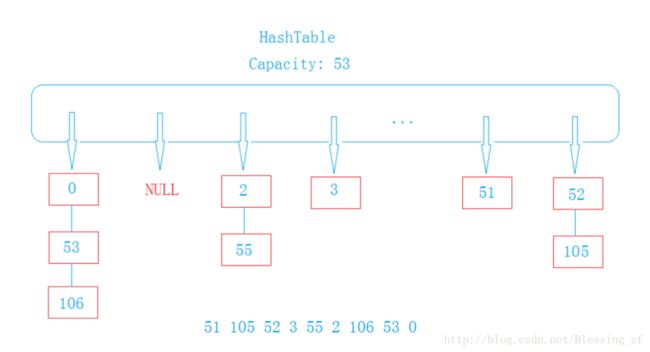
哈希表之开放定址法(闭散列方法)和拉链法
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
给定表M,存在函数f(key),对任意给定的关键字值key,代入函数后若能得到包含该关键字的记录在表中的地址,则称表M为哈希(Hash)表,函数f(key)为哈希(Hash) 函数。
散列函数能使对一个数据序列的访问过程更加迅速有效,通过散列函数,数据元素将被更快地定位。实际工作中需视不同的情况采用不同的哈希函数,通常考虑的因素有:
· 计算哈希函数所需时间
· 关键字的长度
· 哈希表的大小
· 关键字的分布情况
· 记录的查找频率
哈希算法有多种,最常用的就是开放定址法和开链法(哈希桶),之后又有公共溢出区等等算法。
首先,我们来通过图理解这两种主要的算法。
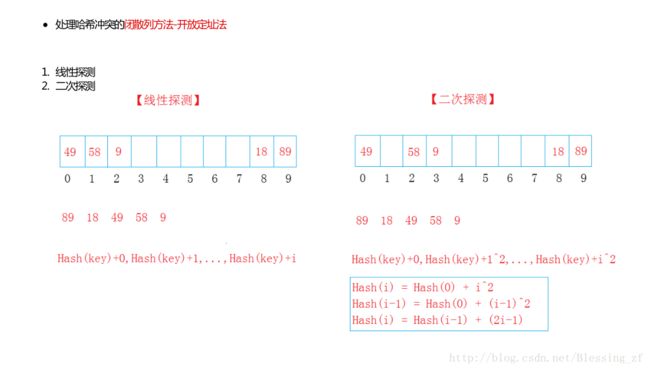
1. 开放定址法:Hi=(H(key) + di) MOD m,i=1,2,…,k(k<=m-1),其中H(key)为散列函数,m为散列表长,di为增量序列,可有下列三种取法:
(1)线性探测再散列;
基础版
#pragma once
#include Node;
public:
bool Insert(const K&key, const V&value)
{
CheckCapacity();
size_t index = HashFunc(key);
while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST)
{//
if (_tables[index]._key == key)
{
return false;
}
++index;
if (index == _tables.size())
{
index = 0;
}
}
_tables[index]._key = key;
_tables[index]._value = value;
_tables[index]._state = EXIST;
++_size;
return true;
}
protected:
size_t HashFunc(const K& key)
{
return key%_tables.size();
}
void Swap(HashTable& hash)
{
this->_tables.swap(hash._tables);
swap(_size, hash._size);
}
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _size * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable newTable;
newTable._tables.resize(newSize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
newTable.Insert(_tables[i]._key, _tables[i]._value);
}
this->Swap(newTable);
}
}
private:
size_t _size;
vector 进阶版(获取素数表来做哈希表容量解决哈希冲突,仿函数和BKDR哈希算法来解决key类型的转换问题)
template<class K>
struct _HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<> //特化string
class _HashFunc<string>
{
static size_t BKDRHash(const char * str)//字符串处理BKDRhash算法
{
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF);
}
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
return BKDRHash(key.c_str());
}
};
template<class K,class V,class __HashFunc=_HashFunc>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode Node;
public:
HashTable()
:_size(0)
{
_tables.resize(GetPrimenum(0));
}
bool Insert(const K&key, const V&value)
{
CheckCapacity();
size_t index = HashFunc(key);
while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST)
{
if (_tables[index]._key == key)
{
return false;
}
++index;
if (index == _tables.size())
{
index = 0;
}
}
_tables[index]._key = key;
_tables[index]._value = value;
_tables[index]._state = EXIST;
++_size;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
assert(key);
size_t index = HashFunc(key);
while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST)
{
if (_tables[index]._key == key)
{
return &_tables[index];
}
if (index == _tables.size() - 1)
{
index = 0;
}
++index;
}
return NULL;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)//伪删除,改状态
{
size_t index = HashFunc(key);
while (_tables[index]._state==EXIST)
{
if (_tables[index]._key == key)
{
_tables[index]._state = DELETE;
--_size;
return true;
}
if (index == _tables.size() - 1)
{
index = 0;
}
++index;
}
return false;
}
protected:
size_t HashFunc(const K& key)
{
__HashFunc h;
return h(key) % _tables.size(); //仿函数为了字符串到整型转换
//return key%_tables.size();
}
void Swap(HashTable& hash)
{
this->_tables.swap(hash._tables);
swap(_size, hash._size);
}
size_t GetPrimenum(size_t value) //获取素数表
{
const int Primesize = 28;
//ul unsigned long
static const unsigned long Primenum[Primesize] =
{
53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,
1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,
49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul,
786433ul,
1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul,
25165843ul,
50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul,
805306457ul,
1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};
for (int i = 0; i < Primesize; ++i)
{
if (Primenum[i] >value)
{
return Primenum[i];
}
}
return value;
}
void CheckCapacity()
{
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _size * 10 / _tables.size() >= 7)//保证表中有空间,而且利用率小于0.7
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable newTable;
newTable._tables.resize(GetPrimenum(_tables.size()));
//newTable._tables.resize(newSize);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
{
newTable.Insert(_tables[i]._key, _tables[i]._value);
}
this->Swap(newTable);
}
}
private:
size_t _size; //注意哈希表的_size和vector中size()的区别。
vector 注:其他代码和基础版一致
(2) di=1^2,-1^2,2^2,-2^2,⑶^2,…,±(k)^2,(k<=m/2)称二次探测再散列;
(3) di=伪随机数序列,称伪随机探测再散列。
后续会有补充…..