yolov3-tiny 训练一个检测器(1)
文章目录
- 一.数据收集和数据标注
- 二. 下载编译darknet
- 三. 数据格式转换
- 四 文件配置
- 五 开始训练
- 六 使用YOLO v3 训练自己的模型
一.数据收集和数据标注
1.收集相关数据
图像编号参见https://blog.csdn.net/Mihu_Tutu/article/details/103726384
数据增广参考https://blog.csdn.net/Mihu_Tutu/article/details/103728290
2.图像标注,本次使用的是Labeling,具体使用教程参考https://blog.csdn.net/syyyy712/article/details/80234287
在标注完成后,将制作好的数据集放到你的数据集文件夹内(我的是/home/xxx/dataset/VOC2007),其文件夹构成如图:

其中,JPEGImages里是你的所有图片,Annotation里是与你的图片一一对应的XML标注文件(如果某个图不包含物体,请在标注时随便圈一下再删除,随后保存,否则不会生成XML,会报错!)
3.接下来,在Main里创建一个训练与测试列表。在VOC2007文件夹内创建一个split.py,将下列代码复制进去:
import os
import random
# 训练集和测试比例分配
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations' # xml 位置
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
接着,命令行执行该文件
$ python split.py
执行后你应该能在Main里看到4个文件,里面分别存储了被作为四类数据的文件的名称。
二. 下载编译darknet
darknet安装教程详见yolo官网
三. 数据格式转换
labelImg使用的是VOC的数据格式,而YOLO则需要使用txt数据。因此,需要对数据格式进行转换。
在darknet/scripts文件夹下有一个文件voc_label就是干这个用的。
将该文件复制至darknet文件夹内,然后修改该文件,将上面部分修改的适配你的数据集,比如我只需要检测car,则改为:
sets=[('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')]
classes = ["car"] # 自己数据的类别名称
文件最下面两行可以删除:
os.system("cat 2007_train.txt 2007_val.txt 2012_train.txt 2012_val.txt > train.txt")
os.system("cat 2007_train.txt 2007_val.txt 2007_test.txt 2012_train.txt 2012_val.txt > train.all.txt")
然后执行该文件
$ python voc_label.py
需要注意的有
1. 需要先运行split.py
2. darknet/scripts/voc_label.py
注意 路径问题,非常容易出错
list_file.write('%s/VOCdevkit/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg\n'%(wd, year, image_id))
此时生成的文件中路径容易出现问题,wd是取文件的路径,可以换成绝对路径
list_file.write(' /xxx/.../VOCdevkit/VOC%s/JPEGImages/%s.jpg\n'%(year, image_id))
另一种方法:在图像标注中,将图片的格式选为yolo(图中为voc)
 此时可以直接得到 txt文件,此时darknet/scripts/voc_label.py需要简单的修改
此时可以直接得到 txt文件,此时darknet/scripts/voc_label.py需要简单的修改

conver_annotation 是将annotation中的xml文件转化成txt文件。在这里就不需要了。
四 文件配置
1 voc.names
修改data/voc.name(记得备份),里面放你的所有类的名称(回车分隔,最后一行无回车)。
2 cfg / yolov3-tiny.cfg
创建修改新的cfg / yolov3-tiny.cfg最上面部分,注释掉test对应部分,使用train部分。这里batch指每次读取了多少张图片,subdivisions是指将数据分为多少份输入,例如batch=64,subdivisions=16则是每次输入64/16=4张图同时训练,最后64张图的所有结果视为一个batch,共同优化。这里需要根据GPU显存自行调整。(想提高训练速度的话,应该是提高cfg中的batch值,并适当较少subdivision,这样net->batch=batch / subdivision适当变大,意味着每次参加训练的图片数目增加)

修改[yolo]层中 classes 个数 ,以及[yolo]层上面的[convolutuonal]层中的filters的个数 filters = 3 * (classes +5).
共有两处需要修改

