Android Studio实现一个PC和Android端的聊天室
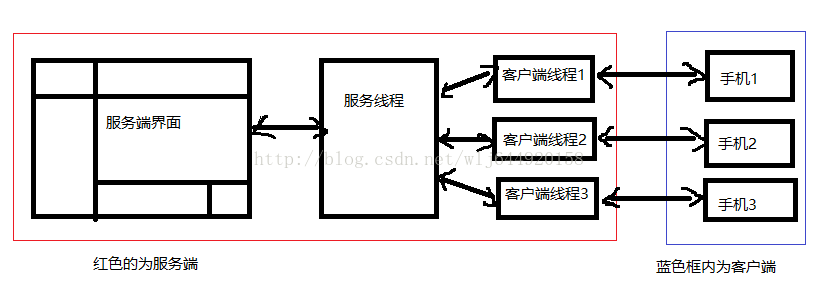
最近想学一下关于Socket 通信相关知识,所以果断来个demo,一个很老套的东西,一个简单的聊天室功能,服务端和android端可以一起聊天,好了不多说了,先上一个结构图
图是画的有点点丑,但是还是能理解的哈,接下来就可以动手了,反正是做个demo不需要想太多,我们打开AndroidStudio新建项目SocketDemo,工程创建完成后我们在项目下面创建一个javalib的module如下图
名字随便起,包名无所谓,我这里新建了一个Test 的类包含main方法,类如下
package com.example;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}接下来我们把服务端的界面创建起来,这里用到了java图形开发的东西,我是一个做android的也不是很熟悉,百度了半天哈哈先上一个完成图吧再来代码这样直观一点好解释,
完成图如下
服务端的界面就是这么简单,有了这个图下面代码就很容易就看懂了,
public class Chatroom extends JFrame implements ActionListener {
private JLabel clientLabel;//客户列表标签
private JList clientList;//客户列表
private JLabel historyLabel;//聊天记录标签
private JScrollPane jScrollPane;//嵌套在聊天记录外面的一个容器,让里面的内容可以滚动
private JTextArea historyContentLabel;//聊天记录显示的控件
private JTextField messageText;//服务端输入框
private JButton sendButton;//服务端发送的按钮
public Chatroom() {
clientLabel = new JLabel("客户列表");
clientLabel.setBounds(0, 0, 100, 30);
clientList = new JList<>();
clientList.setBounds(0, 30, 100, 270);
historyLabel = new JLabel("聊天记录");
historyLabel.setBounds(100, 0, 500, 30);
historyContentLabel = new JTextArea();
jScrollPane=new JScrollPane(historyContentLabel);
jScrollPane.setBounds(100, 30, 500, 230);
//分别设置水平和垂直滚动条自动出现
jScrollPane.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(
JScrollPane.HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED);
jScrollPane.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(
JScrollPane.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED);
messageText = new JTextField();
messageText.setBounds(100, 270, 440, 30);
sendButton = new JButton("发送");
sendButton.setBounds(540, 270, 60, 30);
//-----------代码分割线----------------
sendButton.addActionListener(this);
this.setLayout(null);
add(clientLabel);
add(clientList);
add(historyLabel);
add(jScrollPane);
add(messageText);
add(sendButton);
//设置窗体
this.setTitle("客服中心");//窗体标签
this.setSize(600, 330);//窗体大小
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//在屏幕中间显示(居中显示)
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出关闭JFrame
this.setVisible(true);//显示窗体
this.setResizable(false);
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (e.getSource() == sendButton) {
}
}首先是声明一些控件,这个不用说很好理解,代码分割线下面的是设置事件回调,我们只需要给button设置事件回调就行,在下面一行是设置这个Jframe 的Layout,我这里设置为null 的意思就是不需要任何布局方式,我们利用位置来自己定位,再往下的一系列add不用说就是把声明的控件添加到当前的JFrame里面,再往下就是堆窗口的设置了,这些都不是重点,略过,到这里我们服务端的界面就完成了.
