使用哈夫曼编码实现数据的压缩和解压(java版)
1、哈夫曼树
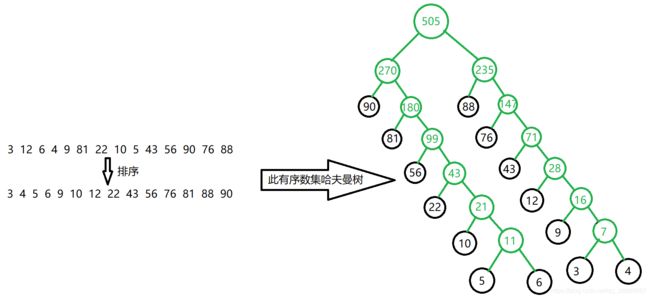
哈夫曼编码使用哈夫曼树的数据结构,哈夫曼树图解如下,即构造一个带权路径最小的数;
2、哈夫曼编码
使用哈夫曼树生成哈夫曼编码,已实现减少传输中数据的冗余;截取网络课程中的几张图来说明;
3、代码实现
package tree.huffmanTree.huffmanCode;
public class HuffmenNode implements Comparable {
//存储的字符(用Byte不用byte的原因是,对于新创建的节点是没有字符的,即data可能为null)
Byte data;
//权重(记录出现的次数)
int weight;
HuffmenNode leftNode;
HuffmenNode rightNode;
public HuffmenNode(Byte data, int weight) {
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HuffmenNode{" +
"data=" + data +
", weight=" + weight +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(HuffmenNode o) {
return o.weight - this.weight;
}
}
package tree.huffmanTree.huffmanCode;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class HuffmenCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String msg = "can you can a can as a can canner can a can.";
byte[] bytes = msg.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
System.out.println("压缩前的数据长度:" + bytes.length);
//使用赫夫曼编码压缩
byte[] tar = huffmenZip(bytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的数据长度:" + tar.length);
//使用赫夫曼编码表解压
byte[] sourceByte = decodeByHuffmen(tar, mapCode);
System.out.println(new String(sourceByte));
String src = "D:\\javaproject\\DataStructure\\src\\tree\\huffmanTree\\huffmanCode\\white.png";
String dst = "D:\\javaproject\\DataStructure\\src\\tree\\huffmanTree\\huffmanCode\\tar.zip";
// try {
// zipFile(src, dst);
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
try {
decodeZip(dst, src);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 使用哈夫曼编码进行文件压缩
*
* @param src 原文件地址
* @param dst 压缩后的文件地址
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void zipFile(String src, String dst) throws IOException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(src);
byte[] srcBytes = new byte[in.available()];
in.read(srcBytes);
in.close();
System.out.println("文件压缩前的大小:" + srcBytes.length);
//使用哈夫曼压缩
byte[] tarBytes = huffmenZip(srcBytes);
System.out.println("文件压缩后的大小:" + tarBytes.length);
//输出文件不仅包含压缩后的字节数据,还包含产生的哈夫曼编码,故使用包装类ObjectOutputStream
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(dst);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
oos.writeObject(tarBytes);
oos.writeObject(mapCode);
oos.close();
out.close();
}
/**
* 解压文件
*
* @param zipPath
* @param newPath
*/
public static void decodeZip(String zipPath, String newPath) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(zipPath);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(in);
//读取byte数组
byte[] filedatas = (byte[]) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(filedatas));
//读取哈夫曼编码表
Map mapCode = (Map) ois.readObject();
//解码
byte[] source = decodeByHuffmen(filedatas, mapCode);
//byte[]输出到文件
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(newPath);
out.write(source);
out.close();
}
/**
* 使用赫夫曼编码解压
*
* @param tar 目标数据
* @param huffmenCode 赫夫曼编码表
* @return
*/
private static byte[] decodeByHuffmen(byte[] tar, Map huffmenCode) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//将byte[]转为二进制字符串
for (int i = 0; i < tar.length; i++) {
if (i == tar.length - 1) {
sb.append(Integer.toBinaryString(tar[i]));
} else {
sb.append(byteToString(tar[i]));
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
//将哈夫曼编码表里面的键值对互换,方便下一步查询
Map temp = new HashMap<>();
for (Map.Entry entry : huffmenCode.entrySet()) {
temp.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
System.out.println("哈夫曼编码表键值对互换:" + temp);
//根据哈夫曼编码表将二进制字符串转换成原数据
List source = getSource(sb.toString(), temp);
// System.out.println(source);
//把集合转变成数组
byte[] byteSource = new byte[source.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < byteSource.length; i++) {
byteSource[i] = source.get(i);
}
return byteSource;
}
private static List getSource(String codeStr, Map byteMap) {
List tempList = new ArrayList<>();
