程序的本质之二ELF文件的文件头、section header和program header
操作系统:CentOS Linux release 7.7.1908
内核版本:3.10.0-1062.1.1.el7.x86_64
运行平台:x86_64
参考文献:http://refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/
本文根据/usr/include/elf.h文件和程序编译的详细过程文中所述的tanglinux来分析可执行文件的文件头、section header和program header的构成。
本文只介绍32位的可执行文件,64位的可执行文件与32位的构成基本一致,除了地址和偏移量的长度不同以外。Elf32_Half、Elf32_Section和Elf32_Versym等类型都是16位的无符号整数;Elf32_Addr和Elf32_Off都是32位的无符号整数;Elf32_Word和Elf32_Sword分别为32位的无符号和有符号整数(带S);Elf32_Xword和Elf32_Sxword分别为64位的无符号和有符号整数(带S)。
一、ELF文件头
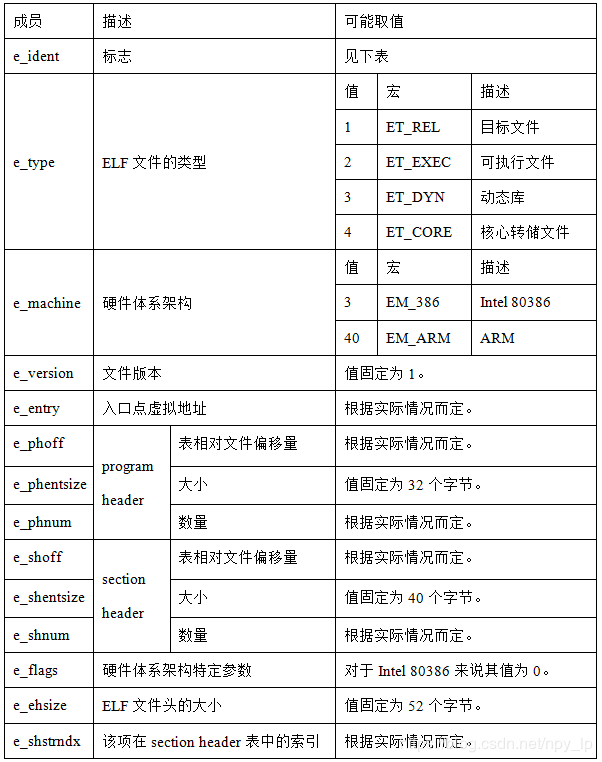
Linux可执行文件采用ELF(Executable and Linkable Format)格式来存储数据。每个ELF文件都以以下的数据来开头:
#define EI_NIDENT (16)
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf32_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf32_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf32_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf32_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf32_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf32_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf32_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf32_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf32_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf32_Ehdr;从中可知,ELF文件中的主要内容为program header和section header,两者的大小、在ELF文件中的位置和数量都能通过文件头来获取。而后又可以通过program header来获得每个segment的属性,通过section header来获得每个section的属性。
ELF文件头的说明如下表所示:
其中,由于每个section header的大小是固定的,而它们的名称属性不可能一样长,所以需要一个专门的string section来保存它们的名称属性,而用来描述这个string section的section header在section表中的位置就由e_shstrndx来确认(e_shoff+ e_shentsize* e_shstrndx),以达到快速查询的目的。
如果e_phnum的值为PN_XNUM(即0xffff),则表示program header的数量超过了它所能存储的最大值,因此它的值另外保存在索引号为SHN_UNDEF(即0)的section的Elf32_Shdr. sh_info的位置。
ELF文件头的标志位总共有16个字节的大小,目前只用到9个字节,剩余字节的值都为0。它们的说明如下表所示:
其中,2's complement的意思就是补码,而1's complement的意思为反码。
通过执行readelf命令可获得可执行文件tanglinux的文件头信息,如下所示:
$ readelf -h tanglinux
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF32
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: EXEC (Executable file)
Machine: Intel 80386
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x80482e0
Start of program headers: 52 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 5944 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 52 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 32 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 9
Size of section headers: 40 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 31
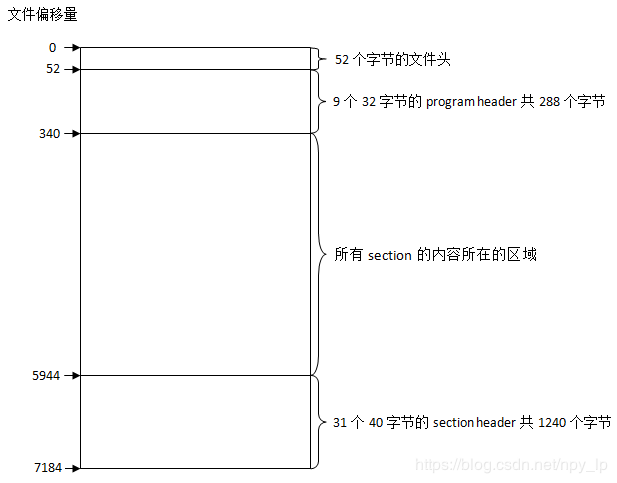
Section header string table index: 30从以上所输出的文件头信息可知可执行文件tanglinux中数据的大概分布,如下图所示:
文件的总大小为7184个字节。
二、ELF文件中的section header
section header用来描述每个section的特性,如大小、类型、名称等等,它们都使用以下的数据结构来表示:
typedef struct
{
Elf32_Word sh_name; /* Section name (string tbl index) */
Elf32_Word sh_type; /* Section type */
Elf32_Word sh_flags; /* Section flags */
Elf32_Addr sh_addr; /* Section virtual addr at execution */
Elf32_Off sh_offset; /* Section file offset */
Elf32_Word sh_size; /* Section size in bytes */
Elf32_Word sh_link; /* Link to another section */
Elf32_Word sh_info; /* Additional section information */
Elf32_Word sh_addralign; /* Section alignment */
Elf32_Word sh_entsize; /* Entry size if section holds table */
} Elf32_Shdr;在ELF文件中,每个section header都有一个索引号,从1开始,依次递增。不过section header表的开头必须定义一个类型为SHT_NULL的表项,它的索引号为SHN_UNDEF(也就是0)。由于section header使用相同的数据结构来定义,并且它们的大小相同,所以所有的section header依次存储在一起看起来就是一个表,因此可以叫它section header表。类似的,所有program header看起来也是一个表。
1、sh_name表示section的名称。由于每个section名称的长度不相同,并且为了节约空间,于是就将所有section的名称都存放在一个特定的名叫.shstrtab的section(文件头信息中的Elf32_Ehdr. e_shstrndx就是用来快速查找它)中,所以这里的sh_name的值指的就是在这个特定section中的偏移量,通过它可以获得一个字符串,也就是所需要的section名。0值表示无名称,一般用于类型为SHT_NULL的section中。
2、sh_type表示section的类型。它可能的取值有以下这些:
#define SHT_NULL 0 /* Section header table entry unused */
#define SHT_PROGBITS 1 /* Program data */
#define SHT_SYMTAB 2 /* Symbol table */
#define SHT_STRTAB 3 /* String table */
#define SHT_RELA 4 /* Relocation entries with addends */
#define SHT_HASH 5 /* Symbol hash table */
#define SHT_DYNAMIC 6 /* Dynamic linking information */
#define SHT_NOTE 7 /* Notes */
#define SHT_NOBITS 8 /* Program space with no data (bss) */
#define SHT_REL 9 /* Relocation entries, no addends */
#define SHT_SHLIB 10 /* Reserved */
#define SHT_DYNSYM 11 /* Dynamic linker symbol table */
#define SHT_INIT_ARRAY 14 /* Array of constructors */
#define SHT_FINI_ARRAY 15 /* Array of destructors */
#define SHT_PREINIT_ARRAY 16 /* Array of pre-constructors */
#define SHT_GROUP 17 /* Section group */
#define SHT_SYMTAB_SHNDX 18 /* Extended section indeces */
#define SHT_NUM 19 /* Number of defined types. */
#define SHT_LOOS 0x60000000 /* Start OS-specific. */
#define SHT_GNU_ATTRIBUTES 0x6ffffff5 /* Object attributes. */
#define SHT_GNU_HASH 0x6ffffff6 /* GNU-style hash table. */
#define SHT_GNU_LIBLIST 0x6ffffff7 /* Prelink library list */
#define SHT_CHECKSUM 0x6ffffff8 /* Checksum for DSO content. */
#define SHT_LOSUNW 0x6ffffffa /* Sun-specific low bound. */
#define SHT_SUNW_move 0x6ffffffa
#define SHT_SUNW_COMDAT 0x6ffffffb
#define SHT_SUNW_syminfo 0x6ffffffc