接下来我们要实现的就是服务线程的代码了,服务端最核心的一个东西就是ServerSocket,我们通过serversocket循环监听客户端的链接,并且把已经链接的客户端保存起来就可以了,就是这么简单,先上代码
public class Server extends Thread {
boolean started = false;//标记服务是否已经启动
ServerSocket ss = null;
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.run();
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
started = true;
System.out.println("server is started");
} catch (BindException e) {
System.out.println("port is not available....");
System.out.println("please restart");
System.exit(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
while (started) {
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
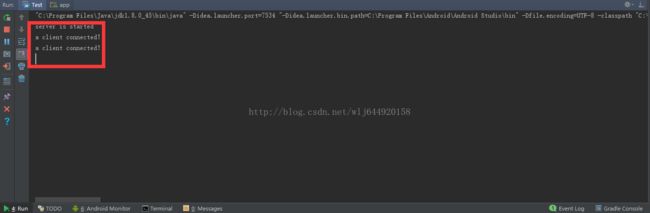
上面的就是server线程的一个整体的框架,开启的是本地8888端口,后面我们慢慢加进去东西就行了,isStarted这个是循环的标记位,我们在前面的Chatroom类的构造最下面加入启动server线程的代码跑起来看看
通过AS的控制台我们看到这个服务已经启动起来了,接下来我们就要监听客户端的到来了 ,这里我们定义一个Client线程类,作为服务端对应的客户,看代码
public class Client implements Runnable{
private Socket s;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
private boolean bConnected = false;
public Socket getSocket() {
return s;
}
public Client(Socket s) {
this.s=s;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
bConnected = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void send(String str) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void run() {
try {
while (bConnected) {
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
System.out.println("Client closed!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dis != null)
dis.close();
if (dos != null)
dos.close();
if (s != null) {
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Client client = (Client) o;
return s.equals(client.s);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return s.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.toString();
}
}
客户端类最重要的一个东西就是Socket类,在这个Client类里面加了get方法,toString,hash以及equals都是围绕这个socket来的,因为它是这个类的大佬,client类的整体框架就是这样了,另外对于消息的接受我们放在while循环里面,对于消息的发送我们调用socket 的writeUTF方法实现,客户端的东西弄完了,我们现在回到server类里面我们维护一个客户端的列表
List clients = new ArrayList(); public synchronized void addClient(Client client) {
clients.add(client);
}
public synchronized void removeClient(Client client) {
clients.remove(client);
} Socket s = ss.accept();
Client c = new Client(s, Server.this);
System.out.println("a client connected!");
new Thread(c).start();
addClient(c);先上布局文件

这里界面我们先不管,先把Android端的client线程写好
public class SocketThread extends Thread {
private Socket socket;
private boolean isConnected = false;
private DataInputStream dataInputStream;
private DataOutputStream dataOutputStream;
public SocketThread() {
}
public void disconnect() {
try {
dataInputStream.close();
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
// 创建一个Socket对象,并指定服务端的IP及端口号
socket = new Socket("10.137.213.28", 8888);
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~连接成功~~~~~~~~!");
isConnected = true;
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (isConnected) {
try {
while (isConnected) {
String str = dataInputStream.readUTF();
if (str != null) {
}
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dataInputStream != null)
dataInputStream.close();
if (dataOutputStream != null)
dataOutputStream.close();