getSingleItem(tempList, codeStr, byteMap);
return tempList;
}
private static void getSingleItem(List tempList, String codeStr, Map byteMap) {
for (int i = 0; i <= codeStr.length(); i++) {
if (byteMap.keySet().contains(codeStr.substring(0, i))) {
tempList.add(byteMap.get(codeStr.substring(0, i)));
getSingleItem(tempList, codeStr.substring(i), byteMap);
break;
}
}
}
private static String byteToString(byte b) {
//将8位扩大到32位,便于 或 运算,提取原来数值中的8位
int temp = b;
temp |= 256;
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp);
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
}
private static byte[] huffmenZip(byte[] bytes) {
//先将每个byte元素以及出现的次数包装成HuffmanNode节点,输出节点列表
List nodeList = getNodeList(bytes);
// System.out.println(nodeList);
//按出现次数的大小排序(从大到小)
Collections.sort(nodeList);
// System.out.println(nodeList);
//创建哈夫曼树
HuffmenNode rootNode = createHuffmenTree(nodeList);
// System.out.println(rootNode);
//创建哈夫曼编码表
Map byteStringMap = createHuffmenCode(rootNode);
// System.out.println(byteStringMap);
//按照哈夫曼编码表对原bytes进行编码
byte[] targetBytes = encodeByHuffmenCode(bytes, byteStringMap);
return targetBytes;
}
/**
* 数据压缩
* 根据哈夫曼编码表对原bytes进行编码
*
* @param bytes 原bytes数据
* @param huffmenCodeMap 哈夫曼编码表
* @return
*/
private static byte[] encodeByHuffmenCode(byte[] bytes, Map huffmenCodeMap) {
//将bytes转换成二进制字符串
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (byte b : bytes) {
String str = huffmenCodeMap.get(b);
sb.append(str);
}
// System.out.println(sb.toString());
//将二进制字符串转变为处理后的byte
int len = sb.length();
int newLenght = (len % 8 == 0) ? (len / 8) : (len / 8 + 1);
byte[] targetBytes = new byte[newLenght];
for (int i = 0; i < targetBytes.length; i++) {
if ((i + 1) * 8 > len) {
targetBytes[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(sb.substring(i * 8), 2);
} else {
targetBytes[i] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(sb.substring(i * 8, (i + 1) * 8), 2);
}
}
return targetBytes;
}
//临时存储编码表
static Map mapCode = new HashMap();
private static Map createHuffmenCode(HuffmenNode rootNode) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
if (rootNode != null) {
getCodes(rootNode.leftNode, "0", sb);
getCodes(rootNode.rightNode, "1", sb);
return mapCode;
}
return null;
}
private static void getCodes(HuffmenNode node, String s, StringBuffer sb) {
StringBuffer tempSb = new StringBuffer(sb);
tempSb.append(s);
if (node.data == null) {
getCodes(node.leftNode, "0", tempSb);
getCodes(node.rightNode, "1", tempSb);
} else {
mapCode.put(node.data, tempSb.toString());
}
}
/**
* 创建哈夫曼树
*
* @param nodeList
*/
private static HuffmenNode createHuffmenTree(List nodeList) {
int length = nodeList.size();
while (length > 1) {
HuffmenNode huffmenNode01 = nodeList.get(length - 1);
HuffmenNode huffmenNode02 = nodeList.get(length - 2);
HuffmenNode huffmenNodeNew = new HuffmenNode(null, huffmenNode01.weight + huffmenNode02.weight);
huffmenNodeNew.leftNode = huffmenNode01;
huffmenNodeNew.rightNode = huffmenNode02;
nodeList.remove(huffmenNode01);
nodeList.remove(huffmenNode02);
nodeList.add(huffmenNodeNew);
Collections.sort(nodeList);
length = nodeList.size();
}
return nodeList.get(0);
}
/**
* 将bytes的中的元素以及出现次数包装成HuffmanNode列表
*
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private static List getNodeList(byte[] bytes) {
List nodeList = new ArrayList<>();
Map byteIntegerMap = new HashMap<>();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = byteIntegerMap.get(b);
if (count == null) {
byteIntegerMap.put(b, 1);
} else {
byteIntegerMap.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
for (Map.Entry item : byteIntegerMap.entrySet()) {
Byte b = item.getKey();
Integer weigth = item.getValue();
HuffmenNode node = new HuffmenNode(b, weigth);
nodeList.add(node);
}
return nodeList;
}
}
注:哈夫曼编码不仅可用于数据的精简,还可用于文件的压缩(无损压缩),压缩效果受原文件的类型限制,相同率越高,压缩效果越好。