#define SHT_GNU_verdef 0x6ffffffd /* Version definition section. */
#define SHT_GNU_verneed 0x6ffffffe /* Version needs section. */
#define SHT_GNU_versym 0x6fffffff /* Version symbol table. */
#define SHT_HISUNW 0x6fffffff /* Sun-specific high bound. */
#define SHT_HIOS 0x6fffffff /* End OS-specific type */
#define SHT_LOPROC 0x70000000 /* Start of processor-specific */
#define SHT_HIPROC 0x7fffffff /* End of processor-specific */
#define SHT_LOUSER 0x80000000 /* Start of application-specific */
#define SHT_HIUSER 0x8fffffff /* End of application-specific */其中,每个ELF文件中都有一个SHT_NULL类型的section,它只有section header,没有相应的section数据,section header中的数据都为0,没有意义。
SHT_PROGBITS类型的section中的内容为程序数据,如代码、全局变量等。例如,.interp section用于保存动态链接器的绝对地址,如/lib/ld-linux.so.2;.comment section用于保存版本控制信息,如GCC: (GNU) 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39);.eh_frame_hdr和.eh_frame section用于保存异常处理信息,.eh_frame_hdr是对.eh_frame的补充,通过执行$ readelf -wf tanglinux命令可以查看.eh_frame section中的内容。
NOBITS类型一般用于名叫.bss的section,该section也只有section header,没有实际的内容,不占用可执行文件的空间。
SHT_STRTAB类型的section用于保存字符串,它的格式如下例所示:
通过图中的索引Index就可以获得从Index开始到空字符为止的一段字符串。例如若Index取值为1则可获得字符串“name.”。
.shstrtab就是一个典型的SHT_STRTAB类型的section,执行以下命令就可以输出该段中的内容,如下所示:
$ readelf -p .shstrtab tanglinux
String dump of section '.shstrtab':
[ 1] .symtab
[ 9] .strtab
[ 11] .shstrtab
[ 1b] .interp
[ 23] .note.ABI-tag
[ 31] .note.gnu.build-id
[ 44] .gnu.hash
[ 4e] .dynsym
[ 56] .dynstr
[ 5e] .gnu.version
[ 6b] .gnu.version_r
[ 7a] .rel.dyn
[ 83] .rel.plt
[ 8c] .init
[ 92] .plt.got
[ 9b] .text
[ a1] .fini
[ a7] .rodata
[ af] .eh_frame_hdr
[ bd] .eh_frame
[ c7] .init_array
[ d3] .fini_array
[ df] .jcr
[ e4] .dynamic
[ ed] .got.plt
[ f6] .data
[ fc] .bss
[ 101] .comment中括号[]中的数字就是用来获取其后所示字符串的索引。
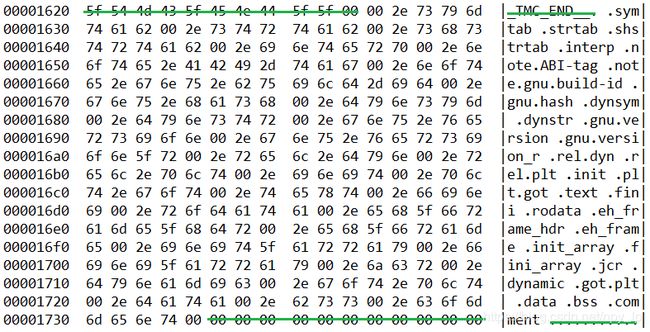
也可以通过执行$ hexdump -C tanglinux命令打印文件中每个字节的数值,然后根据文件偏移量sh_offset(如0x162b)和该section的大小sh_entsize(如0x10a)来获取.shstrtab section的所有内容,如下图所示:
命令hexdump对非打印字符采用点(﹒)来代替,在上图中为了区分section名称前的点,则将空字符对应的点用空格代替。
3、sh_flags表示section的标志。它的可能取值如下所示:
#define SHF_WRITE (1 << 0) /* Writable */
#define SHF_ALLOC (1 << 1) /* Occupies memory during execution */
#define SHF_EXECINSTR (1 << 2) /* Executable */
#define SHF_MERGE (1 << 4) /* Might be merged */
#define SHF_STRINGS (1 << 5) /* Contains nul-terminated strings */
#define SHF_INFO_LINK (1 << 6) /* `sh_info' contains SHT index */
#define SHF_LINK_ORDER (1 << 7) /* Preserve order after combining */
#define SHF_OS_NONCONFORMING (1 << 8) /* Non-standard OS specific handling required */