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void sendMessage(String message) {
try {
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}到这里为止,我们看到我们的两个手机都能成功连接到服务端了对吧?其实已经成功了一大半了,接下来就是实现消息的接受和发送,我们来修改一下Server类,因为Server类要和服务端界面交互,这里我采用回调的方式通知服务界面客户端的变化,消息的变化,看下Server类加入接口后的代码
public class Server extends Thread {
public interface OnServiceListener {
void onClientChanged(List clients);
void onNewMessage(String message, Client client);
}
private OnServiceListener listener;
public void setOnServiceListener(OnServiceListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
boolean started = false;
ServerSocket ss = null;
List clients = new ArrayList();
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.run();
try {
ss = new ServerSocket(8888);
started = true;
System.out.println("server is started");
} catch (BindException e) {
System.out.println("port is not available....");
System.out.println("please restart");
System.exit(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
while (started) {
Socket s = ss.accept();
Client c = new Client(s, Server.this);
System.out.println("a client connected!");
new Thread(c).start();
addClient(c);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void newMessage(String msg, Client client) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onNewMessage(msg, client);
}
}
public synchronized void addClient(Client client) {
clients.add(client);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onClientChanged(clients);
}
}
public synchronized void removeClient(Client client) {
clients.remove(client);
if (listener != null) {
listener.onClientChanged(clients);
}
}
}
看下修改后的代码
public class Chatroom extends JFrame implements Server.OnServiceListener, ActionListener {
private JLabel clientLabel;
private JList clientList;
private JLabel historyLabel;
private JScrollPane jScrollPane;
private JTextArea historyContentLabel;
private JTextField messageText;
private JButton sendButton;
private Server server;
private StringBuffer buffers;
public Chatroom() {
buffers = new StringBuffer();
clientLabel = new JLabel("客户列表");
clientLabel.setBounds(0, 0, 100, 30);
clientList = new JList<>();
clientList.setBounds(0, 30, 100, 270);
historyLabel = new JLabel("聊天记录");
historyLabel.setBounds(100, 0, 500, 30);
historyContentLabel = new JTextArea();
jScrollPane=new JScrollPane(historyContentLabel);
jScrollPane.setBounds(100, 30, 500, 230);
//分别设置水平和垂直滚动条自动出现
jScrollPane.setHorizontalScrollBarPolicy(
JScrollPane.HORIZONTAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED);
jScrollPane.setVerticalScrollBarPolicy(
JScrollPane.VERTICAL_SCROLLBAR_AS_NEEDED);
messageText = new JTextField();
messageText.setBounds(100, 270, 440, 30);
sendButton = new JButton("发送");
sendButton.setBounds(540, 270, 60, 30);
sendButton.addActionListener(this);
this.setLayout(null);
add(clientLabel);
add(clientList);
add(historyLabel);
add(jScrollPane);
add(messageText);
add(sendButton);
//设置窗体
this.setTitle("聊天室");//窗体标签
this.setSize(600, 330);//窗体大小
this.setLocationRelativeTo(null);//在屏幕中间显示(居中显示)
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出关闭JFrame
this.setVisible(true);//显示窗体
this.setResizable(false);
server = new Server();
server.setOnServiceListener(this);
