 结点的度数(Degree):结点拥有子结点的数量
- 树的高度(Height):所有结点的深度的最大值
- 无根树的叶结点(Leaf Node):度数不超过1的结点(N==1时,只有一个结点,度数为0)
- 有根树的叶结点(Leaf Node):没有子结点的结点。
Part Two 只适用于有根树
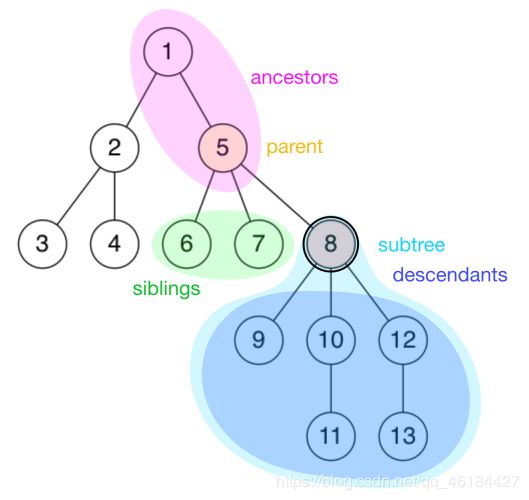
- 父亲结点**(Parent Node):从该结点到根路径上的第二个**结点(自己是第一个)根结点没有父结点
- 祖先结点**(Ancestor):一个结点到根结点的路径上**,除了它本身外的结点;根结点的祖先集合为空
- 子结点**(Child Node):如果 u 是 v 的父亲,那么 v 是 u 的子结点(二叉树区分子结点顺序**)
- 兄弟结点**(Sibling):同一个父亲的多个子结点**互为兄弟
- 后代(Descendant):子结点和子结点的后代**;如果 u 是 v 的祖先,那么 v 是 u 的后代(有些地方称子孙结点)
- 子树**(Subtree)**:删掉与父亲相连的边后,该结点所在的子图
特殊的树
- 链(Chain/Path Graph):满足与任一结点相连的边不超过2条的树
- 菊花/星星(Star):满足存在 u 使得所有除 u 以外结点均与 u 相连的树
- 二叉树(Binary Tree):每个结点最多只有两个儿子(子结点,且分左子结点和右子结点)
- 有根二叉树 (Rooted Binary Tree):二叉树中的有根树;大多数情况下, 二叉树一词均指有根二叉树
- 完整二叉树 (Full/Proper binary tree):每个结点的子结点数量均为 0 或者 2 (叶子结点or左右子树均非空)的二叉树
- 完全二叉树 (Complete Binary Tree):仅叶子结点度数为1,其他度数都达到最大,叶子结点从左到右依次排布
- 完美二叉树 (Perfect Binary Tree):所有叶子结点的深度均相同的二叉树(满二叉树:多指完美二叉树)
树的存储
Part One 链式前向星
#define fzhead EDGE(int _from,int _to,int _w,int _next)
#define fzbody from(_from),to(_to),w(_w),next(_next)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+10;
int head[maxn],edgecount;
struct EDGE
{
int from,to,w,next;
/*
Edge(){}是个用来给变量初始化0的函数
fzhead:fzbody{}为结构体赋初值
*/
EDGE(){}//后面别加分号
fzhead:fzbody{}//后面别加分号
}edge[maxn];
void init()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
edgecount=-1;
}
/*
i:边的编号;从u到v;w:权值;next:下一条边的编号
head[i]:由i出发的第一条边的编号
仅插入一条从u1开始的边,则next是-1,head[u1]为该边的编号
再读入u1开始的边,则其为第一条边,next是上一条边的编号
*/
void addEdge(int from,int to,int w)//链序和读入顺序相反
{
edge[++edgecount]=EDGE(from,to,w,head[from]);
head[from]=edgecount;
}
Part Two Vector邻接表
#define fzhead EDGE(int _to,int _w)
#define fzbody to(_to),w(_w)
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+10;
int n;
struct EDGE
{
int to,w;
/*
Edge(){}是个用来给变量初始化0的函数
fzhead:fzbody{}为结构体赋初值
*/
EDGE(){}//后面别加分号
fzhead:fzbody{}//后面别加分号
};
vector<EDGE> edge[maxn];
void init()
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) edge[i].clear();
}
/*
i:边的编号;从u到v;w:权值;next:下一条边的编号
head[i]:由i出发的第一条边的编号
仅插入一条从u1开始的边,则next是-1,head[u1]为该边的编号
再读入u1开始的边,则其为第一条边,next是上一条边的编号
*/
void addEdge(int from,int to,int w)//链序和读入顺序相反
{
edge[from].push_back(EDGE(to,w));
}
树的遍历
前言
- 按照结点被访问的顺序,进行标号,可以形成DFS序和BFS序
- 【DFS序的性质】
- 记录某结点第一次被访问到的序号和第二次被访问到的序号(也就是递归完退回来时候的序号)
两个序号之差就是子树的大小,同时两个序号之间连续的一段都在子树内
也就是说子树的关系被压缩到一维了,可以用一维的数据结构来维护了,比如线段树 - 对于树上任何一个结点,它祖先的DFS序一定小于它自己
- 【BFS序的性质】
- 深度越深的结点标号越大,按照标号从大到小遍历,就相当于从子树向根遍历了,不用递归
二叉树的深度优先搜索
- 先序遍历
先访问根节点,然后依次访问左儿子和右儿子 - 中序遍历
先访问左儿子,然后依次访问根节点和右儿子 - 后序遍历
先访问左儿子,然后依次访问右儿子和根节点 - 已知中序遍历和另外一个,可以还原整颗树
- ps:三序遍历的顺序可按照根结点被遍历的位置来记忆
Part One DFS深度优先搜索
**以链式前向星存储为例**
void DFS(int root)//传入根结点序号
{
num[root]=1;
vis[root]=true;
for(int i=head[root];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
if(vis[edge[i].to]==true) continue;//如果子结点已被访问则跳过(防无向图)
DFS(edge[i].to);
}
}
Part Two BFS广度优先搜索
**以链式前向星存储为例**
void BFS(int u)//传入根结点序号
{
Max=0;
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(u);
vis[u]=true;