#define SHF_GROUP (1 << 9) /* Section is member of a group. */
#define SHF_TLS (1 << 10) /* Section hold thread-local data. */
#define SHF_MASKOS 0x0ff00000 /* OS-specific. */
#define SHF_MASKPROC 0xf0000000 /* Processor-specific */
#define SHF_ORDERED (1 << 30) /* Special ordering requirement (Solaris). */
#define SHF_EXCLUDE (1 << 31) /* Section is excluded unless referenced or allocated (Solaris).*/SHF_WRITE表示section可写;SHF_ALLOC表示在程序执行时需要占用内存空间;SHF_EXECINSTR表示可执行。
4、sh_addr表示该section在进程空间中的虚拟地址(首地址)。如果该成员的值为0,则表示该section不会出现在进程空间中。
5、sh_offset表示该section相对ELF文件开头的偏移量,sh_size表示该section的大小(字节数)。通过这两个成员就可以准确的获得某个section的所有内容。
6、sh_addralign表示该section的地址对齐方式(也就是sh_addr对sh_addralign取模的余数为0)。它的可能值为2的倍数,0和1表示不采用对齐方式。
7、sh_entsize表示该section中每个表项的大小(其内容以固定大小的项来存储,如符号表),否则该值为0。
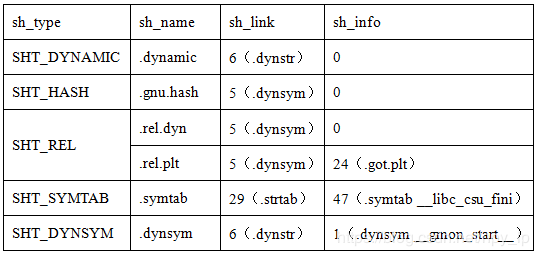
8、sh_link表示链接到其他section header的索引号,sh_info表示附加的段信息。这两个成员的值只对以下表中的类型有效,其他类型的section则都为0。
通过执行readelf命令可获得可执行文件tanglinux中所有的section header信息,如下所示:
$ readelf -S tanglinux
There are 31 section headers, starting at offset 0x1738:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Addr Off Size ES Flg Lk Inf Al
[ 0] NULL 00000000 000000 000000 00 0 0 0
[ 1] .interp PROGBITS 08048154 000154 000013 00 A 0 0 1
[ 2] .note.ABI-tag NOTE 08048168 000168 000020 00 A 0 0 4
[ 3] .note.gnu.build-i NOTE 08048188 000188 000024 00 A 0 0 4
[ 4] .gnu.hash GNU_HASH 080481ac 0001ac 000020 04 A 5 0 4
[ 5] .dynsym DYNSYM 080481cc 0001cc 000040 10 A 6 1 4
[ 6] .dynstr STRTAB 0804820c 00020c 000045 00 A 0 0 1
[ 7] .gnu.version VERSYM 08048252 000252 000008 02 A 5 0 2
[ 8] .gnu.version_r VERNEED 0804825c 00025c 000020 00 A 6 1 4
[ 9] .rel.dyn REL 0804827c 00027c 000008 08 A 5 0 4
[10] .rel.plt REL 08048284 000284 000008 08 AI 5 24 4
[11] .init PROGBITS 0804828c 00028c 000023 00 AX 0 0 4
[12] .plt PROGBITS 080482b0 0002b0 000020 04 AX 0 0 16
[13] .plt.got PROGBITS 080482d0 0002d0 000008 00 AX 0 0 8
[14] .text PROGBITS 080482e0 0002e0 000182 00 AX 0 0 16
[15] .fini PROGBITS 08048464 000464 000014 00 AX 0 0 4
[16] .rodata PROGBITS 08048478 000478 00000c 00 A 0 0 4
[17] .eh_frame_hdr PROGBITS 08048484 000484 00002c 00 A 0 0 4
[18] .eh_frame PROGBITS 080484b0 0004b0 0000b0 00 A 0 0 4
[19] .init_array INIT_ARRAY 08049f08 000f08 000004 04 WA 0 0 4
[20] .fini_array FINI_ARRAY 08049f0c 000f0c 000004 04 WA 0 0 4
[21] .jcr PROGBITS 08049f10 000f10 000004 00 WA 0 0 4
[22] .dynamic DYNAMIC 08049f14 000f14 0000e8 08 WA 6 0 4
[23] .got PROGBITS 08049ffc 000ffc 000004 04 WA 0 0 4
[24] .got.plt PROGBITS 0804a000 001000 000010 04 WA 0 0 4