server.start();
}
@Override
public void onClientChanged(List clients) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
clientList.setListData(clients.toArray());
}
@Override
public void onNewMessage(String message, Client client) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
buffers.append(client.getSocket().getInetAddress().toString()+"\n");
buffers.append(message+"\n");
historyContentLabel.setText(buffers.toString());
}
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (e.getSource() == sendButton) {
Client client = (Client) clientList.getSelectedValue();
client.send(messageText.getText().toString());
buffers.append("服务器"+"\n");
buffers.append(messageText.getText().toString()+"\n");
}
}
} 我们再看看服务端Client修改的代码
public class Client implements Runnable{
private Socket s;
private DataInputStream dis = null;
private DataOutputStream dos = null;
private boolean bConnected = false;
private Server server;
public Socket getSocket() {
return s;
}
public Client(Socket s, Server ser) {
this.s=s;
this.server = ser;
try {
dis = new DataInputStream(s.getInputStream());
dos = new DataOutputStream(s.getOutputStream());
bConnected = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void send(String str) {
try {
dos.writeUTF(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
server.removeClient(this);
}
}
public void run() {
try {
while (bConnected) {
String str = dis.readUTF();
server.newMessage(str,this);
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
System.out.println("Client closed!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dis != null)
dis.close();
if (dos != null)
dos.close();
if (s != null) {
server.removeClient(this);
s.close();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Client client = (Client) o;
return s.equals(client.s);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return s.hashCode();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return s.toString();
}
}
我们先看看Client代码,这里我把Server传了进来,在Client接收到消息和异常退出的时候我们通过Server实例来调用对应的Server里面的方法,再回看Server里面,我们的消息接受和Client退出已经新的Client 的到来我们都通过回调的方式通知服务端的界面ChatRoom类,到这里服务端几个部分的通信基本是完成了,接下来我们完善android端的代码主要是实现消息的发送和接受,这里我们同样以回调的方式来实现,看下android端Client 的实现
public class SocketThread extends Thread {
public interface OnClientListener {
void onNewMessage(String msg);
}
private OnClientListener onClientListener;
public void setOnClientListener(OnClientListener onClientListener) {
this.onClientListener = onClientListener;
}
private Socket socket;
private boolean isConnected = false;
private DataInputStream dataInputStream;
private DataOutputStream dataOutputStream;
public SocketThread(OnClientListener onClientListener) {
this.onClientListener = onClientListener;
}
public void disconnect() {
try {
dataInputStream.close();
dataOutputStream.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
// 创建一个Socket对象,并指定服务端的IP及端口号
socket = new Socket("10.137.213.28", 8888);
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~连接成功~~~~~~~~!");
isConnected = true;
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while (isConnected) {
try {
while (isConnected) {
String str = dataInputStream.readUTF();
if (str != null) {