while(!Q.empty())
{
int root=Q.front();
Q.pop();
for(int i=head[root];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
if(vis[edge[i].to]==true) continue;//如果子结点已被访问则跳过(防无向图)
Q.push(edge[i].to);
vis[edge[i].to]=true;
}
}
}
树的重心
定义
- 对于树上的每一个点,计算其所有子树中最大的子树结点数,这个值最小的点就是这棵树的重心
- 此定义中的 “子树”指无根树的子树,即包括“向上”的那棵子树,并且不包括整棵树自身
性质
- 以树的重心为根时,所有子树的大小都不超过整棵树大小的一半
- 树中所有点到某个点的距离和中,到重心的距离和是最小的;如果有两个重心,那么到它们的距离和一样
- 把两棵树通过一条边相连得到一棵新的树,那么新的树的重心在连接原来两棵树的重心的路径上
- 在一棵树上添加或删除一个叶子,那么它的重心最多只移动一条边的距离
求法(代码)
int get_barycenter(int root,int dady)
{
size[root]=1;//记录一棵子树的结点数(一棵子树的大小),root作根结点初始大小为1
Max[root]=0;
for(int i=head[root];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
if (edge[i].to!=dady)
{
get_barycenter(edge[i].to,root);//递归,从叶子结点大小为 1 开始回推赋值
size[root]+=size[edge[i].to];//结点数累加,对root根结点而言的
Max[root]=max(Max[root],size[edge[i].to]);//对root子树而言的
//对于树上的每一个root,计算其所有子树中最大的子树结点数
}
}
Max[root]=max(Max[root],n-size[root]);
/*
n为总结点数,定义中的**子树**指无根树的子树
size[edge[i].to]是向下的;n-size[root]是向上的
减去自身这整棵树的结点数,剩下的就是向上的子树的结点数啦
用向下的最大值,与向上的比较得到最终的最大值
*/
if (center==0||Max[root]<Max[center]) center=root;
//center初始化为0,还未被更新过值或得到更小的最大子树结点数,就用当前root更新重心center
return center;//center为重心编号
}
例题 POJ-2378-Tree Cutting
Description
After Farmer John realized that Bessie had installed a “tree-shaped” network among his N (1 <= N <= 10,000) barns at an incredible cost, he sued Bessie to mitigate his losses.
Bessie, feeling vindictive, decided to sabotage Farmer John’s network by cutting power to one of the barns (thereby disrupting all the connections involving that barn). When Bessie does this, it breaks the network into smaller pieces, each of which retains full connectivity within itself. In order to be as disruptive as possible, Bessie wants to make sure that each of these pieces connects together no more than half the barns on FJ.
Please help Bessie determine all of the barns that would be suitable to disconnect.
Input
- Line 1: A single integer, N. The barns are numbered 1…N.
- Lines 2…N: Each line contains two integers X and Y and represents a connection between barns X and Y.
Output
- Lines 1…?: Each line contains a single integer, the number (from 1…N) of a barn whose removal splits the network into pieces each having at most half the original number of barns. Output the barns in increasing numerical order. If there are no suitable barns, the output should be a single line containing the word “NONE”.
Sample Input
10
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
3 8
Sample Output
3
8
Hint
INPUT DETAILS:
The set of connections in the input describes a “tree”: it connects all the barns together and contains no cycles.
OUTPUT DETAILS:
If barn 3 or barn 8 is removed, then the remaining network will have one piece consisting of 5 barns and two pieces containing 2 barns. If any other barn is removed then at least one of the remaining pieces has size at least 6 (which is more than half of the original number of barns, 5).