[25] .data PROGBITS 0804a010 001010 000004 00 WA 0 0 1
[26] .bss NOBITS 0804a014 001014 000004 00 WA 0 0 1
[27] .comment PROGBITS 00000000 001014 00002d 01 MS 0 0 1
[28] .symtab SYMTAB 00000000 001044 000410 10 29 47 4
[29] .strtab STRTAB 00000000 001454 0001d7 00 0 0 1
[30] .shstrtab STRTAB 00000000 00162b 00010a 00 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
p (processor specific)只通过命令行选项-S执行readelf命令,Name最多只打印17个字符,会造成第[ 3]项的Name显示不全,完全显示则须要添加-W选项。
根据输出的信息,举例sh_link和sh_info可能的值,如下表所示:
从以上输出的信息中,可以知道所有section的大概分布,如下图所示(没有列出因对齐需要而留下的空白,根据文件偏移量加上长度的和与下一个偏移量比较即可知是否留有空白):
图中的每个section都用名称和长度来说明,如.interp 0x13。
上图的文件偏移量中有两个0x1014,正好说明.bss section的4个字节并不占用可执行文件的空间,但程序运行时该section实际占用[0x0804a014,0x0804a018)等4个字节的内存空间。
0x08049f08(0x08048560),括号中的虚拟地址表示上个section的结束地址,这两个地址之间相差6568个字节,在文件中这部分的内容全为0。留有这么大的空间,一个原因是因为LOAD segment的对齐方式为页对齐(在这个例子里该值为4096个字节),所以.init_array section的首地址最起码为0x08049000。至于这里为什么还要再偏移3848(0xf08)个字节,则在后续的系列文章(链接脚本)中将会讲到。
.comment、.symtab、.strtab和.shstrtab section的虚拟地址为0x00000000,在这里,表示它们不参与程序的运行。
三、ELF文件中的program header
section header用于描述section的特性,而program header用于描述segment的特性,目标文件(也就是文件名以.o结尾的文件)不存在program header,因为它不能运行。一个segment包含一个或多个现有的section,相当于从程序执行的角度来看待这些section。program header使用以下的数据结构来定义:
typedef struct
{
Elf32_Word p_type; /* Segment type */
Elf32_Off p_offset; /* Segment file offset */
Elf32_Addr p_vaddr; /* Segment virtual address */
Elf32_Addr p_paddr; /* Segment physical address */
Elf32_Word p_filesz; /* Segment size in file */
Elf32_Word p_memsz; /* Segment size in memory */
Elf32_Word p_flags; /* Segment flags */
Elf32_Word p_align; /* Segment alignment */
} Elf32_Phdr;1、p_type表示segment的类型。它的可能值如下所示:
#define PT_NULL 0 /* Program header table entry unused */
#define PT_LOAD 1 /* Loadable program segment */
#define PT_DYNAMIC 2 /* Dynamic linking information */
#define PT_INTERP 3 /* Program interpreter */
#define PT_NOTE 4 /* Auxiliary information */
#define PT_SHLIB 5 /* Reserved */
#define PT_PHDR 6 /* Entry for header table itself */
#define PT_TLS 7 /* Thread-local storage segment */
#define PT_NUM 8 /* Number of defined types */
#define PT_LOOS 0x60000000 /* Start of OS-specific */
#define PT_GNU_EH_FRAME 0x6474e550 /* GCC .eh_frame_hdr segment */
#define PT_GNU_STACK 0x6474e551 /* Indicates stack executability */
#define PT_GNU_RELRO 0x6474e552 /* Read-only after relocation */
#define PT_LOSUNW 0x6ffffffa
#define PT_SUNWBSS 0x6ffffffa /* Sun Specific segment */
#define PT_SUNWSTACK 0x6ffffffb /* Stack segment */