if (onClientListener != null) {
onClientListener.onNewMessage(str);
}
}
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dataInputStream != null)
dataInputStream.close();
if (dataOutputStream != null)
dataOutputStream.close();
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public void sendMessage(String message) {
try {
dataOutputStream.writeUTF(message);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
看下MainActivity 的实现
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements SocketThread.OnClientListener{
private SocketThread socketThread;
private StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder();
private TextView serviceTv;
private EditText contentEt;
private Button sendBtn;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
serviceTv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_service);
contentEt = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_content);
sendBtn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_send);
socketThread = new SocketThread(this);
socketThread.start();
sendBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
stringBuilder.append("我:\n");
stringBuilder.append(contentEt.getText().toString());
stringBuilder.append("\n");
serviceTv.setText(stringBuilder.toString());
socketThread.sendMessage(contentEt.getText().toString());
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
socketThread.disconnect();
}
@Override
public void onNewMessage(String msg) {
stringBuilder.append("服务器:");
stringBuilder.append("\n");
stringBuilder.append(msg);
stringBuilder.append("\n");
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
serviceTv.setText(stringBuilder.toString());
}
});
}
}
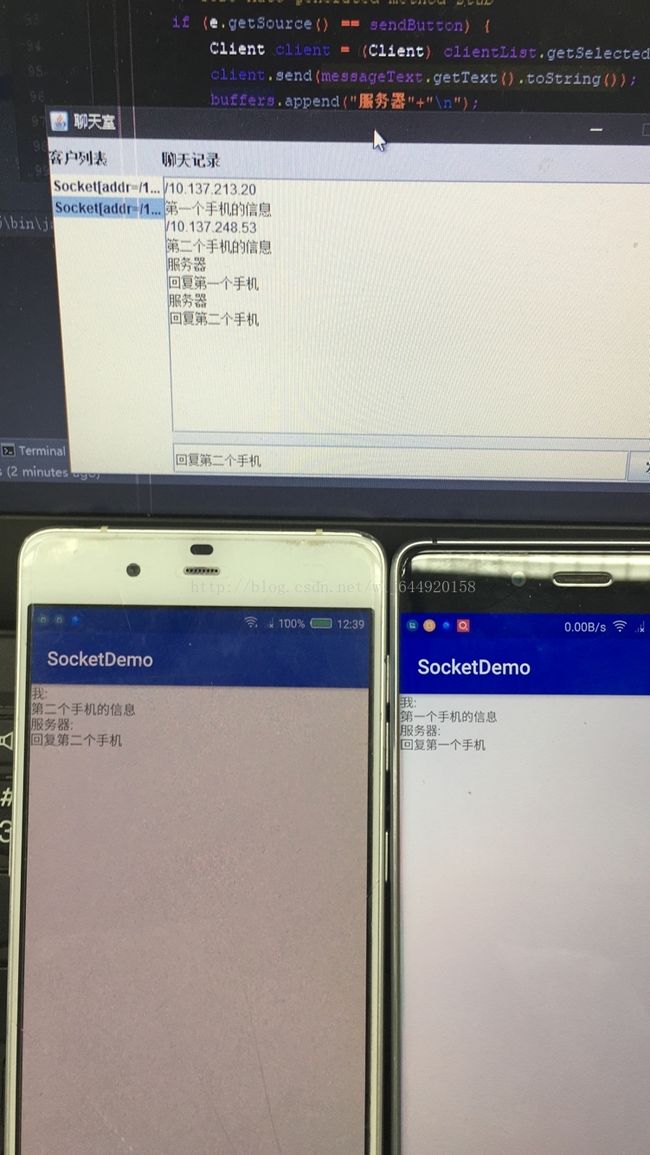
到这里我们实现了手机向服务器发送信息,服务器可以向指定的手机发送信息,这里我在Chatroom类里面实现的是通过点击选中左边的客户来进行消息的发送,我们可以看到基本的样子就是这样了,接下来要实现的就是一个手机发送的信息在另外一个手机能看到,这就需要服务器来转发消息了,这里需要一个小小的协议就是客户端要知道消息是来自谁的
所以我们在服务器转发或者发送信息的时候前面加上谁发送的,这里我们用一个$符号隔开,在android端收到信息的时候拆开就行了,我们修改一下Server类接收到消息的方法,然后新增一个发送消息的方法给Chatroom调用
public synchronized void snedMessage(String msg) {
for (Client client1 : clients) {
client1.send(msg);
}
}
public synchronized void newMessage(String msg, Client client) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onNewMessage(msg, client);
for (Client client1 : clients) {
if (!client1.equals(client)) {
client1.send(client1.getSocket().getInetAddress() + "#" + msg);
}
}
}
}ChatRoom类里面按钮的点击事件修改为
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (e.getSource() == sendButton) {
server.snedMessage("服务器#"+messageText.getText().toString());
buffers.append("服务器"+"\n");
buffers.append(messageText.getText().toString()+"\n");
historyContentLabel.setText(buffers.toString());
}
}android端接受到消息的处理
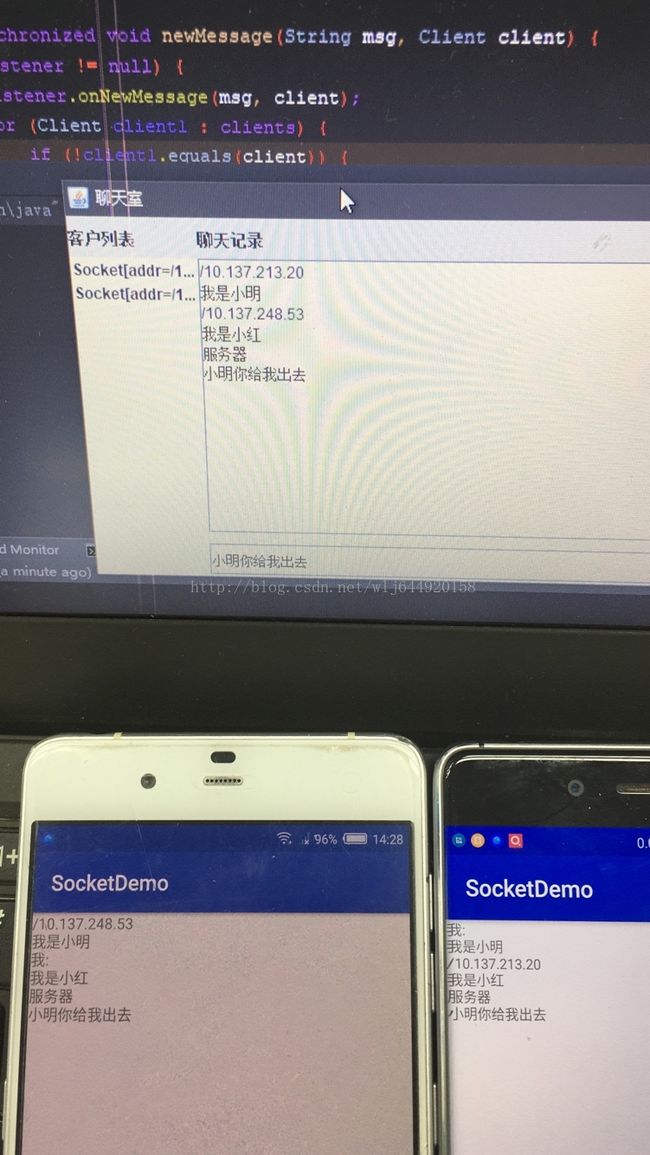
@Override
public void onNewMessage(String msg) {
Log.i("收到的信息i",msg);
String[] s = msg.split("#");
stringBuilder.append(s[0]);
stringBuilder.append("\n");
stringBuilder.append(s[1]);
stringBuilder.append("\n");
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
serviceTv.setText(stringBuilder.toString());
}
});
}到这里就大功告成了,通过Server类的转发我们后面还可以进行点对点通信,通过自定义协议我们可以完成各种各样的业务,自己动手实现一个及时通讯的框架就可以这样完成了,是不是很简单,代码我上传到github
https://github.com/wlj644920158/SocketDemo