seqcc 上 Optional Exercise 7 的代码解析
Description
The program for this assessment calculates the cheapest route between two cities in a mock European rail system. The graph that represents the rail system is pictured below.
Figure 1 A mock European rail system
In this program, a weighted graph is constructed to represent rail services to and from European cities. Each service from a city has an associated destination city, a fee (in Euros), and a distance (in kilometers). The program processes user input of a source city and a destination city. The program then displays the cheapest route from the source city to the destination city. In addition, for each route, the total cost and total distance are displayed. The file services.txt contains the data for the available services.
Classes
This program utilizes three main classes, class City, class Service, and class RailSystem. The implementations for class City and class Service are given. Class City maintains information about a city. Class Service models a rail service from the rail system. This class contains public data members for a destination city, a fee, and a distance. Both of these classes are used by class RailSystem.
Class RailSystem models the rail system using an adjacency list representation. These adjacency lists are represented using the STL class map. Specifically, a map of type string to type list represents the rail system. The following image represents how a portion of the rail system is represented. Note that the ticket fees and distances are left out to simplify the picture.
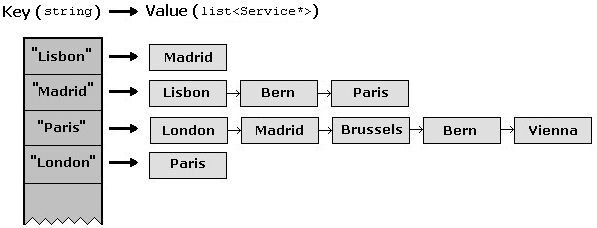
Figure 2 Adjacency list representation of the rail system
Essentially, in the above representation, a linked list of outgoing services can be indexed using a string containing the source city name. For example, notice in the above picture, Madrid has three outgoing services: one to Lisbon, one to Bern, and one to Paris. This matches the picture of the rail system at the top of this handout. In addition to this type of map object, another type of map is used to map city names to pointers to their respective City objects. This map object is used in the search algorithm.
Sample output from this program is shown in the figure below.
Figure 3 Output from a sample solution
The algorithm to be used is a positive-weighted, shortest path algorithm. Each City is a node in a graph, and each Service is an edge. Edges have an associated cost: the fee for the ticket. The goal is to find the cheapest route from the source city to the destination city.
To perform a new search, a pointer to a City object representing the start city should be added to an initially empty candidates queue. The algorithm continues by exploring the services of each candidate city, possibly adding new candidates to the list. The algorithm labels each City object with a number representing the cost of the cheapest route to it from the origin found so far. This is stored in member total_fee of class City. This value may decrease as new routes that are cheaper are found, but the value never increases.
To recover the actual path found by the search, every City object contains a string from_city. This string will be updated by the search algorithm to contain the name of the city by which it was reached through the cheapest path. In other words, if examining Brussels reveals a cheaper path to Paris, update variable total_fee of the City object that corresponds to Paris, and set its from_city equal to "Brussels". Once the search is complete, the cheapest route to the destination has been found, and the from_city strings can be traversed from the destination to the origin to reconstruct the path.
文件相关:
http://q499803363.download.csdn.net/
RailSystem.cpp 文件地址 :
http://download.csdn.net/source/1967146