#define PT_HISUNW 0x6fffffff
#define PT_HIOS 0x6fffffff /* End of OS-specific */
#define PT_LOPROC 0x70000000 /* Start of processor-specific */
#define PT_HIPROC 0x7fffffff /* End of processor-specific */2、p_offset表示该segment相对ELF文件开头的偏移量,p_filesz表示该segment在ELF文件中的大小,p_memsz表示该segment加载到内存后所占用的大小。p_filesz和p_memsz的大小只有在少数情况下不相同,如包含.bss section的segment,因为.bss section在ELF文件中不占用空间,但在内存中需要占用相应字节大小的空间。通过p_offset和p_filesz两个成员就可以获得相应segment中的所有内容,所以这里就不再需要section header的支持,但需要ELF文件头中的信息来确定program header表(每个program header的大小相同)的开头位置,因此ELF文件头(它包含在第一个LOAD segment中)也要加载到内存中。
3、p_vaddr表示segment的虚拟地址,p_paddr表示它的物理地址。在现代常见的体系架构中,很少直接使用物理地址,所以这里p_paddr的值与p_vaddr相同。
4、p_align表示segment的对齐方式(也就是p_vaddr和p_offset对p_align取模的余数为0)。它的可能值为2的倍数,0和1表示不采用对齐方式。p_align的对齐方式不仅针对虚拟地址(p_vaddr),在ELF文件中的偏移量(p_offset)也要采用与虚拟地址相同的对齐方式。PT_LOAD类型的segment需要针对所在操作系统的页对齐。
5、p_flags表示segment的标志。它的可能取值如下所示:
#define PF_X (1 << 0) /* Segment is executable */
#define PF_W (1 << 1) /* Segment is writable */
#define PF_R (1 << 2) /* Segment is readable */
#define PF_MASKOS 0x0ff00000 /* OS-specific */
#define PF_MASKPROC 0xf0000000 /* Processor-specific */PF_X表示segment可执行,PF_W表示可写,PF_R表示可读。
通过执行readelf命令可获得可执行文件tanglinux中所有的program header信息,如下所示:
$ readelf -l tanglinux
Elf file type is EXEC (Executable file)
Entry point 0x80482e0
There are 9 program headers, starting at offset 52
Program Headers:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flg Align
PHDR 0x000034 0x08048034 0x08048034 0x00120 0x00120 R E 0x4
INTERP 0x000154 0x08048154 0x08048154 0x00013 0x00013 R 0x1
[Requesting program interpreter: /lib/ld-linux.so.2]
LOAD 0x000000 0x08048000 0x08048000 0x00560 0x00560 R E 0x1000
LOAD 0x000f08 0x08049f08 0x08049f08 0x0010c 0x00110 RW 0x1000
DYNAMIC 0x000f14 0x08049f14 0x08049f14 0x000e8 0x000e8 RW 0x4
NOTE 0x000168 0x08048168 0x08048168 0x00044 0x00044 R 0x4
GNU_EH_FRAME 0x000484 0x08048484 0x08048484 0x0002c 0x0002c R 0x4
GNU_STACK 0x000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000 0x00000 RW 0x10
GNU_RELRO 0x000f08 0x08049f08 0x08049f08 0x000f8 0x000f8 R 0x1
Section to Segment mapping:
Segment Sections...
00
01 .interp
02 .interp .note.ABI-tag .note.gnu.build-id .gnu.hash .dynsym .dynstr .gnu.version .gnu.version_r .rel.dyn .rel.plt .init .plt .plt.got .text .fini .rodata .eh_frame_hdr .eh_frame
03 .init_array .fini_array .jcr .dynamic .got .got.plt .data .bss
04 .dynamic
05 .note.ABI-tag .note.gnu.build-id
06 .eh_frame_hdr
07
08 .init_array .fini_array .jcr .dynamic .got 从中可以看出section到segment的映射关系,如上图所示。