3 cfg/voc.data
classes = 20
train = /.../.../2007_train.txt
valid = /.../.../2007_test.txt
names = data/voc.names
backup = backup
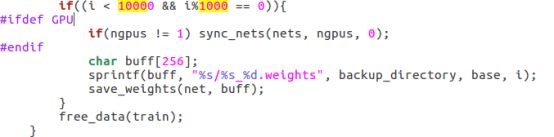
小技巧 Darknet 在模型训练中,保存的weights,1000以内每过100 保存一次,一般来说前面的weights效果都不好,因此可以改成1000次保存一次。
/darknet/examples/detector.c
五 开始训练
使用yolov3-tiny训练模型时,需要加载预训练模型,而官网没给tiny版的预训练模型,可以在原yolov3-tiny.weights上得到,只需如下指令。参考https://blog.csdn.net/chengyq116/article/details/83213699
./darknet partial ./cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg ./yolov3-tiny.weights ./yolov3-tiny.conv.15 15
然后训练:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-tiny.cfg yolov3-tiny.conv.15
# 可视化
./darknet detector train cfg/voc-helmet.data cfg/yolov3-voc-helmet.cfg darknet53.conv.74 | tee visualization/train_yolov3.log
新增部分
训练输入

This entire iteration/block represents one batch of images, divided according to our subdivisions. Have a look at the .cfg file I provided earlier to verify that batch = 64 and subdivision = 8. Looking at the image above, the training iteration has 8 groups of 8 images, reflecting these specific settings.
整个迭代/块代表一批图像,根据我们的细分划分。 看一下我之前提供的.cfg文件,以验证batch = 64和subdivvision =8。看上图,训练迭代有8组,每组8张图像,反映了这些特定的设置。
![]()
9798 indicates the current training iteration/batch.
0.370096 is the total loss.
0.451929 avg is the average loss error, which should be as low as possible. As a rule of thumb, once this reaches below 0.060730 avg, you can stop training.
0.001000 rate represents the current learning rate, as defined in the .cfg file.
3.300000 seconds represents the total time spent to process this batch.
The 627072 images at the end of the line is nothing more than 9778 * 64, the total amount of images used during training so far.
![]()
Region Avg IOU: 0.326577 is the average of the IOU of every image in the current subdivision. A 32,66% overlap in this case, this model still requires further training.
Class: 0.742537 still figuring this out
Obj: 0.033966 still figuring this out
No Obj: 0.000793 still figuring this out
The Avg Recall: 0.12500 is defined in code as recall/count, and thus a metric for how many positives YOLOv2 detected out of the total amount of positives in this subdivision. In this case only one of the eight positives was correctly detected.
count: 8 is the amount of positives (objects to be detected) present in the current subdivision of images (subdivision with size 8 in our case). Looking at the other lines in the log, you'll see there are also subdivision that only have 6 or 7 positives, indicating there are images in that subdivision that do not contain an object to be detected.
新增结束
随着训练过程进行,IOU应当会越来越高,例如对于我的任务最终都在75%左右。训练好的模型会被存储在darknet/backup中,名字如yolov3-voc_900.weights,这里的数字是执行epoch的数目。YOLO默认最多只会存储到900,后面虽然程序没停,但这个backup不会再增加。所以不要以程序停止作为训练结束的标志。
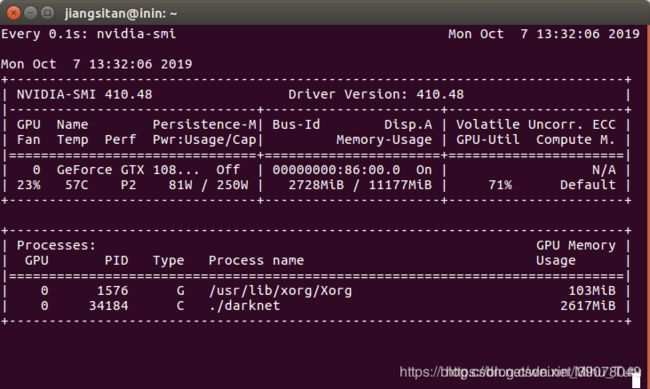
训练过程中可以查看GPU显存占用情况。nvidia-smi可以,但是只能查看一次。如果需要一直监控可执行
watch -n 0.1 nvidia-smi
其中-n后面的数字是多少秒刷新一次。
 未完待续
未完待续
参考 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39078049/article/details/102295561
六 使用YOLO v3 训练自己的模型
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29377279/article/details/83141239
https://blog.csdn.net/lumingha/article/details/89038863
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21578849/article/details/84980298?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.nonecase&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-1.nonecase