AC代码
#include树的直径
定义
- 对于树上任意的两点,他们之间的距离都是固定的(也就是路径上的边权和)
- 对于距离最大的两点连成的链,我们称为树的直径
性质
- 对于树上任意一点x,与x之间距离最远的点一定是直径的两个端点之一
- 对于两棵树,如果一棵的直径是(u,v),另一棵是**(x,y)**
用一条边将两棵树相连,则直径两端点必然是 (x,y,u,v) 之中两点
求法
- 【First】从任意一个点出发找到离它最远的点x
- 【Second】从x出发找到离x最远的点y,则x和y就是直径的两个端点
代码(以BFS为例)
int BFS(int u)//传入根结点
{
Max=0;
memset(dis,0,sizeof(dis));//距离数组
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));//访问标记
queue<int> Q;
Q.push(u);
vis[u]=true;
int to=u;
while(!Q.empty())
{
int root=Q.front();
Q.pop();
used[root]=true;
for(int i=head[root];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
if(!vis[edge[i].to])//如果子结点已被访问则跳过(防无向图)
{
dis[edge[i].to]=dis[root]+edge[i].w;//从上往下累加总路程
if(dis[edge[i].to]>Max)//某一次比Max大的时候
{
Max=dis[edge[i].to];
to=edge[i].to;//用to标记Max最大时的终点
}
Q.push(edge[i].to);//从Max最大的终点继续BFS,若无更大的Max则队列为空return to;
vis[edge[i].to]=true;
}
}
}
return to;//返回的是从传入的根节点开始,最长路径的终点
}
**然后在int main()主函数中调用两次BFS函数**
int start=BFS(1);//第一次随便指定根结点
BFS(start);//第二次从返回的to(赋值给了start)开始(start为根结点,也是直径的一端)
例题 HDU-4514-湫湫系列故事——设计风景线
Description
随着杭州西湖的知名度的进一步提升,园林规划专家湫湫希望设计出一条新的经典观光线路,根据老板马小腾的指示,新的风景线最好能建成环形,如果没有条件建成环形,那就建的越长越好。
现在已经勘探确定了n个位置可以用来建设,在它们之间也勘探确定了m条可以设计的路线以及他们的长度。请问是否能够建成环形的风景线?如果不能,风景线最长能够达到多少?
其中,可以兴建的路线均是双向的,他们之间的长度均大于0。
Input
测试数据有多组,每组测试数据的第一行有两个数字n, m,其含义参见题目描述;
接下去m行,每行3个数字u v w,分别代表这条线路的起点,终点和长度。
[Technical Specification]
1. n<=100000
2. m <= 1000000
3. 1<= u, v <= n
4. w <= 1000
Output
对于每组测试数据,如果能够建成环形(并不需要连接上去全部的风景点),那么输出YES,否则输出最长的长度,每组数据输出一行。
Sample Input
3 3
1 2 1
2 3 1
3 1 1
Sample Output
YES
AC代码
#include树形DP
利用树形知识遍历求值等,实现状态转移
例题 HDU-1520-Anniversary party
Description
There is going to be a party to celebrate the 80-th Anniversary of the Ural State University. The University has a hierarchical structure of employees. It means that the supervisor relation forms a tree rooted at the rector V. E. Tretyakov. In order to make the party funny for every one, the rector does not want both an employee and his or her immediate supervisor to be present. The personnel office has evaluated conviviality of each employee, so everyone has some number (rating) attached to him or her. Your task is to make a list of guests with the maximal possible sum of guests’ conviviality ratings.
Input
Employees are numbered from 1 to N. A first line of input contains a number N. 1 <= N <= 6 000. Each of the subsequent N lines contains the conviviality rating of the corresponding employee. Conviviality rating is an integer number in a range from -128 to 127. After that go T lines that describe a supervisor relation tree. Each line of the tree specification has the form:
L K
It means that the K-th employee is an immediate supervisor of the L-th employee. Input is ended with the line
0 0
Output
Output should contain the maximal sum of guests’ ratings.
Sample Input
7
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1 3
2 3
6 4
7 4
4 5
3 5
0 0
Sample Output
5
AC代码
#include例题 HDU-2196-Computer
Description
A school bought the first computer some time ago(so this computer’s id is 1). During the recent years the school bought N-1 new computers. Each new computer was connected to one of settled earlier. Managers of school are anxious about slow functioning of the net and want to know the maximum distance Si for which i-th computer needs to send signal (i.e. length of cable to the most distant computer). You need to provide this information.
Hint: the example input is corresponding to this graph. And from the graph, you can see that the computer 4 is farthest one from 1, so S1 = 3. Computer 4 and 5 are the farthest ones from 2, so S2 = 2. Computer 5 is the farthest one from 3, so S3 = 3. we also get S4 = 4, S5 = 4.
Input
Input file contains multiple test cases.In each case there is natural number N (N<=10000) in the first line, followed by (N-1) lines with descriptions of computers. i-th line contains two natural numbers - number of computer, to which i-th computer is connected and length of cable used for connection. Total length of cable does not exceed 10^9. Numbers in lines of input are separated by a space.
Output
For each case output N lines. i-th line must contain number Si for i-th computer (1<=i<=N).
Sample Input
5
1 1
2 1
3 1
1 1
Sample Output
3
2
3
4
4
AC代码
**它涉及无根树非假定的根结点到其他节点的最远距离**
**考虑向上和向下的两种子树,并非树的直径类型题**
#include